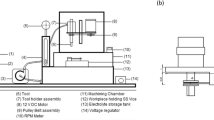
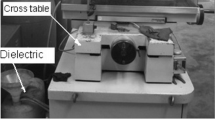
Abstract
This paper introduces an experimental investigation of micro hole drilling on two different categories of material such as silicon and german silver using micro electrical discharge machining (μEDM) process. The conductivities of the two materials are of different levels; silicon being a semiconductor has relatively much lower electrical conductivity as compared to german silver which is an alloy of copper, nickel and zinc. The tool electrode used is tungsten rod of 518 μm diameter. Responses like material removal rate (MRR), taper angle (TA), circularity error (CE) and overcut (OC) have been calculated and their variation with respect to the process parameters such as capacitance and voltage are evaluated. In both the materials, the values of all the responses increases with an increase in both voltage and capacitance. German silver is observed to have a higher MRR and OC than that of silicon while silicon has a higher TA for the same values of process parameters. The CE of silicon is higher at lower capacitance while it is higher for german silver at higher capacitance. From the analysis of variance (ANOVA), it is observed that both the voltage and capacitance played a significant role in all the responses. An optimum condition of micro hole drilling of both the materials is achieved by formulating overall evaluation criteria (OEC), which combines all the response parameters into a single index. In most of the cases, OEC of german silver is found to be higher than silicon, thus justifying the superior machinability performance of german silver. From the ANOVA of OEC, the role of capacitance is found to be more significant as compared to the voltage.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Modica F, Marrocco V, Fassi I (2017) Micro-electro-discharge machining (micro-EDM). In: Fassi I, Shipley D (eds) Springer tracts in mechanical engineering. Springer, Cham, pp 149–173
Bains PS, Sidhu SS, Payal HS (2018) Magnetic field assisted EDM: new horizons for improved surface properties. Silicon 10:1275–1282. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-017-9600-7
Bhaumik M, Maity K (2019) Effect of electrode materials on different EDM aspects of titanium alloy. Silicon 11:187–196. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-018-9844-x
Kumari S, Datta S, Masanta M, Nandi G, Pal PK (2018) Electro-discharge machining of Inconel 825 super alloy: effects of tool material and dielectric Flushing. Silicon 10:2079–2099. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-017-9728-5
Kolli M, Kumar A (2019) Assessing the influence of surfactant and B4C powder mixed in dielectric fluid on EDM of titanium alloy. Silicon 11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-017-9701-3
Katz Z, Tibbles CJ (2005) Analysis of micro-scale EDM process. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 25:923–928. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-003-2007-1
Jahan MP, Wong YS, Rahman M (2009) A study on the quality micro-hole machining of tungsten carbide by micro-EDM process using transistor and RC-type pulse generator. J Mater Process Technol 209:1706–1716. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2008.04.029
Muthuramalingam T, Mohan B, Vignesh S (2018) Performance analysis of pulse generators on residual stress of machined silicon steel using the EDM process. Silicon 10:1785–1792. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-017-9671-5
Petersen KE (1982) Silicon as a mechanical material. Proc IEEE 70:420–457. https://doi.org/10.1109/PROC.1982.12331
Joshi K, Bhandarkar UV, Joshi SS (2019) Surface integrity and wafer-thickness variation analysis of ultra-thin silicon wafers sliced using wire-EDM. Adv Mater Process Technol 5:512–525. https://doi.org/10.1080/2374068X.2019.1636185
Wangikar SS, Patowari PK, Misra RD (2017) Effect of process parameters and optimization for photochemical machining of brass and german silver. Mater Manuf Process 32:1747–1755. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2016.1244848
Sortino M, Belfio S, Totis G, Kuljanic E, Fadelli G (2015) Innovative tool coatings for increasing tool life in milling nickel-coated nickel-silver alloy. Energy Procedia 100:946–952. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2015.01.453
Saxena KK, Srivastava AS, Agarwal S (2016) Experimental investigation into the micro-EDM characteristics of conductive SiC. Ceram Int 42:1597–1610. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2015.09.111
Peng WY, Liao YS (2003) Study of electrical discharge machining technology for slicing silicon ingots. J Mater Process Technol 140:274–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0924-0136(03)00718-0
