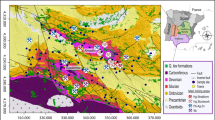
Abstract
This study investigated invasive Ambrosia artemisiifolia from five localities with different levels of anthropogenic pollution in order to determine the potential for accumulation of trace metals and metaloids. Physical characteristics of the soil are presented, together with concentrations of As, B, Ba, Ca, Cd, Co, Cu, Fe, Mg, Mn, Mo, Ni, Pb, Sb, Sr, and Zn in both plant and soil. The tested samples displayed considerable differences in element concentrations, depending on the level of anthropogenic activities, with the highest concentrations of elements observed in samples from Stolice and Piskanja, the sites with most intensive human influence. A trend of shoot accumulation can be observed in A. artemisiifolia, but without hyperaccumulation, along with lower root concentrations in almost all analyzed samples. This may pose an additional environmental risk, as accumulated elements can spread to other components of the ecosystem. While A. artemisiifolia acumulates a high and even toxic rate of B in shoots regardless of boron concentration in soil, there is a high correlation of Ba, Pb, and Zn concentrations in species shoots with their respective concentration in the soil. Successful colonization of both natural and anthropogenically polluted habitats indicates high tolerance of A. artemisiifolia, which complements its wide environmental amplitude.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Addinsoft (2020). XLSTAT statistical and data analysis solution. New York, USA. https://www.xlstat.com.
Alloway, B. J. (2013). Sources of heavy metals and metalloids in soils. In B. Alloway (Ed.), Heavy metals in soils (pp. 11–50). Dordrecht: Springer.
Andrić, N., Fügenschuh, B., Životić, D., & Cvetković, V. (2015). The thermal history of the Miocene Ibar Basin (southern Serbia): new constraints from apatite and zircon fission track and vitrinite reflectance data. Geologica Carpathica, 66(1), 37–50.
Angin, I., Turan, M., Ketterings, Q. M., & Cakici, A. (2008). Humic acid addition enhance B and Pb phytoextraction by vetiver grass (Vetiveria zizanoides (L.) Mash). Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 188, 335–343.
Bani, A., Pavlova, D., Echevarria, G., Mullaj, A., Reeves, R. D., Morel, J. L., & Sulçe, S. (2010). Nickel hyperaccumulation by the species of Alyssum and Thlaspi (Brassicaceae) from the ultramafic soils of the Balkans. Botanica Serbica, 34(1), 3–14.
Bettarini, I., Colzi, I., Coppi, A., Falsini, S., Echevarria, G., Pazzagli, L., Selvi, F., & Gonnelli, C. (2019). Unravelling soil and plant metal relationships in Albanian nickel hyperaccumulators in the genus Odontarrhena (syn. Alyssum sect. Odontarrhena, Brassicaceae). Plant and Soil, 440(1–2), 135–149.
Božić, D. (2018). Ambrosia artemisiifolia L. – ambrozija pelenasta. Acta Herbologica, 27(2), 79–97.
Casado, M., Anawar, H. M., Garcia-Sanchez, A., & Santa Regina, I. (2007). Antimony and arsenic uptake by plants in an abandoned mining area. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 38(9–10), 1255–1275.
Cloutier-Hurteau, B., Gauthier, S., Turmel, M., Comtois, P., & Courchesne, F. (2014). Trace elements in the pollen of Ambrosia artemisiifolia: What is the effect of soil concentrations? Chemosphere, 95, 541–549.
Conesa, H. M., Faz, Á., & Arnaldos, R. (2006). Heavy metal accumulation and tolerance in plants from mine tailings of the semiarid Cartagena–La Unión mining district (SE Spain). Science of the Total Environment, 366(1), 1–11.
Conesa, H. M., Faz, Á., & Arnaldos, R. (2007). Initial studies for the phytostabilization of a mine tailing from the Cartagena-La Union 820 Mining District (SE Spain). Chemosphere, 66(1), 8–44.
Čudić, V., Stojiljković, D., & Jovovic, A. (2016). Phytoremediation potential of wild plants growing on soil contaminated with heavy metals. Arhiv za Higijenu Rada i Toksikologiju, 67(3), 229–239.
