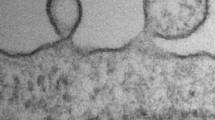
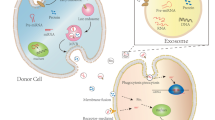
Abstract
Purpose of Review
This review summarizes the effects of microparticles and exosomes in the progression of atherosclerosis and the prospect for their diagnostic and therapeutic potentials.
Recent Findings
Microparticles and exosomes can induce endothelial dysfunction, vascular inflammation, coagulation, thrombosis, and calcification via their components of proteins and noncoding RNAs, which may promote the progression of atherosclerosis. The applications of microparticles and exosomes become the spotlight of clinical diagnosis and therapy.
Summary
Microparticles and exosomes are members of extracellular vesicles, which are generated in various cell types by different mechanisms of cell membrane budding and multivesicular body secretion, respectively. They are important physiologic pathways of cell-to-cell communication in vivo and act as messengers accelerating or alleviating the process of atherosclerosis. Microparticles and exosomes may become diagnostic biomarkers and therapeutic approaches of atherosclerosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Loyer X, Vion AC, Tedgui A, Boulanger CM. Microvesicles as cell-cell messengers in cardiovascular diseases. Circ Res. 2014;114(2):345–53.
Kowal J, Tkach M, Thery C. Biogenesis and secretion of exosomes. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2014;29:116–25.
•• Jian YP, Yuan HX, Hu KH, Chen C, Li YQ, Li Y, et al. Protein compositions changes of circulating microparticles in patients with valvular heart disease subjected to cardiac surgery contribute to systemic inflammatory response and disorder of coagulation. Shock. 2019;52(5):487–96 This proteomic study firstly reported the protein changes in MPs in valvular heart disease patients subjected to cardiac surgery and raised many new probable inflammatory factors in MPs.
Kalluri R, LeBleu VS. Discovery of double-stranded genomic DNA in circulating exosomes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2016;81:275–80.
Li S, Li Y, Chen B, Zhao J, Yu S, Tang Y, et al. exoRBase: a database of circRNA, lncRNA and mRNA in human blood exosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018;46(D1):D106–D12.
Skotland T, Sandvig K, Llorente A. Lipids in exosomes: current knowledge and the way forward. Prog Lipid Res. 2017;66:30–41.
•• Coumans FAW, Brisson AR, Buzas EI, Dignat-George F, Drees EEE, El-Andaloussi S, et al. Methodological guidelines to study extracellular vesicles. Circ Res. 2017;120(10):1632–48 This article provided useful suggestions on methods and cautions of EV research.
Kalluri R, LeBleu VS. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science. 2020;367(6478):eaau6977.
Fernandez M, Calligaris SD. Circulating microparticles in cardiovascular disease: going on stage! Biomarkers. 2019;24(5):423–8.
Back M, Yurdagul A Jr, Tabas I, Oorni K, Kovanen PT. Inflammation and its resolution in atherosclerosis: mediators and therapeutic opportunities. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2019;16(7):389–406.
Souilhol C, Serbanovic-Canic J, Fragiadaki M, Chico TJ, Ridger V, Roddie H, et al. Endothelial responses to shear stress in atherosclerosis: a novel role for developmental genes. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2020;17(1):52–63.
Navab M, Reddy ST, Van Lenten BJ, Fogelman AM. HDL and cardiovascular disease: atherogenic and atheroprotective mechanisms. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2011;8(4):222–32.
Kwak BR, Back M, Bochaton-Piallat ML, Caligiuri G, Daemen MJ, Davies PF, et al. Biomechanical factors in atherosclerosis: mechanisms and clinical implications. Eur Heart J. 2014;35(43):3013–20 20a-20d.
Rautou PE, Vion AC, Amabile N, Chironi G, Simon A, Tedgui A, et al. Microparticles, vascular function, and atherothrombosis. Circ Res. 2011;109(5):593–606.
Wolf P. The nature and significance of platelet products in human plasma. Br J Haematol. 1967;13(3):269–88.
Ratajczak J, Wysoczynski M, Hayek F, Janowska-Wieczorek A, Ratajczak MZ. Membrane-derived microvesicles: important and underappreciated mediators of cell-to-cell communication. Leukemia. 2006;20(9):1487–95.
