Abstract
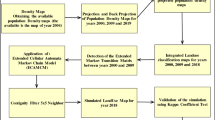
This study validates the applicability of the extended Markov chain modeling for predicting the dynamics of land use in Lebanon by using (i) the current available population density maps, (ii) Landsat satellite images, (iii) ArcGIS software and (iv) TerrSet software. An extended Markov chain model was developed to predict future land use dynamics by integrating the built-up area into three categories as per the development density based on population density maps for years 2000, 2009 and 2018. Land use classification maps were generated by integrating medium-resolution Landsat images of 30 meters into ArcGIS. The population density maps were combined with the classified land use maps in order to divide the built-up land use areas into three categories: high-, medium- and low-density urban development. The observed transition matrices were computed using TerrSet software. A Markov chain projection of land use for year 2018 was generated based on the actual transition matrix and compared to the observed land use. A Pearson’s chi-square test was conducted to validate the proposed model. Then, a projection of land use for 2036 was conducted based on the actual transition matrix between 2000 and 2018. Finally, insights and recommendations were proposed to address future Lebanese land use dynamics.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ching, W.; Ng, M.K.: Markov Chains: Models, Algorithms and Applications, p. 207. Springer, New York (2006)
Gagniuc, P.A.: Markov Chains: From Theory to Implementation and Experimentation, p. 235. Wiley, Hoboken (2017)
Grinstead, C.M.; Snell, J.L.: Grinstead and snell’s introduction to probability. In: Doyle, P.G. (eds.) p. 510. The American Mathematical Society (2006)
Iacono, M.; Levinson, D.; El-Geneidy, A.; Wasfi, R.: A Markov chain model of land use change in the twin cities, 1958–2005. TeMA J. Land Use Mobil. Environ. 8(3), 263–276 (2012). https://doi.org/10.6092/1970-9870/2985
Muller, M.R.; Middleton, J.: A Markov model of land-use change dynamics in the Niagara Region, Ontario, Canada. Landsc. Ecol. 9(2), 151–157 (1994)
Weng, Q.: Land use change analysis in the Zhujiang Delta of China using satellite remote sensing, GIS and stochastic modelling. J. Environ. Manag. 64, 273–284 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1006/jema.2001.0509
Levinson, D.; Chen, W.: Paving new ground: a markov chain model of the change in transportation networks and land use. In: Levinson D.M.; Krizek, K.J. (eds.) Access to Destinations, pp. 243–266. Emerald (2005). https://doi.org/10.1108/9780080460550-012. Accessed 4 May 2019
Takada, T.; Miyamoto, A.; Hasegawa, S.F.: Derivation of a yearly transition probability matrix for land-use dynamics and its applications. Landsc. Ecol. 25, 561–572 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10980-009-9433-x
Subedi, P.; Subedi, K.; Thapa, B.: Application of a hybrid cellular automaton Markov (CA-Markov) Model in land-use change prediction: a case study of saddle creek drainage Basin, Florida. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 1(6), 126–132 (2013). https://doi.org/10.12691/aees-1-6-5
Han, H.; Yang, C.; Song, J.: Scenario simulation and the prediction of land use and land cover change in Beijing, China. Sustainability 7, 4260–4279 (2015). https://doi.org/10.3390/su7044260
Rozario, P.F.; Oduor, P.; Kotchman, L.; Kangas, M.: Transition modeling of land-use dynamics in the Pipestem Creek, North Dakota, USA. J. Geosci. Environ. Prot. 5, 182–201 (2017). https://doi.org/10.4236/gep.2017.53013
Hamad, R.; Balzter, H.; Kolo, K.: Predicting land use/land cover changes using a CA-Markov model under two different scenarios. Sustainability 10, 23 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3390/su10103421
Bourne, L.: Physical adjustment processes and land use succession: a conceptual review and central city example. Econ. Geogr. 47(1), 1–15 (1971). https://doi.org/10.2307/143220
Bell, E.J.: Markov analysis of land use change—an application of stochastic processes to remotely sensed data. Socio Econ. Plan. Sci. 8, 311–316 (1974)
Turner, M.G.: Spatial simulation of landscape changes in Georgia: a comparison of 3 transition models. Landsc. Ecol. 1(1), 29–36 (1987)
Chakir, R.; Parent, O.: Determinants of land use changes: a spatial multinomial probit approach. Pap. Reg. Sci. 88(2), 327–344 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1435-5957.2009.00239.x
Wang, X.; Kockelman, K.M.: Application of the dynamic spatial ordered probit model—patterns of land development change in Austin, Texas. Pap. Reg. Sci. 88(2), 345–365 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1435-5957.2009.00249.x
Wang, W.; Zhang, C.; Allen, J.M.; Li, W.; Boyer, M.A.; Segerson, K.; Silander Jr., J.A.: Analysis and prediction of land use changes related to invasive species and major driving forces in the state of Connecticut. Land 5, 22 (2016). https://doi.org/10.3390/land5030025
Nouri, J.; Gharagozlou, A.; Arjmandi, R.; Faryadi, S.; Adl, M.: Predicting urban land use changes using a CA-Markov model. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 39(7), 5565–5573 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-014-1119-2
Hua, A.K.: Application of CA-markov model and land use/land cover changes in Malacca River Watershed, Malaysia. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 15(4), 605–622 (2017). https://doi.org/10.15666/aeer/1504_605622
Fawaz, M.: Constraints of land use planning in Lebanon. Al Mouhandess magazine 26, 16–17 (2011)
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO): Country Study on Status of Land Tenure, Planning and Management in Oriental near East Countries: Case of Lebanon. FAO, New York (2012)
“EarthExplorer” EarthExplorer. https://earthexplorer.usgs.gov/. Accessed July 2019
Abdallah, C.: Gateway to Land and Water Information Lebanon National Report. National Council for Scientific Research, Beirut (2002)
Masri, T.; Khawlie, M.; G, Faour: Land cover change over the last 40 years in Lebanon. Leban. Sci. J. 3(2), 17–28 (2002)
“Lebanese population density map” Localiban, last modified on 23 June 2016. https://www.localiban.org/lebanese-population-density-map. Accessed 13 July 2019
“Lebanon Population” WorldPopulationReview, last modified on 1-August-2019. http://worldpopulationreview.com/countries/lebanon-population/#popGrowth. Accessed 6 Aug 2019
“World Population Prospects 2019” United Nations DESA/Population Division. https://population.un.org/wpp/. Accessed 6 Aug 2019
Sisodia, P.S.; Tiwari, V.; Kumar, A.: Analysis of supervised maximum likelihood classification for remote sensing image. In: Paper Presented in the IEEE International Conference on Recent Advances and Innovations in Engineering (ICRAIE), p. 4. Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), Jaipur, India (2014)
Ozturk, D.: Urban growth simulation of Atakum (Samsun, Turkey) using cellular automata-Markov chain and multi-layer perceptron-Markov chain models. Remote Sens. 7, 5918–5950 (2015). https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70505918
Weng, Q.H.: Remote Sensing and GIS Integration, p. 416. McGraw-Hill, New York (2010)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Shaar, W., Nehme, N. & Adjizian Gérard, J. The Applicability of the Extended Markov Chain Model to the Land Use Dynamics in Lebanon. Arab J Sci Eng 46, 495–508 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-04645-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-04645-w