Đorđević, D., Stanković, M., Krstić, N., Dimitrijević, V., Anastasijević, N., Đorđević, M., & Nikolić, M. (2018). Geochemical analysis of Kostolac power plant fly ash: working and living environment influence aspect. Safety Engineering, 18(1), 15–20.
Đuričković, A. (1982). Metallogeny of the Brasina mining field, Zajača, Stolice, Dobri Potok. Bulletin of Institute for Geological and Geophysical Research, 40, 17–53.
Filipović, I., Pavlović, Z., Marković, B., Radin, V., Marković, O., Gagić, N., Atin, B., & Milićević, M. (1967-1971). Geological map sheet Gornji Milanovac 1:100 000. Belgrade: Geologic map of Yugoslavia. Federal Geological Institute.
Fumanal, B., Girod, C., Fried, G., Bretagnolle, F., & Chauvel, B. (2008). Can the large ecological amplitude of Ambrosia artemisiifolia explain its invasive success in France? Weed Research, 48(4), 349–359.
Gajić, G., Mitrović, M., & Pavlović, P. (2019). Ecorestoration of fly ash deposits by native plant species at thermal power stations in Serbia. In V. C. Pandey & K. Bauddh (Eds.), Phytomanagement of Polluted Sites (pp. 113–177). Amsterdam: Elsevier.
Garg, N., & Singla, P. (2011). Arsenic toxicity in crop plants: physiological effects and tolerance mechanisms. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 9(3), 303–321.
Geologic map of Yugoslavia (1970). Geological map sheet Vrnjci 1:100 000. Federal Geological Institute, Belgrade.
Ghaderian, S. M., & Baker, A. J. M. (2007). Geobotanical and biogeochemical reconnaissance of the ultramafics of Central Iran. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 92(1), 34–42.
Global Invasive Species Database (2020). Species profile: Ambrosia artemisiifolia. http://www.iucngisd.org/gisd/species.php?sc=1125. Accessed 17 Jan 2020.
Hammel, W., Debus, R., & Steubing, L. (2000). Mobility of antimony in soil and its availability to plants. Chemosphere, 41(11), 1791–1798.
Hassan, Z., & Aarts, M. G. (2011). Opportunities and feasibilities for biotechnological improvement of Zn, Cd or Ni tolerance and accumulation in plants. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 72(1), 53–63.
Hijmans, R.J. Guarino, L., & Mathur, P. (2012). DIVA-GIS version 7.5. http://www.diva-gis.org/ accessed 20 December 2019.
Huang, J., & Cunningham, S. (1996). Lead phytoextraction: species variation in lead uptake and translocation. New Phytologist, 134, 75–84.
ISO 11466 (1995). International Standard. Soil quality – extraction of trace elements soluble in aqua regia. Geneva: International Organization for Standardization.
ISO 3166/2. (1998). Codes for the representation of names of countries and their subdivisions–part 2: Country subdivision code. Geneva: International Organization for Standardization.
Ivković, M. (2012). Sistematizacija prirodno-geoloških uslova eksplaoatacije uglja u podzemnim rudnicima u Srbiji. Resavica: Komitet za podzemnu eksploataciju.
Jakovljević, K., Đurović, S., Antušević, M., Mihailović, N., Buzurović, U., & Tomović, G. (2019). Heavy metal tolerance of Pontechium maculatum (Boraginaceae) from several ultramafic localities in Serbia. Botanica Serbica, 43(1), 73–83.
Jakovljević, K., Mišljenović, T., Savović, J., Ranković, D., Ranđelović, D., Mihailović, N., & Jovanović, S. (2020). Accumulation of trace elements in Tussilago farfara colonizing post-flotation tailing sites in Serbia. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27, 4089–4103.
Jim, C. Y., (1998). Urban soil characteristics and limitations for landscape planting in Hong Kong. Landscape and Urban Planning, 40(4), 235–249.
