Abstract
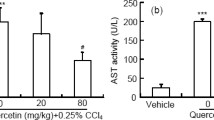
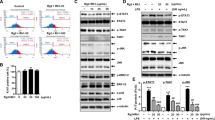
Apigenin, a flavonoid found in many plants, has various biological properties. We aimed to investigate the anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative activity of apigenin against carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)-induced acute liver injury in mice and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)-induced oxidative stress in HepG2 cells and possible mechanism. In vivo, apigenin significantly reduced alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) activity in serum of mice challenged by CCl4 and markedly alleviated the lipid peroxidation as indicated by the increased level of superoxide dismutase (SOD), reduced glutathione (GSH), glutathione peroxidases (GSH-Px) and catalase (CAT), and the decreased malondialdehyde (MDA) in liver tissue. Apigenin also ameliorated inflammation by downregulating tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and upregulating IL-10. Consistently, the elevated ALT and AST level; the impaired balance between SOD, GSH activity, and excessive ROS; and the increased gene expression of TNF-α and IL-6 resulting from H2O2-induced oxidative stress were restored by apigenin. Moreover, the results from Western blot, real-time qPCR, and immunofluorescence assay indicated that apigenin enhanced the activity of TNF receptor-associated factor (TRAF) 2/3 and cellular inhibitor of apoptosis protein (c-IAP) 1, ameliorated NF-κB-inducing kinase (NIK), and mediated the nuclear translocation of NF-κB2, therefore had an inhibitory effect on the non-canonical NF-κB pathway which was activated in both models. siNIK canceled the protective effect of apigenin on H2O2-induced HepG2 cells. Altogether, our results demonstrated that apigenin mitigated liver injury by ameliorating inflammation and oxidative stress through suppression of the non-canonical NF-κB pathway, indicating the potential of apigenin for treatment of the liver injury.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhakuni, Ganesh Singh, Onkar Bedi, Jitender Bariwal, Rahul Deshmukh, and Puneet Kumar. 2016. Animal models of hepatotoxicity. Inflammation Research 65. Springer International Publishing: 13–24. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-015-0883-0.
Protzer, Ulrike, Mala K. Maini, and Percy A. Knolle. 2012. Living in the liver: hepatic infections. Nature Reviews Immunology 12. Nature Publishing Group: 201–213. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri3169.
Sun, B., and M. Karin. 2008. NF-κB signaling, liver disease and hepatoprotective agents. Oncogene 27: 6228–6244. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.300.
Torres, Lucillia R. de O., Fernanda C. de Santana, Francisco L. Torres-Leal, Illana L.P. de Melo, Luciana T. Yoshime, Emidio M. Matos-Neto, Marília C.L. Seelaender, Cintia M.M. Araújo, Bruno Cogliati, and Jorge Mancini-Filho. 2016. Pequi (Caryocar brasiliense Camb.) almond oil attenuates carbon tetrachloride-induced acute hepatic injury in rats: Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. Food and Chemical Toxicology 97. Pergamon: 205–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FCT.2016.09.009.
Huang, Cheng, Yang Yang, Wan-Xia Li, Xiao-Qin Wu, Xiao-Feng Li, Tao-Tao Ma, Lei Zhang, Xiao-Ming Meng, and Jun Li. 2015. Hyperin attenuates inflammation by activating PPAR-γ in mice with acute liver injury (ALI) and LPS-induced RAW264.7 cells. International Immunopharmacology 29: 440–447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2015.10.017.
Weber, Lutz W.D., Meinrad Boll, and Andreas Stampfl. 2003. Hepatotoxicity and mechanism of action of haloalkanes: carbon tetrachloride as a toxicological model. Critical Reviews in Toxicology 33.Taylor & Francis: 105–136. https://doi.org/10.1080/713611034.
Rashid, Kahkashan, Krishnendu Sinha, and Parames C. Sil. 2013. An update on oxidative stress-mediated organ pathophysiology. Food and Chemical Toxicology 62. Pergamon: 584–600. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FCT.2013.09.026.