Piccin A, Murphy WG, Smith OP. Circulating microparticles: pathophysiology and clinical implications. Blood Rev. 2007;21(3):157–71.
Italiano JE Jr, Mairuhu AT, Flaumenhaft R. Clinical relevance of microparticles from platelets and megakaryocytes. Curr Opin Hematol. 2010;17(6):578–84.
Camaioni C, Gustapane M, Cialdella P, Della Bona R, Biasucci LM. Microparticles and microRNAs: new players in the complex field of coagulation. Intern Emerg Med. 2013;8(4):291–6.
Harding C, Heuser J, Stahl P. Receptor-mediated endocytosis of transferrin and recycling of the transferrin receptor in rat reticulocytes. J Cell Biol. 1983;97(2):329–39.
Raimondo F, Morosi L, Chinello C, Magni F, Pitto M. Advances in membranous vesicle and exosome proteomics improving biological understanding and biomarker discovery. Proteomics. 2011;11(4):709–20.
van Niel G, D'Angelo G, Raposo G. Shedding light on the cell biology of extracellular vesicles. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2018;19(4):213–28.
Valadi H, Ekstrom K, Bossios A, Sjostrand M, Lee JJ, Lotvall JO. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2007;9(6):654–9.
Barry OP, Praticò D, Savani RC, FitzGerald GA. Modulation of monocyte-endothelial cell interactions by platelet microparticles. J Clin Invest. 1998;102(1):136–44.
Combes V, Simon AC, Grau GE, Arnoux D, Camoin L, Sabatier F, et al. In vitro generation of endothelial microparticles and possible prothrombotic activity in patients with lupus anticoagulant. J Clin Invest. 1999;104(1):93–102.
Mulcahy LA, Pink RC, Carter DR. Routes and mechanisms of extracellular vesicle uptake. J Extracell Vesicles. 2014;3.
• Fu L, Hu X-X, Lin Z-B, Chang F-J, Ou Z-J, Wang Z-P, et al. Circulating microparticles from patients with valvular heart disease and cardiac surgery inhibit endothelium-dependent vasodilation. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2015;150(3):666–72 This article firstly reported that MPs from patients with valvular heart disease and cardiac surgery can inhibit endothelium-dependent vasodilation.
• Lin ZB, Ci HB, Li Y, Cheng TP, Liu DH, Wang YS, et al. Endothelial microparticles are increased in congenital heart diseases and contribute to endothelial dysfunction. J Transl Med. 2017;15(1):–4 This article firstly reported the role of EMPs in congenital heart diseases.
Densmore JC, Signorino PR, Ou J, Hatoum OA, Rowe JJ, Shi Y, et al. Endothelium-derived microparticles induce endothelial dysfunction and acute lung injury. Shock. 2006;26(5):464–71.
Peterson DB, Sander T, Kaul S, Wakim BT, Halligan B, Twigger S, et al. Comparative proteomic analysis of PAI-1 and TNF-alpha-derived endothelial microparticles. Proteomics. 2008;8(12):2430–46.
Sander TL, Ou J-S, Densmore JC, Kaul S, Matus I, Twigger S, et al. Protein composition of plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1-derived endothelial microparticles. Shock. 2008;29(4):504–11.
Ou Z-J, Chang F-J, Luo D, Liao X-L, Wang Z-P, Zhang X, et al. Endothelium-derived microparticles inhibit angiogenesis in the heart and enhance the inhibitory effects of hypercholesterolemia on angiogenesis. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2011;300(4):E661–E8.
Ci H-B, Ou Z-J, Chang F-J, Liu D-H, He G-W, Xu Z, et al. Endothelial microparticles increase in mitral valve disease and impair mitral valve endothelial function. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2013;304(7):E695–702.
Lukasik M, Rozalski M, Luzak B, Michalak M, Ambrosius W, Watala C, et al. Enhanced platelet-derived microparticle formation is associated with carotid atherosclerosis in convalescent stroke patients. Platelets. 2013;24(1):63–70.
Esposito K, Ciotola M, Schisano B, Gualdiero R, Sardelli L, Misso L, et al. Endothelial microparticles correlate with endothelial dysfunction in obese women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006;91(9):3676–9.