Jose, S., Pal Singh, H., Batis, D., & Kumar Kohli, R. (2013). Invasive plant ecology. Boca Raton: CRC Press.
Kabata-Pendias, A. (2011). Trace elements in soils and plants. Boca Raton: CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group.
Karanović, L., Rosić, A., & Poleti, D. (2004). Crystal structure of nobleite, Ca [B6O9 (OH) 2]˙ 3H2O, from Jarandol (Serbia). European Journal of Mineralogy, 16(5), 824–832.
Kazakou, E., Dimitrakopoulos, P. G., Baker, A. J. M., Reeves, R. D., & Troumbis, A. Y. (2008). Hypotheses, mechanisms and trade-offs of tolerance and adaptation to serpentine soils: from species to ecosystem level. Biological Reviews, 83(4), 495–508.
Kazinczi, G., Béres, I., Novák, R., Bíró, K., & Pathy, Z. (2008). Common ragweed (Ambrosia artemisiifolia): a review with special regards to the results in Hungary. I. Taxonomy, origin and distribution, morphology, life cycle and reproduction strategy. Herbologia, 9(1), 55–91.
Kostić, N. M., Wilson, M. J., Jakovljević, M. D., & Stevanović, D. (1996). Chemical and mineralogical studies of some Yugoslav deposols in relation to their possible agricultural use. Journal of Environmental Science & Health Part A, 31(7), 1575–1594.
Lemke, D., Schweitzer, C. J., Tazisong, I. A., Wang, Y., & Brown, J. A. (2013). Invasion of a mined landscape: what habitat characteristics are influencing the occurrence of invasive plants? International Journal of Mining. Reclamation and Environment, 27(4), 275–293.
Makra, L., Matyasovszky, I., & Deák, Á. J. (2014). Ragweed in Eastern Europe. In L. H. Ziska & J. S. Dukes (Eds.), Invasive species and global climate change (pp. 117–128). Boston: CAB International, Wallingford.
Makra, L., Matyasovszky, I., Hufnagel, L., & Tusnády, G. (2015). The history of ragweed in the world. Applied Ecology and Environmental Research, 13(2), 489–512.
Mandzhieva, S., Minkina, T., Chaplygin, V., Chaplygin, V., Motuzova, G., Sushkova, S., Bauer, T., & Nevidomskaya, D. (2016). Plant contamination by heavy metals in the impact zone of Novocherkassk Power Station in the south of Russia. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 16, 1383.
Markert, B. (1993). Occurrence and distribution of chemical elements in plants - outlook and further research plans. Toxicological & Environmental Chemistry, 40(1–4), 31–41.
Minkina, T., Mandzhieva, S., Chaplygin, V., Motuzova, G., Burachevskaya, M., Bauer, T., Sushkova, S., & Nevidomskaya, D. (2017). Eurasian Soil Science, 50(6), 746–755.
Montagnani, C., Gentili ,R., Smith, M., Guarino, M., & Citterio, S. (2017). The worldwide spread, success and impact of ragweed (Ambrosia spp.). Critical Reviews in Plant Sciences, 36(3), 139–178.
Mudrinić, Č. (1975). Primary dispersion aureoles of the antimony deposit Stolice (Western Serbia). Transactions of the Faculty of Mining and Geology, University of Belgrade, 18, 57–66.
Mudrinić, Č. (1978). Geohemijske karakteristike Sb-As asocijacije u Srpsko-Makedonskoj provinciji. Dissertation, University of Belgrade.
Nable, R. O., Bañuelos, G. S., & Paull, J. G. (1997). Boron toxicity. Plant and Soil, 193(1–2), 181–198.
Nouri, J., Khorasani, N., Lorestani, B., Karami, M., Hassani, A. H., & Yousefi, N. (2009). Accumulation of heavy metals in soil and uptake by plant species with phytoremediation potential. Environmental Earth Sciences, 59(2), 315–323.
Official Gazette RS 39/2016. Regulation on the establishment of the State pollution remediation program for the Kostajnička, Korenita and Jadar River due to discharge of the flotation tailing spill from the antimony mine “Stolice” [in Serbian].
