Abstract
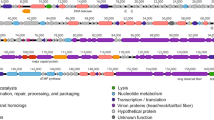
Acinetobacter pittii is an important pathogen causing nosocomial infection worldwide. In this study, a multidrug-resistant A. pittii ABC38 was used as host bacterium to isolate the lytic phage vB_ApiP_XC38. The biological characteristics of vB_ApiP_XC38 were studied and the genome was sequenced and analyzed. vB_ApiP_XC38 belonged to Podoviridae family. The phage had double-stranded genome, which comprised 79,328 bp with 39.58% G+C content displaying very low similarity (< 1% identity) with published genomes of other phages and bacteria. A total of 97 open reading frames (ORFs) were predicted and contained nucleotide metabolism and replication module, structural components module, and lysis module. The ANI, AAI, and phylogenetic analysis indicated that all phages were found distant from vB_ApiP_XC38. Altogether, morphological, genomics, and phylogenetic analysis suggest that vB_ApiP_XC38 is more likely a novel phage of A. pittii.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nemec A, Krizova L, Maixnerova M, van der Reijden TJ, Deschaght P, Passet V, Vaneechoutte M, Brisse S, Dijkshoorn L (2011) Genotypic and phenotypic characterization of the Acinetobacter calcoaceticus-Acinetobacter baumannii complex with the proposal of Acinetobacter pittii sp. nov. (formerly Acinetobacter genomic species 3) and Acinetobacter nosocomialis sp. nov. (formerly Acinetobacter genomic species 13TU). Res Microbiol 162(4):393–404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resmic.2011.02.006
Wisplinghoff H, Paulus T, Lugenheim M, Stefanik D, Higgins PG, Edmond MB, Wenzel RP, Seifert H (2012) Nosocomial bloodstream infections due to Acinetobacter baumannii, Acinetobacter pittii and Acinetobacter nosocomialis in the United States. J Infect 64(3):282–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jinf.2011.12.008
Liu YM, Lee YT, Kuo SC, Chen TL, Liu CP, Liu CE (2017) Comparison between bacteremia caused by Acinetobacter pittii and Acinetobacter nosocomialis. J Microbiol Immunol Infect 50(1):62–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmii.2015.01.003
Chagas TPG, Tavares EOTR, D'Alincourt Carvalho-Assef AP, Albano RM, Asensi MD (2017) Carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter pittii strain harboring blaOXA-72 from Brazil. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 88(1):93–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2017.01.022
Brasiliense DM, Lima KVB, Perez-Chaparro PJ, Mamizuka EM, de Oliveira SC, Dutra LMG, McCulloch JA (2019) Emergence of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter pittii carrying the blaOXA-72 gene in the Amazon region Brazil. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 93(1):82–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2018.07.017
Park YK, Jung SI, Park KH, Kim SH, Ko KS (2012) Characteristics of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter spp. other than Acinetobacter baumannii in South Korea. Int J Antimicrob Agents 39(1):81–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2011.08.006
Deglmann RC, Kobs VC, Oliveira D, Burgardt P, Franca PHC, Pillonetto M (2019) Earliest identification of New Delhi metallo-beta-lactamase 1 (NDM-1) in Acinetobacter pittii in Brazil. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop 52:e20180348. https://doi.org/10.1590/0037-8682-0348-2018
Pailhories H, Tiry C, Eveillard M, Kempf M (2018) Acinetobacter pittii isolated more frequently than Acinetobacter baumannii in blood cultures: the experience of a French hospital. J Hosp Infect 99(3):360–363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhin.2018.03.019
Zhang G, Leclercq SO, Tian J, Wang C, Yahara K, Ai G, Liu S, Feng J (2017) A new subclass of intrinsic aminoglycoside nucleotidyltransferases, ANT(3")-II, is horizontally transferred among Acinetobacter spp. by homologous recombination. PLoS Genet 13(2):e1006602. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1006602
Jamal M, Bukhari S, Andleeb S, Ali M, Raza S, Nawaz MA, Hussain T, Rahman SU, Shah SSA (2019) Bacteriophages: an overview of the control strategies against multiple bacterial infections in different fields. J Basic Microbiol 59(2):123–133. https://doi.org/10.1002/jobm.201800412
Ur Rahman S, Ali T, Ali I, Khan NA, Han B, Gao J (2018) The growing genetic and functional diversity of extended spectrum beta-lactamases. Biomed Res Int 2018:9519718. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/9519718
Schooley RT, Biswas B, Gill JJ, Hernandez-Morales A, Lancaster J, Lessor L, Barr JJ, Reed SL, Rohwer F, Benler S, Segall AM, Taplitz R, Smith DM, Kerr K, Kumaraswamy M, Nizet V, Lin L, McCauley MD, Strathdee SA, Benson CA, Pope RK, Leroux BM, Picel AC, Mateczun AJ, Cilwa KE, Regeimbal JM, Estrella LA, Wolfe DM, Henry MS, Quinones J, Salka S, Bishop-Lilly KA, Young R, Hamilton T (2017) Development and use of personalized bacteriophage-based therapeutic cocktails to treat a patient with a disseminated resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Infection. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.00954-17