Tramontano AF, Lyubarova R, Tsiakos J, Palaia T, Deleon JR, Ragolia L. Circulating endothelial microparticles in diabetes mellitus. Mediat Inflamm. 2010;2010:250476.
Morel O, Toti F, Morel N, Freyssinet JM. Microparticles in endothelial cell and vascular homeostasis: are they really noxious? Haematologica. 2009;94(3):313–7.
•• Xie Z, Wang X, Liu X, Du H, Sun C, Shao X, et al. Adipose-derived exosomes exert proatherogenic effects by regulating macrophage foam cell formation and polarization. J Am Heart Assoc. 2018;7(5):e007442 This article provided a direct evidence that exosomes can promote macrophage foam cell formation and prominently increase lipid deposition in aorta.
Goetzl EJ, Schwartz JB, Mustapic M, Lobach IV, Daneman R, Abner EL, et al. Altered cargo proteins of human plasma endothelial cell-derived exosomes in atherosclerotic cerebrovascular disease. FASEB J. 2017;31(8):3689–94.
Zheng B, Yin WN, Suzuki T, Zhang XH, Zhang Y, Song LL, et al. Exosome-mediated miR-155 transfer from smooth muscle cells to endothelial cells induces endothelial injury and promotes atherosclerosis. Mol Ther. 2017;25(6):1279–94.
Chen L, Yang W, Guo Y, Chen W, Zheng P, Zeng J, et al. Exosomal lncRNA GAS5 regulates the apoptosis of macrophages and vascular endothelial cells in atherosclerosis. PLoS One. 2017;12(9):e0185406.
Huang PL, Huang Z, Mashimo H, Bloch KD, Moskowitz MA, Bevan JA, et al. Hypertension in mice lacking the gene for endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Nature. 1995;377(6546):239–42.
Gimbrone MA Jr, Garcia-Cardena G. Endothelial cell dysfunction and the pathobiology of atherosclerosis. Circ Res. 2016;118(4):620–36.
Virmani R, Kolodgie FD, Burke AP, Farb A, Schwartz SM. Lessons from sudden coronary death: a comprehensive morphological classification scheme for atherosclerotic lesions. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2000;20(5):1262–75.
McCarthy EM, Wilkinson FL, Parker B, Alexander MY. Endothelial microparticles: pathogenic or passive players in endothelial dysfunction in autoimmune rheumatic diseases? Vasc Pharmacol. 2016;86:71–6.
Sheldon H, Heikamp E, Turley H, Dragovic R, Thomas P, Oon CE, et al. New mechanism for Notch signaling to endothelium at a distance by delta-like 4 incorporation into exosomes. Blood. 2010;116(13):2385–94.
Hergenreider E, Heydt S, Treguer K, Boettger T, Horrevoets AJ, Zeiher AM, et al. Atheroprotective communication between endothelial cells and smooth muscle cells through miRNAs. Nat Cell Biol. 2012;14(3):249–56.
Jansen F, Yang X, Hoelscher M, Cattelan A, Schmitz T, Proebsting S, et al. Endothelial microparticle-mediated transfer of microRNA-126 promotes vascular endothelial cell repair via SPRED1 and is abrogated in glucose-damaged endothelial microparticles. Circulation. 2013;128(18):2026–38.
Huang C, Huang Y, Zhou Y, Nie W, Pu X, Xu X, et al. Exosomes derived from oxidized LDL-stimulated macrophages attenuate the growth and tube formation of endothelial cells. Mol Med Rep. 2018;17(3):4605–10.
Incalza MA, D'Oria R, Natalicchio A, Perrini S, Laviola L, Giorgino F. Oxidative stress and reactive oxygen species in endothelial dysfunction associated with cardiovascular and metabolic diseases. Vasc Pharmacol. 2018;100:1–19.
Brodsky SV, Zhang F, Nasjletti A, Goligorsky MS. Endothelium-derived microparticles impair endothelial function in vitro. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2004;286(5):H1910–H5.
Xiong J, Miller VM, Li Y, Jayachandran M. Microvesicles at the crossroads between infection and cardiovascular diseases. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2012;59(2):124–32.