Abouzied, Mekky M., Heba M. Eltahir, Ashraf Taye, and Mahran S. Abdelrahman. 2016. Experimental evidence for the therapeutic potential of tempol in the treatment of acute liver injury. Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry 411. Springer US: 107–115. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-015-2572-2.
Shen, Hong, Sheng Liang, Chen Zheng, Jiang Lin, Su Haoran, Lei Yin, M. Bishr Omary, and Liangyou Rui. 2014. Mouse hepatocyte overexpression of NF-κB-inducing kinase (NIK) triggers fatal macrophage-dependent liver injury and fibrosis. Hepatology 60. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd: 2065–2076. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.27348.
Ai, Xiao-Yu, Yuan Qin, Hui-Jua Liu, Zhan-Hong Cui, Meng Li, Jia-Huan Yang, Wei-Long Zhong, et al. 2017. Apigenin inhibits colonic inflammation and tumorigenesis by suppressing STAT3-NF-κB signaling. Oncotarget 8. Impact Journals, LLC: 100216–100226. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.22145.
Zarnegar, Brian J., Yaya Wang, Douglas J. Mahoney, Paul W. Dempsey, Herman H. Cheung, Jeannie He, Travis Shiba, et al. 2008. Noncanonical NF-κB activation requires coordinated assembly of a regulatory complex of the adaptors cIAP1, cIAP2, TRAF2 and TRAF3 and the kinase NIK. Nature Immunology 9: 1371–1378. https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.1676.
Dejardin, Emmanuel, Nathalie M. Droin, Mireille Delhase, Elvira Haas, Yixue Cao, Constantin Makris, Zhi-Wei Li, Michael Karin, Carl F. Ware, and Douglas R. Green. 2002. The lymphotoxin-beta receptor induces different patterns of gene expression via two NF-kappaB pathways. Immunity 17: 525–535.
Claudio, Estefania, Keith Brown, Sun Park, Hongshan Wang, and Ulrich Siebenlist. 2002. BAFF-induced NEMO-independent processing of NF-kappa B2 in maturing B cells. Nature Immunology 3: 958–965. https://doi.org/10.1038/ni842.
Coope, H.J., P.G.P. Atkinson, B. Huhse, M. Belich, J. Janzen, M.J. Holman, G.G.B. Klaus, L.H. Johnston, and S.C. Ley. 2002. CD40 regulates the processing of NF-kappaB2 p100 to p52. The EMBO Journal 21: 5375–5385. https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/cdf542.
Ren, Xiaomeng, Xinzhi Li, Linna Jia, Deheng Chen, Hai Hou, Liangyou Rui, Yujun Zhao, and Chen Zheng. 2017. A small-molecule inhibitor of NF-κB-inducing kinase (NIK) protects liver from toxin-induced inflammation, oxidative stress, and injury. The FASEB Journal 31. Federation of American Societies for Experimental BiologyBethesda, MD, USA: 711–718. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.201600840R.
Jiang, Bijie, Hong Shen, Chen Zheng, Lei Yin, Linsen Zan, and Liangyou Rui. 2015. Carboxyl terminus of HSC70-interacting protein (CHIP) down-regulates NF-κB-inducing kinase (NIK) and suppresses NIK-induced liver injury. The Journal of Biological Chemistry 290. American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology: 11704–11714. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M114.635086.
Lefort, Émilie C., and Jonathan Blay. 2013. Apigenin and its impact on gastrointestinal cancers. Molecular Nutrition & Food Research 57: 126–144. https://doi.org/10.1002/mnfr.201200424.
Zhou, Qian, Hui Xu, Wenzhe Yu, Edmund Li, and Mingfu Wang. 2019. Anti-inflammatory effect of an apigenin-Maillard reaction product in macrophages and macrophage-endothelial cocultures. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity 2019. Hindawi Limited: 9026456. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/9026456.