Leshkasheli L, Kutateladze M, Balarjishvili N, Bolkvadze D, Save J, Oechslin F, Que YA, Resch G (2019) Efficacy of newly isolated and highly potent bacteriophages in a mouse model of extensively drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii bacteraemia. J Glob Antimicrob Resist 19:255–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgar.2019.05.005
Fan N, Qi R, Yang M (2017) Isolation and characterization of a virulent bacteriophage infecting Acinetobacter johnsonii from activated sludge. Res Microbiol 168(5):472–481. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resmic.2017.01.006
Pulkkinen E, Wicklund A, Oduor JMO, Skurnik M, Kiljunen S (2019) Characterization of vB_ApiM_fHyAci03, a novel lytic bacteriophage that infects clinical Acinetobacter strains. Adv Virol 164(8):2197–2199. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-019-04284-z
Oliveira H, Costa AR, Konstantinides N, Ferreira A, Akturk E, Sillankorva S, Nemec A, Shneider M, Dotsch A, Azeredo J (2017) Ability of phages to infect Acinetobacter calcoaceticus-Acinetobacter baumannii complex species through acquisition of different pectate lyase depolymerase domains. Environ Microbiol 19(12):5060–5077. https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.13970
Gu J, Xu W, Lei L, Huang J, Feng X, Sun C, Du C, Zuo J, Li Y, Du T, Li L, Han W (2011) LysGH15, a novel bacteriophage lysin, protects a murine bacteremia model efficiently against lethal methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection. J Clin Microbiol 49(1):111–117. https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.01144-10
Heo YJ, Lee YR, Jung HH, Lee J, Ko G, Cho YH (2009) Antibacterial efficacy of phages against Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections in mice and Drosophila melanogaster. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 53(6):2469–2474. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.01646-08
Xi H, Dai J, Tong Y, Cheng M, Zhao F, Fan H, Li X, Cai R, Ji Y, Sun C, Feng X, Lei L, Rahman SU, Han W, Gu J (2019) The characteristics and genome analysis of vB_AviM_AVP, the first phage infecting Aerococcus viridans. Viruses. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11020104
Hyman P, Abedon ST (2009) Practical methods for determining phage growth parameters. Methods Mol Biol 501:175–202. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-60327-164-6_18
Nurk S, Bankevich A, Antipov D, Gurevich AA, Korobeynikov A, Lapidus A, Prjibelski AD, Pyshkin A, Sirotkin A, Sirotkin Y, Stepanauskas R, Clingenpeel SR, Woyke T, McLean JS, Lasken R, Tesler G, Alekseyev MA, Pevzner PA (2013) Assembling single-cell genomes and mini-metagenomes from chimeric MDA products. J Comput Biol 20(10):714–737. https://doi.org/10.1089/cmb.2013.0084
Gu J, Liu X, Lu R, Li Y, Song J, Lei L, Sun C, Feng X, Du C, Yu H, Yang Y, Han W (2012) Complete genome sequence of Staphylococcus aureus bacteriophage GH15. J Virol 86(16):8914–8915. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.01313-12
Aziz RK, Bartels D, Best AA, DeJongh M, Disz T, Edwards RA, Formsma K, Gerdes S, Glass EM, Kubal M, Meyer F, Olsen GJ, Olson R, Osterman AL, Overbeek RA, McNeil LK, Paarmann D, Paczian T, Parrello B, Pusch GD, Reich C, Stevens R, Vassieva O, Vonstein V, Wilke A, Zagnitko O (2008) The RAST server: rapid annotations using subsystems technology. BMC Genom 9:75. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-9-75
Garneau JR, Depardieu F, Fortier LC, Bikard D, Monot M (2017) PhageTerm: a tool for fast and accurate determination of phage termini and packaging mechanism using next-generation sequencing data. Sci Rep 7(1):8292. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-07910-5
Lowe TM, Chan PP (2016) tRNAscan-SE online: integrating search and context for analysis of transfer RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res 44(W1):W54–57. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw413
Krogh A, Larsson B, von Heijne G, Sonnhammer EL (2001) Predicting transmembrane protein topology with a hidden Markov model: application to complete genomes. J Mol Biol 305(3):567–580. https://doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.2000.4315
Grant JR, Stothard P (2008) The CGView server: a comparative genomics tool for circular genomes. Nucleic Acids Res 36:W181–W184. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkn179
Darling AC, Mau B, Blattner FR, Perna NT (2004) Mauve: multiple alignment of conserved genomic sequence with rearrangements. Genome Res 14(7):1394–1403. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.2289704
Zhao Y, Wu J, Yang J, Sun S, Xiao J, Yu J (2012) PGAP: pan-genomes analysis pipeline. Bioinformatics 28(3):416–418. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btr655
Lee I, Ouk Kim Y, Park SC, Chun J (2016) OrthoANI: an improved algorithm and software for calculating average nucleotide identity. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 66(2):1100–1103. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.000760