Subbu SK, Dhamodaran S, Ramkumar J (2012) Investigation of single pulse discharge on silicon: crater and plasma characteristics. Int J Mechatronics Manuf Syst 5:455. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJMMS.2012.049973
Joshi K, Ananya A, Bhandarkar U, Joshi SS (2017) Ultra thin silicon wafer slicing using wire-EDM for solar cell application. Mater Des 124:158–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2017.03.059
Joshi K, Sharma G, Dongre G, Joshi SS (2017) Numerical modelling of wire-EDM for predicting erosion rate of silicon. J Inst Eng Ser C 98:63–73. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40032-016-0237-x
Zeller F, Müller C, Miranzo P, Belmonte M (2017) Exceptional micromachining performance of silicon carbide ceramics by adding graphene nanoplatelets. J Eur Ceram Soc 37:3813–3821. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2017.03.072
Tan T-H, Yan J (2017) Atomic-scale characterization of subsurface damage and structural changes of single-crystal silicon carbide subjected to electrical discharge machining. Acta Mater 123:362–372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2016.10.045
Roy RK (2001) Design of experiments using the Taguchi approach: 16 steps to product and process improvement. Wiley
Kar S, Patowari PK (2019) Effect of non-electrical parameters in fabrication of micro rod using BEDG. Mater Manuf Process 34:1262–1273. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2019.1643475
Haashir A, Debnath T, Patowari PK (2020) A comparative assessment of micro drilling in boron carbide using ultrasonic machining. Mater Manuf Process 35:86–94. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2019.1697447
Liu W, Jia Z, Zou S, Zheng X (2014) A new measurement method of relative volume Wear ratio based on discharge debris composition analysis in micro-EDM. Adv Mech Eng 6:479609. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/479609
Silicon, Si. http://www.matweb.com/search/DataSheet.aspx?MatGUID=7d1b56e9e0c54ac5bb9cd433a0991e27. Accessed 16 Sep 2019
Copper, Cu; Annealed. http://www.matweb.com/search/DataSheet.aspx?MatGUID=9aebe83845c04c1db5126fada6f76f7e. Accessed 16 Sep 2019
Nickel, Ni. http://www.matweb.com/search/DataSheet.aspx?MatGUID=e6eb83327e534850a062dbca3bc758dc. Accessed 16 Sep 2019
Zinc, Zn. http://www.matweb.com/search/DataSheet.aspx?MatGUID=8909140a76074049809ad74d536ed606. Accessed 16 Sep 2019
Kar S, Patowari PK (2019) Experimental investigation of machinability and surface characteristics in microelectrical discharge milling of titanium, stainless steel and copper. Arab J Sci Eng 44:7843–7858. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-019-03918-3
Kar S, Patowari PK (2018) Electrode wear phenomenon and its compensation in micro electrical discharge milling: a review. Mater Manuf Process 33:1491–1517. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2018.1453144
Jahan MP, Wong YS, Rahman M (2010) A comparative experimental investigation of deep-hole micro-EDM drilling capability for cemented carbide (WC-Co) against austenitic stainless steel (SUS 304). Int J Adv Manuf Technol 46:1145–1160. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-009-2167-8
Liu H-S, Yan B-H, Huang F-Y, Qiu K-H (2005) A study on the characterization of high nickel alloy micro-holes using micro-EDM and their applications. J Mater Process Technol 169:418–426. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2005.04.084
Paul TR, Saha A, Majumder H, Dey V, Dutta P (2019) Multi-objective optimization of some correlated process parameters in EDM of Inconel 800 using a hybrid approach. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng 41:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-019-1805-9
Majumder H, Maity KP (2018) Predictive analysis on responses in WEDM of titanium grade 6 using general regression neural network (GRNN) and multiple regression analysis (MRA). Silicon 10:1763–1776. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-017-9667-1
Majumder H, Maity K (2018) Application of GRNN and multivariate hybrid approach to predict and optimize WEDM responses for Ni-Ti shape memory alloy. Appl Soft Comput J 70:665–679. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2018.06.026
Feng W, Chu X, Hong Y, Zhang L (2018) Studies on the surface of high-performance alloys machined by micro-EDM. Mater Manuf Process 33:616–625. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2017.1364758
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deka, S., Kar, S. & Patowari, P.K. Machinability of Silicon and German Silver in Micro Electrical Discharge Machining: a Comparative Study. Silicon 13, 1065–1077 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-020-00496-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-020-00496-0