Olujić, J., & Karović, J. (1970–1980). Geological map sheet Višegrad 1:100 000. Geologic map of Yugoslavia. Belgrade: Federal Geological Institute.
Ozturk, M., Sakcali, S., Gucel, S., & Tombuloglu, H. (2010). Boron and plants. In M. Ashraf, M. Ozturk, & M. Ahmad (Eds.), Plant adaptation and phytoremediation (pp. 275–311). Dordrecht: Springer.
Panaullah, G. M., Alam, T., Hossain, M. B., Loeppert, R. H., Lauren, J. G., Meisner, C. A., Ahmed, Z. U., & Duxbury, J. M. (2009). Arsenic toxicity to rice (Oryza sativa L.) in Bangladesh. Plant and Soil, 317(1–2), 31.
Pequerul, A., Pérez, C., Madero, P., Val, J., & Monge, E. (1993). A rapid wet digestion method for plant analysis. In M.A.C. Fragoso, M.L. Van Beusichem, & A. Houwers (Eds.), Optimization of plant nutrition, Developments in plant and soil sciences, vol 53 (pp. 3–6). Dordrecht: Springer.
Pichtel, J., Kuroiwa, K., & Sawyerr, H. (2000). Distribution of Pb, Cd and Ba in soils and plants of two contaminated sites. Environmental Pollution, 110, 171–178.
Pinke, G., Karácsony, P., Czúcz, B., & Botta-Dukát, Z. (2011). Environmental and land-use variables determining the abundance of Ambrosia artemisiifolia in arable fields in Hungary. Preslia, 83, 219–235.
Porter, E. K., & Peterson, P. J. (1975). Arsenic accumulation by plants on mine waste (United Kingdom). Science of the Total Environment, 4(4), 365–371.
Proctor, J. (1999). Toxins, nutrient shortages and droughts: the serpentine challenge. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 14(9), 334–335.
R Core Team (2019). R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. https://www.R-project.org/ Accessed 25 December 2019.
Ranđelović, D., Mutić, J., Marjanović, P., Đorđević, T., & Kašanin-Grubin, M. (2019). Geochemical distribution of selected elements in flotation tailings and soils/sediments from the dam spill at the abandoned antimony mine Stolice, Serbia. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07348-4.
Rat, M., Simonović, P., Glavendekić, M., Paunovic, M., Stojanović, V., Karaman, M., Radišić, D., & Anačkov, G. (2016). Overview of the invasive alien species in Serbia. ESENIAS Country Report, 91–114.
Sasmaz, M., & Sasmaz, A. (2017). The accumulation of strontium by native plants grown on Gumuskoy mining soils. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 181, 236–242.
Savić, D., Nišić, D., Malić, N., Dragosavljević, Z., & Medenica, D. (2018). Research on power plant ash impact on the quality of soil in Kostolac and Gacko coal basins. Minerals, 54(2), 1–16.
Shacklette, H.T., Erdman, J.A., Harms, T.F., & Papp, C.S. (1978). Trace elements in plant foodstuffs. Toxicity of heavy metals in the environment, Part 1, 25–43.
Singh, A., Zeng, D. H., & Chen, F. S. (2005). Heavy metal concentrations in redeveloping soil of mine spoil under plantations of certain native woody species in dry tropical environment, India. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 17, 168–174.
Širka, V. H., Jakovljević, K., Mihailović, N., & Jovanović, S. (2016). Heavy metal accumulation in invasive Reynoutria × bohemica Chrtek & Chrtková in polluted areas. Environmental Earth Sciences, 75(11), 951.
Slavnić, Ž. (1953). Prilog flori našeg Podunavlja (pp. 4–6). Zagreb: Glasnik biološke sekcije, Serija II/BT.
Soil Science Division Staff. (2017). Soil survey manual. USDA Handbook, 18, 120–131.
Tomović, G., Buzurović, U., Đurović, S., Vicić, D., Mihailović, N., & Jakovljević, K. (2018). Strategies of heavy metal uptake by three Armeria species growing on different geological substrates in Serbia. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 25(1), 507–522.