Xiong Y, Chen L, Yan C, Zhou W, Endo Y, Liu J, et al. Circulating exosomal miR-20b-5p inhibition restores Wnt9b signaling and reverses diabetes-associated impaired wound healing. Small. 2020;16(3):e1904044-e.
Wang X, Huang W, Liu G, Cai W, Millard RW, Wang Y, et al. Cardiomyocytes mediate anti-angiogenesis in type 2 diabetic rats through the exosomal transfer of miR-320 into endothelial cells. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2014;74:139–50.
Libby P, Ridker PM, Maseri A. Inflammation and atherosclerosis. Circulation. 2002;105(9):1135–43.
Milasan A, Tessandier N, Tan S, Brisson A, Boilard E, Martel C. Extracellular vesicles are present in mouse lymph and their level differs in atherosclerosis. J Extracell Vesicles. 2016;5:31427.
Mause SF, Weber C. Microparticles: protagonists of a novel communication network for intercellular information exchange. Circ Res. 2010;107(9):1047–57.
Cheng X, Dang A, Lv N, Zhao T. Microparticles from endothelial cells and immune cells in patients with Takayasu arteritis. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2019;26(6):547–58.
Hosseinkhani B, Kuypers S, van den Akker NMS, Molin DGM, Michiels L. Extracellular vesicles work as a functional inflammatory mediator between vascular endothelial cells and immune cells. Front Immunol. 2018;9:1789.
Vajen T, Benedikter BJ, Heinzmann ACA, Vasina EM, Henskens Y, Parsons M, et al. Platelet extracellular vesicles induce a pro-inflammatory smooth muscle cell phenotype. J Extracell Vesicles. 2017;6(1):1322454.
Wen C, Seeger RC, Fabbri M, Wang L, Wayne AS, Jong AY. Biological roles and potential applications of immune cell-derived extracellular vesicles. J Extracell Vesicles. 2017;6(1):1400370.
Milbank E, Soleti R, Martinez E, Lahouel B, Hilairet G, Martinez MC, et al. Microparticles from apoptotic RAW 264.7 macrophage cells carry tumour necrosis factor-alpha functionally active on cardiomyocytes from adult mice. J Extracell Vesicles. 2015;4:28621.
Li C, Li S, Zhang F, Wu M, Liang H, Song J, et al. Endothelial microparticles-mediated transfer of microRNA-19b promotes atherosclerosis via activating perivascular adipose tissue inflammation in apoE−/− mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;495(2):1922–9.
He S, Wu C, Xiao J, Li D, Sun Z, Li M. Endothelial extracellular vesicles modulate the macrophage phenotype: potential implications in atherosclerosis. Scand J Immunol. 2018;87(4):e12648.
Nguyen MA, Karunakaran D, Geoffrion M, Cheng HS, Tandoc K, Perisic Matic L, et al. Extracellular vesicles secreted by atherogenic macrophages transfer microRNA to inhibit cell migration. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2018;38(1):49–63.
Grover SP, Mackman N. Intrinsic pathway of coagulation and thrombosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2019;39(3):331–8.
Furie B, Furie BC. Mechanisms of thrombus formation. N Engl J Med. 2008;359(9):938–49.
Nielsen T, Kristensen AF, Pedersen S, Christiansen G, Kristensen SR. Investigation of procoagulant activity in extracellular vesicles isolated by differential ultracentrifugation. J Extracell Vesicles. 2018;7(1):1454777.
Owens AP 3rd, Mackman N. Microparticles in hemostasis and thrombosis. Circ Res. 2011;108(10):1284–97.
Gardiner C, Harrison P, Belting M, Boing A, Campello E, Carter BS, et al. Extracellular vesicles, tissue factor, cancer and thrombosis - discussion themes of the ISEV 2014 Educational Day. J Extracell Vesicles. 2015;4:26901.
Benedikter BJ, Bouwman FG, Heinzmann ACA, Vajen T, Mariman EC, Wouters EFM, et al. Proteomic analysis reveals procoagulant properties of cigarette smoke-induced extracellular vesicles. J Extracell Vesicles. 2019;8(1):1585163.