Ali, Fahad, Falaq Naz Rahul, Smita Jyoti, and Yasir Hasan Siddique. 2014. Protective effect of apigenin against N-nitrosodiethylamine (NDEA)-induced hepatotoxicity in albino rats. Mutation Research, Genetic Toxicology and Environmental Mutagenesis 767: 13–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrgentox.2014.04.006.
Balez, Rachelle, Nicole Steiner, Martin Engel, Sonia Sanz Muñoz, Jeremy Stephen Lum, Yizhen Wu, Dadong Wang, et al. 2016. Neuroprotective effects of apigenin against inflammation, neuronal excitability and apoptosis in an induced pluripotent stem cell model of Alzheimer’s disease. Scientific Reports 6. Nature Publishing Group: 31450. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep31450.
Tan, Cheau Yih, Ruenn Chai Lai, Winnie Wong, Yock Young Dan, Sai-Kiang Lim, and Han Kiat Ho. 2014. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes promote hepatic regeneration in drug-induced liver injury models. Stem Cell Research & Therapy 5. BioMed Central: 76. https://doi.org/10.1186/scrt465.
Sadek, K.M., and E.A. Saleh. 2014. Fasting ameliorates metabolism, immunity, and oxidative stress in carbon tetrachloride-intoxicated rats. Human & Experimental Toxicology 33: 1277–1283. https://doi.org/10.1177/0960327114527629.
Vallabhapurapu, Sivakumar, Atsushi Matsuzawa, Weizhou Zhang, Ping-Hui Tseng, Jonathan J. Keats, Haopeng Wang, Dario A.A. Vignali, P. Leif Bergsagel, and Michael Karin. 2008. Nonredundant and complementary functions of TRAF2 and TRAF3 in a ubiquitination cascade that activates NIK-dependent alternative NF-kappaB signaling. Nature Immunology 9: 1364–1370. https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.1678.
Sun, Shao-Cong. 2011. Non-canonical NF-κB signaling pathway. Cell Research 21. Nature Publishing Group: 71–85. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2010.177.
Yarnpakdee, Suthasinee, Soottawat Benjakul, Hordur G. Kristinsson, and Hilma Eiðsdóttir Bakken. 2015. Preventive effect of Nile tilapia hydrolysate against oxidative damage of HepG2 cells and DNA mediated by H2O2 and AAPH. Journal of Food Science and Technology 52: 6194–6205. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-014-1672-4.
Amacher, David E. 1998. Serum transaminase elevations as indicators of hepatic injury following the administration of drugs. Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology 27: 119–130. https://doi.org/10.1006/rtph.1998.1201.
Ozer, Josef, Marcia Ratner, Martin Shaw, Wendy Bailey, and Shelli Schomaker. 2008. The current state of serum biomarkers of hepatotoxicity. Toxicology 245. Elsevier: 194–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TOX.2007.11.021.
Kubes, Paul, and Wajahat Z. Mehal. 2012. Sterile inflammation in the liver. Gastroenterology 143. W.B. Saunders: 1158–1172. https://doi.org/10.1053/J.GASTRO.2012.09.008.
Luan, Jingyun, and Ju. Dianwen. 2018. Inflammasome: a double-edged sword in liver diseases. Frontiers in Immunology 9: 2201. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2018.02201.
Tacke, Frank, Tom Luedde, and Christian Trautwein. 2009. Inflammatory pathways in liver homeostasis and liver injury. Clinical Reviews in Allergy & Immunology 36: 4–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12016-008-8091-0.
Jaeschke, H., Gregory J. Gores, Arthur I. Cederbaum, Jack A. Hinson, Dominique Pessayre, and John J. Lemasters. 2002. Mechanisms of hepatotoxicity. Toxicological Sciences 65. Narnia: 166–176. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/65.2.166.
Hong, Feng, Won-Ho Kim, Zhigang Tian, Barbara Jaruga, Edward Ishac, Xuening Shen, and Bin Gao. 2002. Elevated interleukin-6 during ethanol consumption acts as a potential endogenous protective cytokine against ethanol-induced apoptosis in the liver: involvement of induction of Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL proteins. Oncogene 21. Nature publishing group: 32–43. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1205016.