Vaculík, M., Jurkovič, L., Matejkovič, P., Molnárová, M., & Lux, A. (2013). Potential risk of arsenic and antimony accumulation by medicinal plants naturally growing on old mining sites. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 224, 1546.
Vardaki, C., & Kelepertsis, A. (1999). Environmental impact of heavy metals (Fe, Ni, Cr, Co) in soils waters and plants of Triada in Euboea from ultrabasic rocks and nickeliferous mineralization. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 21, 211–226.
Vidanović, N., Dimitrijević, B., & Tokalić, R. (2005). Deposits of borate raw materials and their industrial use. Underground Mining Engineering, 14, 157–162.
Vidotto, F., Tesio, F., & Ferrero, A. (2013). Allelopathic effects of Ambrosia artemisiifolia L. in the invasive process. Crop Protection, 54, 161–167.
Vrbničanin, S., Malidža, G., Stefanović, L., Elezović, I., Stanković-Kalezić, R., Marisavljević, D., Radovanov-Jovanović, K., Pavlović, D., & Gavrić, M. (2008). Distribution of some harmful, invasive and quarantine weeds on the territory of Serbia Part I: spatial distribution and frequency of eight weeds species on the territory of Serbia. Biljni lekar, 36, 303–313.
Vukanović Pešić, V., & Rajaković, L. (2014). Chemical composition and some trace element contents in coals and coal ash from Tamnava-Zapadno Polje coal field, Serbia. Energy Sources, Part A: Recovery,Utilization, and Environmental Effects, 31(17), 1583–1589.
Wanat, N., Joussein, E., Soubrand, M., & Lenain, J. F. (2014). Arsenic (As), antimony (Sb), and lead (Pb) availability from Au-mine technosols: a case study of transfer to natural vegetation cover in temperate climates. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 36, 783–795.
Wei, T., & Simko, V. (2017). R package “corrplot”: visualization of a correlation matrix (version 0.84). https://github.com/taiyun/corrplot accessed 14 January 2020.
Xue, S. G., Chen, Y. X., Reeves, R. D., Baker, A. J., Lin, Q., & Fernando, D. R. (2004). Manganese uptake and accumulation by the hyperaccumulator plant Phytolacca acinosa Roxb. (Phytolaccaceae). Environmental Pollution, 131(3), 393–399.
Yang, R. Y., Tang, J. J., Yang, Y. S., & Chen, X. (2007). Invasive and non-invasive plants differ in response to soil heavy metal lead contamination. Botanical Studies, 48(4), 453–458.
Yoon, J., Cao, X., Zhou, Q., & Ma, L. (2006). Accumulation of Pb, Cu, and Zn in native plants growing on a contaminated Florida site. Science of the Total Environment, 368(2–3), 456–464.
Zeng, F., Ali, S., Zhang, H., Ouyang, Y., Qiu, B., Wu, F., & Zhang, G. (2011). The influence of pH and organic matter content in paddy soil on heavy metal availability and their uptake by rice plants. Environmental Pollution, 159(1), 84–91.
Životić, D., Gržetić, I., Simić, V., Popović, V., & Milićević, V. (2008). Potentially hazardous trace elements in coal from the Kostolac coal basin. Tehnika - Rudarstvo, Geologija i Metalurgija, 59(1), 5–12.
Životić, D., Cvetković, O., Vulić, P., Gržetić, I., Simić, V., Ilijević, K., Dojčinović, B., Erić, S., Radić, B., Stojadinović, S., & Trifunović, S. (2019). Distribution of major and trace elements in the Kovin lignite (Serbia). Geologia Croatica, 72(1), 51–79.
Funding
The Ministry of Education, Science and Technological Development of the Republic of Serbia supported this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ranđelović, D., Jakovljević, K., Mišljenović, T. et al. Accumulation of Potentially Toxic Elements in Invasive Ambrosia artemisiifolia on Sites with Different Levels of Anthropogenic Pollution. Water Air Soil Pollut 231, 272 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04655-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04655-2