Falati S, Liu Q, Gross P, Merrill-Skoloff G, Chou J, Vandendries E, et al. Accumulation of tissue factor into developing thrombi in vivo is dependent upon microparticle P-selectin glycoprotein ligand 1 and platelet P-selectin. J Exp Med. 2003;197(11):1585–98.
Dolz S, Gorriz D, Tembl JI, Sanchez D, Fortea G, Parkhutik V, et al. Circulating microRNAs as novel biomarkers of stenosis progression in asymptomatic carotid stenosis. Stroke. 2017;48(1):10–6.
Bi S, Wang C, Jin Y, Lv Z, Xing X, Lu Q. Correlation between serum exosome derived miR-208a and acute coronary syndrome. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(3):4275–80.
Zarà M, Guidetti GF, Camera M, Canobbio I, Amadio P, Torti M, et al. Biology and role of extracellular vesicles (EVs) in the pathogenesis of thrombosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(11):2840.
Kapustin AN, Chatrou ML, Drozdov I, Zheng Y, Davidson SM, Soong D, et al. Vascular smooth muscle cell calcification is mediated by regulated exosome secretion. Circ Res. 2015;116(8):1312–23.
Goettsch C, Hutcheson JD, Aikawa E. MicroRNA in cardiovascular calcification: focus on targets and extracellular vesicle delivery mechanisms. Circ Res. 2013;112(7):1073–84.
Reynolds JL, Joannides AJ, Skepper JN, McNair R, Schurgers LJ, Proudfoot D, et al. Human vascular smooth muscle cells undergo vesicle-mediated calcification in response to changes in extracellular calcium and phosphate concentrations: a potential mechanism for accelerated vascular calcification in ESRD. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2004;15(11):2857–67.
Bakhshian Nik A, Hutcheson JD, Aikawa E. Extracellular vesicles as mediators of cardiovascular calcification. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2017;4:78.
Aikawa E, Nahrendorf M, Figueiredo JL, Swirski FK, Shtatland T, Kohler RH, et al. Osteogenesis associates with inflammation in early-stage atherosclerosis evaluated by molecular imaging in vivo. Circulation. 2007;116(24):2841–50.
Kapustin AN, Schoppet M, Schurgers LJ, Reynolds JL, McNair R, Heiss A, et al. Prothrombin loading of vascular smooth muscle cell-derived exosomes regulates coagulation and calcification. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2017;37(3):e22–32.
New SE, Goettsch C, Aikawa M, Marchini JF, Shibasaki M, Yabusaki K, et al. Macrophage-derived matrix vesicles: an alternative novel mechanism for microcalcification in atherosclerotic plaques. Circ Res. 2013;113(1):72–7.
• Kelly-Arnold A, Maldonado N, Laudier D, Aikawa E, Cardoso L, Weinbaum S. Revised microcalcification hypothesis for fibrous cap rupture in human coronary arteries. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110(26):10741–6 This research supported the concept that microcalcification of fibrous contributes to plaque rupture via high-resolution microcomputed tomography.
Hutcheson JD, Goettsch C, Bertazzo S, Maldonado N, Ruiz JL, Goh W, et al. Genesis and growth of extracellular-vesicle-derived microcalcification in atherosclerotic plaques. Nat Mater. 2016;15(3):335–43.
George M, Ganesh MR, Sridhar A, Jena A, Rajaram M, Shanmugam E, et al. Evaluation of endothelial and platelet derived microparticles in patients with acute coronary syndrome. J Clin Diagn Res. 2015;9(12):OC09–13.
Wendt S, Goetzenich A, Goettsch C, Stoppe C, Bleilevens C, Kraemer S, et al. Evaluation of the cardioprotective potential of extracellular vesicles – a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):15702.
Jing T, Ya-Shu K, Xue-Jun W, Han-Jing H, Yan L, Yi-An Y, et al. Sirt6 mRNA-incorporated endothelial microparticles (EMPs) attenuates DM patient-derived EMP-induced endothelial dysfunction. Oncotarget. 2017;8(69):114300–13.
Davidson SM, Riquelme JA, Takov K, Vicencio JM, Boi-Doku C, Khoo V, et al. Cardioprotection mediated by exosomes is impaired in the setting of type II diabetes but can be rescued by the use of non-diabetic exosomes in vitro. J Cell Mol Med. 2018;22(1):141–51.
