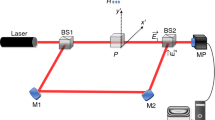
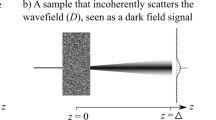
Abstract
Ionizing radiations are being widely used in a variety of medical and industrial applications in which the exact determination of the absorbed dose distribution is of crucial importance. Digital holographic interferometry (DHI) is an optical technique that uses lasers to produce fringe patterns which must be reconstructed to measure the physical quantities of interest. The DHI technique is sensitive to noise that makes it difficult to adopt this technique for practically measuring the absorbed dose. In this paper, a new approach to DHI has been developed based on using fringe contouring, polynomial phase fitting and inverse Abel transformation, to reconstruct the three-dimensional dose distribution in noisy conditions. In order to assess the feasibility of this approach in measuring the absorbed dose distributions in noisy conditions, the whole approach is modeled for high energy electrons. It is shown that the three-dimensional dose distribution inside the absorbing medium can be obtained with good accuracy even in the presence of considerable amounts of deliberately added noise to the holograms.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Falahati et al., J. Instrum. 13, P02028 (2018)
E. Hussmann, Appl. Opt. 10, 182 (1971)
J. Seuntjens, A. DuSautoy, Standards and Codes of Practice in Medical Radiation Dosimetry, vol. 37 (2002)
A.M. Beigzadeh et al., Lasers Surg. Med. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/lsm.23193
A. Krauss, Metrologia 43, 259 (2006)
N.V. Klassen, C.K. Ross, J. Res. Natl. Inst. Stand. Technol. 102, 63 (1997)
A. Miller, W. McLaughlin, Phys. Med. Biol. 21, 285 (1976)
E. Flores-Martinez, M.J. Malin, L.A. DeWerd, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 87, 114301 (2016)
L. Heflinger, R. Wuerker, R. Brooks, J. Appl. Phys. 37, 642 (1966)
J. Devanney, Nucl. Instrum. Methods 120, 77 (1974)
A. Miller, W.L. McLaughlin, Nucl. Instrum. Methods 128, 337 (1975)
M.R. Vaziri, F. Hajiesmaeilbaigi, M. Maleki, J. Opt. 15, 035202 (2013)
E. Hussmann, W. McLaughlin, Radiat. Res. 47, 1 (1971)
A. Miller, Nukleonika 24, 907 (1979)
A. Miller, E. Hussmann, W. McLaughlin, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 46, 1635 (1975)
S. Nicolau, D.G. Sporea, V. Niculescu, in International Conference on Optical Metrology (International Society for Optics and Photonics, 1999), p. 393
U. Schnars, W. Jüptner, Appl. Opt. 33, 179 (1994)
U. Schnars et al., in Digital Holography and Wavefront Sensing, ed. by U. Schnars, C. Falldorf, J. Watson, W. Jüptner (Springer, Berlin, 2015), p. 69
A. Cavan, J. Meyer, Med. Phys. 41, 022102 (2014)
Z. Malacara, M. Servin, Interferogram Analysis for Optical Testing (CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2016)
Y. Huang et al., Opt. Exp. 19, 606 (2011)
E. Flores-Martinez, et al., in AIP Conference Proceedings (AIP Publishing, 2016), p. 110001
U. Schnars, JOSA A 11, 2011 (1994)
R. Arizaga et al., Opt. Commun. 108, 209 (1994)
P. O’shea, IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 9, 251 (2002)
M.R.R. Vaziri, F. Hajiesmaeilbaigi, M.H. Maleki, Opt. Eng. 51, 044301 (2012)
J.F. Briesmeister, MCNP–A General Monte Carlo Code for Neutron and Photon Transport (Los Alamos National Laboratory, Los Alamos, 1986)
E. Kazemi et al., Anal. Chim. Acta 905, 85 (2016)
A. Beigzadeh, M.R. Vaziri, F. Ziaie, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. 864, 40 (2017)
T. Kreis, Handbook of Holographic Interferometry: Optical and Digital Methods (Wiley, New York, 2006)
B. Farmanfarmaei, M.R. RashidianVaziri, F. Hajiesmaeilbaigi, Quantum Electron. 44, 1029 (2014)
A. Beigzadeh et al., Radiat. Meas. 119, 132 (2018)
J.B. Schemm, C.M. Vest, Appl. Opt. 22, 2850 (1983)
J.J. Snyder, Appl. Opt. 19, 1223 (1980)
G.A. Mastin, D.C. Ghiglia, Appl. Opt. 24, 1727 (1985)
K.J. Gasvik, K.G. Robbersmyr, T. Vadseth, in 33rd Annual Technical Symposium (International Society for Optics and Photonics, 1989), p. 64
T. Yatagai et al., Opt. Eng. 21, 213432 (1982)
C. Hilditch, Mach. Intell. 6, 403 (1969)
M. Cheriet et al., Character Recognition Systems: A Guide for Students and Practitioners (Wiley, New York, 2007)
G. Pretzier, Z. Naturforsch. A 46, 639 (1991)
G. Pretzier, H. Jager, T. Neger, Meas. Sci. Technol. 4, 649 (1993)
M. Berger, S. Seltzer, in Studies in Penetration of Charged Particles in Matter, vol. 205 (1964)
M.J. Berger, S.M. Seltzer, National Standard Reference Data System (1982)
G.M. Hale, M.R. Querry, Appl. Opt. 12, 555 (1973)
L. Tilton, J. Taylor, J. Res. Natl. Bur. Stand. 20, 419 (1938)
D.B. Leviton, B.J. Frey, in SPIE Astronomical Telescopes + Instrumentation (International Society for Optics and Photonics, 2006), p. 62732K
K. Itoh, Appl. Opt. 21, 2470 (1982)
D.C. Ghiglia, M.D. Pritt, Two-Dimensional Phase Unwrapping: Theory, Algorithms, and Software (Wiley, New York, 1998)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rashidian Vaziri, M.R., Beigzadeh, A.M., Ziaie, F. et al. Digital holographic interferometry for measuring the absorbed three-dimensional dose distribution. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 135, 436 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-020-00443-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-020-00443-3