Farmer NG, Wood TL, Chamakura KR, Kuty Everett GF (2013) Complete genome of Acinetobacter baumannii N4-Like podophage presley. Genome Announc. https://doi.org/10.1128/genomeA.00852-13
Choi KH, McPartland J, Kaganman I, Bowman VD, Rothman-Denes LB, Rossmann MG (2008) Insight into DNA and protein transport in double-stranded DNA viruses: the structure of bacteriophage N4. J Mol Biol 378(3):726–736. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2008.02.059
Zehring WA, Rothman-Denes LB (1983) Purification and characterization of coliphage N4 RNA polymerase II activity from infected cell extracts. J Biol Chem 258(13):8074–8080
Kazmierczak KM, Davydova EK, Mustaev AA, Rothman-Denes LB (2002) The phage N4 virion RNA polymerase catalytic domain is related to single-subunit RNA polymerases. EMBO J 21(21):5815–5823. https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/cdf584
Carter RH, Demidenko AA, Hattingh-Willis S, Rothman-Denes LB (2003) Phage N4 RNA polymerase II recruitment to DNA by a single-stranded DNA-binding protein. Genes Dev 17(18):2334–2345. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1121403
Lenneman BR, Rothman-Denes LB (2015) Structural and biochemical investigation of bacteriophage N4-encoded RNA polymerases. Biomolecules 5(2):647–667. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom5020647
Wilson GW, Edgell DR (2009) Phage T4 mobE promotes trans homing of the defunct homing endonuclease I-TevIII. Nucleic Acids Res 37(21):7110–7123. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkp769
Mumm IP, Wood TL, Chamakura KR, Kuty Everett GF (2013) Complete genome of Acinetobacter baumannii podophage Petty. Genome Announc. https://doi.org/10.1128/genomeA.00850-13
Young R (2014) Phage lysis: three steps, three choices, one outcome. J Microbiol 52(3):243–258. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-014-4087-z
Pang T, Savva CG, Fleming KG, Struck DK, Young R (2009) Structure of the lethal phage pinhole. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(45):18966–18971. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0907941106
Catalao MJ, Gil F, Moniz-Pereira J, Sao-Jose C, Pimentel M (2013) Diversity in bacterial lysis systems: bacteriophages show the way. FEMS Microbiol Rev 37(4):554–571. https://doi.org/10.1111/1574-6976.12006
Wang IN, Smith DL, Young R (2000) Holins: the protein clocks of bacteriophage infections. Annu Rev Microbiol 54:799–825. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.micro.54.1.799
Catalano CE, Cue D, Feiss M (1995) Virus DNA packaging: the strategy used by phage lambda. Mol Microbiol 16(6):1075–1086. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2958.1995.tb02333.x
Konstantinidis KT, Tiedje JM (2005) Genomic insights that advance the species definition for prokaryotes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(7):2567–2572. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0409727102
Wittmann J, Klumpp J, Moreno Switt AI, Yagubi A, Ackermann HW, Wiedmann M, Svircev A, Nash JH, Kropinski AM (2015) Taxonomic reassessment of N4-like viruses using comparative genomics and proteomics suggests a new subfamily-"Enquartavirinae". Adv Virol 160(12):3053–3062. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-015-2609-6
Casjens SR, Gilcrease EB, Winn-Stapley DA, Schicklmaier P, Schmieger H, Pedulla ML, Ford ME, Houtz JM, Hatfull GF, Hendrix RW (2005) The generalized transducing Salmonella bacteriophage ES18: complete genome sequence and DNA packaging strategy. J Bacteriol 187(3):1091–1104. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.187.3.1091-1104.2005
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported through grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 31872505 and U19A2038), the Natural Science Foundation of Jilin Province (Changchun, China; No. 20200201120JC), the Jilin Province Science Foundation for Youths (Changchun, China; No. 20190103106JH), the Achievement Transformation Project of the First Hospital of Jilin University (No. JDYYZH-1902025) the Shanghai Municipal Health Commission Scientific Research Project (No. 20194Y0061) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
NW, TZ, JG: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition and Investigation. MC, ML and HX: Methodology. YZ, DT, L-KC, TW: Data curation, Draft preparation. MC and SL: Writing. SR, YG and WH: Reviewing and Editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no competing financial and non-financial conflict of interests. The collection of sewage sample had obtained permission of Changchun sewerage system.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Edited by Andrew Millard.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, M., Luo, M., Xi, H. et al. The characteristics and genome analysis of vB_ApiP_XC38, a novel phage infecting Acinetobacter pittii. Virus Genes 56, 498–507 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11262-020-01766-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11262-020-01766-0