Abstract
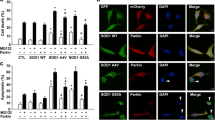
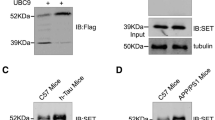
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a neurodegenerative disease specific to motor neurons. Pathogenic mutations in an ALS-associated gene encoding superoxide dismutase 1 (SOD1) have been identified in familial ALS (fALS) cases. SOD1 with fALS-linked mutations is prone to form cytotoxic aggregates that cause cellular dysfunction. We previously demonstrated that the modification of SOD1 by small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO) 3 enhances the aggregation of fALS-linked SOD1 mutants. SUMOylation is a reversible post-translational modification targeting lysine residues. SUMO conjugation is mediated by the enzymes E1, E2, and E3, and deconjugation is catalyzed by deSUMOylation enzymes. To understand the process of SOD1 aggregation, we examined the involvement of protein inhibitor of activated STAT (PIAS) family and sentrin-specific protease (SENP) family proteins in the SUMOylation of SOD1 mutants. We found that all four types of PIAS family proteins, E3 ligase of SUMOylation, increased SUMOylation of SOD1 mutants. Among three SENP family proteins tested, deSUMOylation enzymes, SENP1, exhibited the most efficient deconjugation effect. In co-expression experiments, PIASy and SENP1 increased and decreased the number of cells exhibiting SOD1-mutant aggregation, respectively, confirming the effect of these enzymes on SOD1 aggregation. These findings suggest that regulation of SUMOylation affects the pathogenesis of ALS.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arora T, Liu B, He H, Kim J, Murphy TL, Murphy KM, Modlin RL, Shuai K (2003) PIASx is a transcriptional co-repressor of signal transducer and activator of transcription 4. J Biol Chem 278:21327–21330. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.C300119200
Bischof O, Schwamborn K, Martin N, Werner A, Sustmann C, Grosschedl R, Dejean A (2006) The E3 SUMO ligase PIASy is a regulator of cellular senescence and apoptosis. Mol Cell 22:783–794. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2006.05.016
Cheng J, Kang X, Zhang S, Yeh ETH (2007) SUMO-specific protease 1 is essential for stabilization of HIF1α during hypoxia. Cell 131:584–595. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2007.08.045
Chowdhury D, Singh A, Gupta A, Tulsawani R, Meena RC, Chakrabarti A (2019) p38 MAPK pathway-dependent SUMOylation of Elk-1 and phosphorylation of PIAS2 correlate with the downregulation of Elk-1 activity in heat-stressed HeLa cells. Cell Stress Chaperones 24:393–407. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-019-00974-4
Chung CD, Liao J, Liu B et al (1997) Specific inhibition of Stat3 signal transduction by PIAS3. Science (80-) 278:1803–1805. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.278.5344.1803
Dangoumau A, Marouillat S, Burlaud Gaillard J, Uzbekov R, Veyrat-Durebex C, Blasco H, Arnoult C, Corcia P, Andres CR, Vourc'h P (2016) Inhibition of pathogenic mutant SOD1 aggregation in cultured motor neuronal cells by prevention of its SUMOylation on lysine 75. Neurodegener Dis 16:161–171. https://doi.org/10.1159/000439254
Fei E, Jia N, Yan M, Ying Z, Sun Q, Wang H, Zhang T, Ma X, Ding H, Yao X, Shi Y, Wang G (2006) SUMO-1 modification increases human SOD1 stability and aggregation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 347:406–412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.06.092
Feligioni M, Brambilla E, Camassa A, Sclip A, Arnaboldi A, Morelli F, Antoniou X, Borsello T (2011) Crosstalk between JNK and SUMO signaling pathways: deSUMOylation is protective against H2O2-induced cell injury. PLoS One 6:e28185. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0028185
Gong L, Yeh ETH (2006) Characterization of a family of nucleolar SUMO-specific proteases with preference for SUMO-2 or SUMO-3. J Biol Chem 281:15869–15877. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M511658200
Guo C, Henley JM (2014) Wrestling with stress: roles of protein SUMOylation and deSUMOylation in cell stress response. IUBMB Life 66:71–77. https://doi.org/10.1002/iub.1244
Henley JM, Craig TJ, Wilkinson KA (2014) Neuronal SUMOylation: mechanisms, physiology, and roles in neuronal dysfunction. Physiol Rev 94:1249–1285. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00008.2014
Huang C, Han Y, Wang Y, Sun X, Yan S, Yeh ETH, Chen Y, Cang H, Li H, Shi G, Cheng J, Tang X, Yi J (2009) SENP3 is responsible for HIF-1 transactivation under mild oxidative stress via p300 de-SUMOylation. EMBO J 28:2748–2762. https://doi.org/10.1038/emboj.2009.210
