Abstract
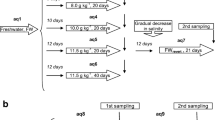
A hypothesis on the involvement of high-density lipoproteins (HDL) in maintaining osmotic homeostasis in fish was proposed. For its verification, structural reorganizations of serum HDL in the goldfish Carassius auratus L. were investigated under natural conditions (during the seasonal dynamics) and in experiments on the effect of critical salinity. A common algorithm of HDL rearrangements in wild freshwater fish and those acclimated experimentally to critical salinity was established. It consists in reversible dissociation–association of HDL particles. In the natural (freshwater) habitat, this algorithm is congruent with the dynamics of total protein distribution across the capillary wall, while under experimental conditions with changes in water salinity. These findings imply the possibility of multiple strategies of maintaining osmotic homeostasis with the involvement of HDL in higher teleosts the blood of which, in contrast to mammals, lacks a specialized osmotically active protein albumin. The role of HDL as universal metabolic regulators and stabilizers is discussed.




Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Levitt, D. and Levitt, M., Human serum albumin homeostasis: a new look at the roles of synthesis, catabolism, renal and gastrointestinal excretion, and the clinical value of serum albumin measurements, Int. J. Gen. Med., 2016, vol. 9, pp. 229–255.
Braasch, I., Gehrke, A.R., Smith, J.J., et al., The spotted gar genome illuminates vertebrate evolution and facilitates human-teleost comparison, Nat. Genet., 2016, vol. 48(4), pp. 427–437.
Pasquier, J., Cabau, C., Nguyen, T., et al., Gene evolution and gene expression after whole genome duplication in fish: the PhyloFish database, BMC Genomics, 2016, vol. 17(368), pp. 1–10.
Noel, E.S., Reis, M., Arain, Z., and Ober, E.A., Analysis of the Albumin/alpha-Fetoprotein/Afamin/Group specific component gene family in the context of zebrafish liver differentiation, Gene Expr. Patterns, 2010, vol. 10(6), pp. 237–243.
Metcalf, V.J., Brennan, S.O., and George, P.M., The Antarctic toothfish (Dissostichus mawsoni) lacks plasma albumin and utilises high density lipoprotein as its major palmitate binding protein, Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B, 1999, vol. 124(2), pp. 147–155.
Jerkovic, L., Voegele, A.F., Chwatal, S., et al., Afamin is a novel human vitamin E-binding glycoprotein characterization and in vitro expression, J. Proteome Res., 2005, vol. 4(3), pp. 889–899.
Babin, P.J. and Vernier, J.M., Plasma lipoproteins in fish, J. Lipid Res., 1989, vol. 30, pp. 467–489.
Andreeva, A.M., Lamash, N.E., Serebryako-va, M.V., et al., Reorganization of low-molecular-weight fraction of plasma proteins in the annual cycle of cyprinidae, Biochem. (Moscow), 2015, vol. 80, pp. 208–218.
Concha, M.I., Smith, V.J., Castro, K., et al., Apolipoproteins A-I and A-II are potentially important effectors of innate immunity in the teleost fish Cyprinus carpio, Eur. J. Biochem., 2004, vol. 271(14), pp. 2984–2990.
Harel, A., Fainaru, M., Rubinstein, M., et al., Fish apolipoprotein-A-I has heparin binding activity: implication for nerve regeneration, J. Neurochem., 1990, vol. 55(4), pp. 1237–1243.
Andreeva, A.M., The role of structural organization of blood plasma proteins in the stabilization of water metabolism in bony fish (Teleostei), J. Ichthyol., 2010, vol. 50(7), pp. 552–558.
Lahlou, B., Henderson, I.W., and Sawyer, W.H., Sodium exchanges in goldfish (Carassius auratus L.) adapted to a hypertonic saline solution, Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B, 1969, vol. 28, pp. 1427–1433.
IOC, SCOR and IAPSO. The International Thermodynamic Equation of Seawater—2010: Calculation and Use of Thermodynamic Properties. Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission, Manuals and Guides, no. 56, UNESCO, 2010.
Itzhaki, R.F. and Gill, D.M., A micro-biuret method for estimating protein, Anal. Biochem., 1964, vol. 9(4), pp. 401–410.
Olson, K.R., Blood and extracellular fluid volume regulation: role of the renin-angiotensin system, kallikrein-kinin system, and atrial natriuretic peptides, Fish Physiology, Part B. The Cardiovascular System, Hoar, W.S., Randall, D.J., and Far-rell, A.P., Eds., San Diego, 1992, pp. 136–254.
Andreeva, A.M., Serebryakova, M.V., and Lamash, N.E., Oligomeric protein complexes of apolipoproteins stabilize the internal fluid environment of organism in redfins of the Tribolodon genus [Pisces; Cypriniformes, Cyprinidae], Comp. Biochem. Physiol. D: Genomics and Proteomics, 2017, vol. 22, pp. 90–97.
Laemmli, U.K., Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage, Nature, 1970, vol. 227, pp. 680–685.
Gaal, O., Medgyesi, G.A., and Vereczkey, L., Electrophoresis in the Separation of Biological Macromolecules, Budapest (Akadémia Kiadó), 1980.
Chen, J., Shi, H., Hu, H.Q., et al., Apolipoprotein A-I, a hyperosmotic adaptation-related protein in ayu (Plecoglossus altivelis), Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B, 2009, vol. 152, pp. 196–201.
Detlaf, A.A. and Yavorsky, B.M., Kurs fiziki: uchebnoe posobie dlya vuzov (The Course of Physics: A Manual for Universities), Moscow, 1989.
Vaisar, T., Proteomics investigations of HDL: challenges and promise, Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol., 2012, vol. 10, pp. 410–421.
Borhani, D.W., Rogers, D.P., Engler, J.A., and Brouillette, C.G., Crystal structure of truncated human apolipoprotein A-I suggests a lipid-bound conformation, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1997, vol. 94(23), pp. 12291–12296.
Nguyen, M. and Kurtz, I., Quantitative interrelationship between Gibbs-Donnan equilibrium, osmolality of body fluid compartments, and plasma water sodium concentration, J. Appl. Physiol., 2006, vol. 100, pp. 1293–1300.
Martemyanov, V.I., An assessment of the fish status in relation to environmental salinity as based on osmotic regulation types, Trudy Zool. Inst. RAN, 2013, suppl. 3, pp. 175–181.
Sarin, H., Physiologic upper limits of pore size of different blood capillary types and another perspective on the dual pore theory of microvascular permeability, J. Angiogenes Res., 2010, vol. 2, pp. 1–19.
Metcalf, V.J., Brennan, S.O., Chambers, G.K., and George, P.M., The albumin of the brown trout (Salmo trutta) is a glycoprotein, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1998, vol. 1386(1), pp. 90–96.
Funding
This work was implemented within a state assignment to Papanin Institute for Biology of Inland Waters of the Russian Academy of Sciences (AAAA-A18-118012690123-4) and supported by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research (grant no. 16-04-00120-a).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All applicable international, national and institutional principles of handling and using experimental animals for scientific purposes were observed. This study did not involve human subjects as research objects.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Andreeva, A.M., Toropygin, I.Y., Garina, D.V. et al. The Role of High-Density Lipoproteins in Maintaining Osmotic Homeostasis in the Goldfish Carassius auratus L. (Cyprinidae). J Evol Biochem Phys 56, 102–112 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0022093020020027
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0022093020020027