Jansen F, Yang X, Proebsting S, Hoelscher M, Przybilla D, Baumann K, et al. MicroRNA expression in circulating microvesicles predicts cardiovascular events in patients with coronary artery disease. J Am Heart Assoc. 2014;3(6):e001249.
• Hou Z, Qin X, Hu Y, Zhang X, Li G, Wu J, et al. Longterm exercise-derived exosomal miR-342-5p: a novel exerkine for cardioprotection. Circ Res. 2019;124(9):1386–400 This article provided a novel cardioprotective mechanism related to exosomal miRNA.
Ren XS, Tong Y, Qiu Y, Ye C, Wu N, Xiong XQ, et al. MiR155-5p in adventitial fibroblasts-derived extracellular vesicles inhibits vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation via suppressing angiotensin-converting enzyme expression. J Extracell Vesicles. 2020;9(1):1698795.
•• Shan K, Jiang Q, Wang XQ, Wang YN, Yang H, Yao MD, et al. Role of long non-coding RNA-RNCR3 in atherosclerosis-related vascular dysfunction. Cell Death Dis. 2016;7(6):e2248 This article firstly reported the exosomal lncRNA in regulating atherosclerosis-related vascular dysfunction.
Luo Q, Guo D, Liu G, Chen G, Hang M, Jin M. Exosomes from MiR-126-overexpressing Adscs are therapeutic in relieving acute myocardial ischaemic injury. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;44(6):2105–16.
Witwer KW, Van Balkom BWM, Bruno S, Choo A, Dominici M, Gimona M, et al. Defining mesenchymal stromal cell (MSC)-derived small extracellular vesicles for therapeutic applications. J Extracell Vesicles. 2019;8(1):1609206.
Jeong H, Yim HW, Park HJ, Cho Y, Hong H, Kim NJ, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell therapy for ischemic heart disease: systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Stem Cells 2018;11(1):1–12.
Takafuji Y, Hori M, Mizuno T, Harada-Shiba M. Humoral factors secreted from adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate atherosclerosis in Ldlr−/− mice. Cardiovasc Res. 2019;115(6):1041–51.
Srikanthan S, Li W, Silverstein RL, McIntyre TM. Exosome poly-ubiquitin inhibits platelet activation, downregulates CD36 and inhibits pro-atherothombotic cellular functions. J Thromb Haemost. 2014;12(11):1906–17.
• Royo F, Cossio U, de Ruiz AA, Llop J, Falcon-Perez JM. Modification of the glycosylation of extracellular vesicles alters their biodistribution in mice. Nanoscale. 2019;11(4):1531–7 This research innovatively revealed that the modification of glycosylation of EVs can alter their biodistribution in mice.
Mooberry MJ, Key NS. Microparticle analysis in disorders of hemostasis and thrombosis. Cytometry A. 2016;89(2):111–22.
Funding
This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grants 81670392, 81770241, 81830013, 81970363, and Distinguished Young Scholar Grant 81325001), the Changjiang Scholars Program from the Ministry of Education of China, International Cooperation project (2015DFA31070) from the Ministry of Science and Technology of China, National Key R&D Program of China (2016YFC0903000), Guangdong Natural Science Fund Committee (Grant 2015A030312009), the Sun Yat-sen University Clinical Research 5010 Program, and Program of National Key Clinical Specialties.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Jing-Song Ou received grants from National Natural Science Foundation of China, grants from the Ministry of Education of China, grants from the Ministry of Science and Technology of China, and grants from Guangdong Natural Science Fund Committee, during the conduct of the study. Zhi-Jun Ou received grants from National Natural Science Foundation of China, during the conduct of the study. Other authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Ethics Approval
All reported studies/experiments with human or animal subjects performed by the authors have been previously published and complied with all applicable ethical standards (including the Helsinki Declaration and its amendments, institutional/national research committee standards, and international/national/institutional guidelines).
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Topical Collection on Genetics and Genomics
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, YT., Yuan, HX., Ou, ZJ. et al. Microparticles (Exosomes) and Atherosclerosis. Curr Atheroscler Rep 22, 23 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11883-020-00841-z
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11883-020-00841-z