Itahana Y, Yeh ETH, Zhang Y (2006) Nucleocytoplasmic shuttling modulates activity and ubiquitination-dependent turnover of SUMO-specific protease 2. Mol Cell Biol 26:4675–4689. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.01830-05
Kang X, Qi Y, Zuo Y, Wang Q, Zou Y, Schwartz RJ, Cheng J, Yeh ETH (2010) SUMO-specific protease 2 is essential for suppression of polycomb group protein-mediated gene silencing during embryonic development. Mol Cell 38:191–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2010.03.005
Kaur SJ, McKeown SR, Rashid S (2016) Mutant SOD1 mediated pathogenesis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Gene 577:109–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2015.11.049
Liu B, Liao J, Rao X, Kushner SA, Chung CD, Chang DD, Shuai K (1998) Inhibition of Stat1-mediated gene activation by PIAS1. Proc Natl Acad Sci 95:10626–10631. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.95.18.10626
Liu B, Gross M, ten Hoeve J, Shuai K (2001) A transcriptional corepressor of Stat1 with an essential LXXLL signature motif. Proc Natl Acad Sci 98:3203–3207. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.051489598
Maruyama T, Abe Y, Niikura T (2018a) SENP1 and SENP2 regulate SUMOylation of amyloid precursor protein. Heliyon 4:e00601. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2018.e00601
Maruyama T, Wada H, Abe Y, Niikura T (2018b) Alteration of global protein SUMOylation in neurons and astrocytes in response to Alzheimer’s disease-associated insults. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 500:470–475. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.04.104
Medinas DB, Valenzuela V, Hetz C (2017) Proteostasis disturbance in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Hum Mol Genet 26:R91–R104. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddx274
Nayak A, Müller S (2014) SUMO-specific proteases/isopeptidases: SENPs and beyond. Genome Biol 15:422. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-014-0422-2
Niikura T, Kita Y, Abe Y (2014) SUMO3 modification accelerates the aggregation of ALS-linked SOD1 mutants. PLoS One 9:e101080. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0101080
Obata Y, Niikura T, Kanekura K, Hashimoto Y, Kawasumi M, Kita Y, Aiso S, Matsuoka M, Nishimoto I (2005) Expression of N19S-SOD1, an SOD1 mutant found in sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients, induces low-grade motoneuronal toxicity. J Neurosci Res 81:720–729. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.20594
Rosonina E, Akhter A, Dou Y, Babu J, Sri Theivakadadcham VS (2017) Regulation of transcription factors by sumoylation. Transcription 8:220–231. https://doi.org/10.1080/21541264.2017.1311829
Rytinki MM, Kaikkonen S, Pehkonen P, Jääskeläinen T, Palvimo JJ (2009) PIAS proteins: pleiotropic interactors associated with SUMO. Cell Mol Life Sci 66:3029–3041. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-009-0061-z
Vijayakumar UG, Milla V, Stafford MYC et al (2019) A systematic review of suggested molecular strata, biomarkers and their tissue sources in ALS. Front Neurol 10:1–17. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2019.00400
Wang J, Zhang H, Iyer D, Feng XH, Schwartz RJ (2008) Regulation of cardiac specific nkx2.5 gene activity by small ubiquitin-like modifier. J Biol Chem 283:23235–23243. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M709748200
Wei H, Teng H, Huan W, Zhang S, Fu H, Chen F, Wang J, Wu C, Zhao J (2012) An upregulation of SENP3 after spinal cord injury: implications for neuronal apoptosis. Neurochem Res 37:2758–2766. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-012-0869-z
Wilkinson KA, Henley JM (2010) Mechanisms, regulation and consequences of protein SUMOylation. Biochem J 428:133–145. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20100158
Wilkinson KA, Nakamura Y, Henley JM (2010) Targets and consequences of protein SUMOylation in neurons. Brain Res Rev 64:195–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresrev.2010.04.002
Yang SH, Sharrocks AD (2006) PIASxα differentially regulates the amplitudes of transcriptional responses following activation of the ERK and p38 MAPK pathways. Mol Cell 22:477–487. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2006.03.037
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. Yoichiro Abe and Dr. Yoshiko Kita for the helpful comments on the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Sophia University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wada, H., Suzuki, D. & Niikura, T. Regulation of ALS-Associated SOD1 Mutant SUMOylation and Aggregation by SENP and PIAS Family Proteins. J Mol Neurosci 70, 2007–2014 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-020-01604-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-020-01604-w