Chong, Wai Chin, Madhur D. Shastri, and Rajaraman Eri. 2017. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and oxidative stress: a vicious Nexus implicated in bowel disease pathophysiology. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18. Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute (MDPI). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18040771.
Niu, Xiaofeng, Fang Liu, Weifeng Li, Wenbing Zhi, Qing Yao, Jinmeng Zhao, Guoxiang Yang, Xiumei Wang, Qin Lin, and Zehong He. 2017. Hepatoprotective effect of fraxin against carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity in vitro and in vivo through regulating hepatic antioxidant, inflammation response and the MAPK-NF-κB signaling pathway. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 95. Elsevier Masson: 1091–1102. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BIOPHA.2017.09.029.
Cigremis, Yilmaz, Huseyin Turel, Kevser Adiguzel, Muslum Akgoz, Asim Kart, Musa Karaman, and Hasan Ozen. 2009. The effects of acute acetaminophen toxicity on hepatic mRNA expression of SOD, CAT, GSH-Px, and levels of peroxynitrite, nitric oxide, reduced glutathione, and malondialdehyde in rabbit. Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry 323. Springer US: 31–38. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-008-9961-8.
Krithika, Rajesh, Ramasamy Mohankumar, Ramtej J. Verma, Pranav S. Shrivastav, Illiyas L. Mohamad, Palani Gunasekaran, and Srinivasan Narasimhan. 2009. Isolation, characterization and antioxidative effect of phyllanthin against CCl4-induced toxicity in HepG2 cell line. Chemico-Biological Interactions 181: 351–358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2009.06.014.
Liu, Yan, Sheng Liang, Yi Xiong, Hong Shen, Yong Liu, and Liangyou Rui. 2017. Liver NF-κB-inducing kinase promotes liver steatosis and glucose counterregulation in male mice with obesity. Endocrinology 158. The Endocrine Society: 1207–1216. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2016-1582.
Sun, Shao-Cong. 2017. The non-canonical NF-κB pathway in immunity and inflammation. Nature Reviews Immunology 17: 545–558. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri.2017.52.
Gardam, Sandra, Frederic Sierro, Antony Basten, Fabienne Mackay, and Robert Brink. 2008. TRAF2 and TRAF3 signal adapters act cooperatively to control the maturation and survival signals delivered to B cells by the BAFF receptor. Immunity 28: 391–401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2008.01.009.
Liao, Gongxian, Minying Zhang, Edward W. Harhaj, and Shao-Cong Sun. 2004. Regulation of the NF-κB-inducing kinase by tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 3-induced degradation. Journal of Biological Chemistry 279: 26243–26250. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M403286200.
Xiao, Gutian, Edward W. Harhaj, and Shao-Cong Sun. 2001. NF-κB-Inducing Kinase Regulates the Processing of NF-κB2 p100. Molecular Cell 7. Cell Press: 401–409. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1097-2765(01)00187-3.
Acknowledgments
This study was conceived by XW. XW and SWY designed the study. SWY performed all experiments in the current study. NX and HLL provided experimental assistance. SWY wrote the original draft. BSH, ZC, and XW reviewed the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20180574, BK20171064), the Technology Incubator Scheme (Social Programs) of Jiangning District (2018Ca12), the Research Foundation of Jiangsu Provincial Medical Youth Talent, the Project of Inviogorating Health Care through Science, Technology and Education (QNRC2016858), the Nanjing Medical University Science Research and Development Foundation (2016NJMU013), the Natural Science Research Fund (General Program) for the Higher Education of Jiangsu Province of China (18KJB350005), and the Zhenjiang City 2017 Science and Technology Innovation Fund (SH2017043).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of China Pharmaceutical University.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yue, S., Xue, N., Li, H. et al. Hepatoprotective Effect of Apigenin Against Liver Injury via the Non-canonical NF-κB Pathway In Vivo and In Vitro. Inflammation 43, 1634–1648 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-020-01238-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-020-01238-5