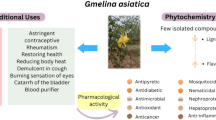
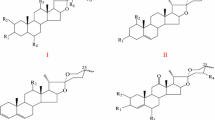
Abstract
Nigella glandulifera Freyn et Sint (N. glandulifera) is frequently added to naan (a kind of crusty pancake and a favorite food of the Uyghur and Kazak people) as a spice. The water decoction of N. glandulifera was used as traditional Uighur medicine to treat tinnitus, amnesia, amenorrhea, hypogalactia, heat stranguria, urethral calculus, alopecia and hair-blacking, edema, and bronchial asthma. This review aimed to give an updated, comprehensive summary on the traditional uses, pharmacology, phytochemistry and toxicology of N. glandulifera to provide some reminders for future research. More than 78 chemical compounds were isolated from N. glandulifera, including essential oils, alkaloids, saponins, phenolic compounds, flavonol glycosides, steroids, and others. The extractions and constituents of N. glandulifera were preliminarily confirmed to exhibit menstrual cycle regulative, anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory, viscera-protective, anti-neoplastic, anti-diabetic properties, and the therapeutic effects on respiratory diseases. Pharmacological investigations supported the traditional use of N. glandulifera to treat endocrine, respiratory, urogenital, and nervous system diseases with little toxicity. N. glandulifera is an excellent tonic to treat many public health problems, including endocrine, respiratory, urogenital, neuronal system disorders and cancer.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad A, Alabbasi FA, Sadath S (2018) Ameliorative effect of camel’s milk and Nigella sativa oil against thioacetamide-induced hepatorenal damage in rats. Pharmacogn Mag 14:27–35
Ainiwaer A, Xiadiya X, Chengyufeng S, Meiliwan A, Dilinuer M (2013) Immunomodulatory and anti-tumor effects of Nigella glandulifera freyn and sint seeds on ehrlich ascites carcinoma in mouse model. Pharmacogn Mag 9:187–191
Askari G, Rouhani MH, Ghaedi E, Ghavami A, Nouri M, Mohammadi H (2019) Effect of Nigella sativa (black seed) supplementation on glycemic control: A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials. Phytother Res 33:1341–1352
Babak BA, Mahmoud B, Pegah T, Nasrollah N, Mahmoud RK (2015) An ethno-medicinal study of medicinal plants used for the treatment of diabetes. J Nephropathol 5:44–50
Bao Q, Bilige W, Ganbold T, Ehexige E, He M, Temuqile T, Baigude H (2018) Neuroprotective and antioxidant activity of Nigella glandulifera Freyn & Sint seeds. Acad J Med Plants 6:412–420
Boubertakh B, Liu XG, Cheng XL, Li P (2013) A spotlight on chemical constituents and pharmacological activities of Nigella glandulifera Freyn et sint seeds. J Chem 2013:1–12
Butt MS, Sultan MT (2010) Nigella sativa: reduces the risk of various maladies. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 50:654–665
Bun SS, Elias R, Baghdikian B, Ciccolini J, Ollivier E, Balansard G (2010) Alpha-hederin potentiates 5-FU antitumor activity in human colon adenocarcinoma cells. Phytother Res 22:1299–1302
Cascella M, Palma G, Barbieri A, Bimonte S, Amruthraj NJ, Muzio MR, Vecchio VD, Rea D, Falco M, Luciano A (2017) Role of Nigella sativa and its constituent thymoquinone on chemotherapy-induced nephrotoxicity: evidences from experimental animal studies. Nutrients 9:2017
Chen QB, Xin XL, Aisa HA (2017) Pyrrolo-isoquinoline and glycosylated pyrrolidine alkaloids from Nigella glandulifera, and their anti-PTP1B activity. Phytochem Lett 19:168–171
Chen QB, Xin XL, Yang Y, Lee SS, Aisa HA (2014) Highly conjugated norditerpenoid and pyrroloquinoline alkaloids with potent PTP1B inhibitory activity from Nigella glandulifera. J Nat Prod 77:807–812
Chen XL, Geng DS (2013) A research on the pharmacodynamics and acute toxicity of Uyghur Herb Nigella glandulifera flavonoid glycoside. J Xinjiang Med Univ 36:574–576
Cheema MAR, Nawaz S, Gul S, Salman T, Naqvi S, Dar A, Haleem DJ (2018) Neurochemical and behavioral effects of Nigella sativa and olea europaea oil in rats. Nutr Neurosci 21:185–194
Dajani EZ, Shahwan TG, Dajani NE (2016) Overview of the preclinical pharmacological properties of Nigella sativa (black seeds): a complementary drug with historical and clinical significance. J Physiol Pharm 67:801–817
Dimitrijević S, Pavlović M, Maksimović S, Ristić M, Filipović V, Antonović D, Dimitrijević-Branković S (2018) Plant growth-promoting bacteria elevate the nutritional and functional properties of black cumin and flaxseed fixed oil. J Sci Food Agric 98:1584–1590
Farooqui Z, Shahid F, Khan AA, Khan F (2017) Oral administration of, Nigella sativa, oil and thymoquinone attenuates long term cisplatin treatment induced toxicity and oxidative damage in rat kidney. Biomed Pharmacother 96:912–923
Gao JB, Zhang XJ, Zhang RH, Zhu LL, Pu DB, Li XL, Li HL, Xu M, Xiao WL (2018) In vitro human dihydroorotate dehydrogenase inhibitory, anti-inflammatory and cytotoxic activities of alkaloids from the seeds of Nigella glandulifera. Planta Med 84:1013–1021
Ge DD, Chen Q, Xu JJ, Jia XG, Wang T, Zhang Y (2011) Isolation and identification of chemical constituents from whole plant of Nigella glandulifera Freyn et Sint (I). J Shenyang Pharm Univ 28:420–424
Goyal SN, Prajapati CP, Gore PR, Patil CR, Mahajan UB, Sharma C, Talla SP, Ojha SK (2017) Therapeutic potential and pharmaceutical development of thymoquinone: A multitargeted molecule of natural origin. Front Pharm 8:656
Guo WH, Li XM, Huang SS, Yang MH, Kong LY (2016) Three new alkaloids from the seeds of Nigella glandulifera J Asian Nat Prod Res 19:9–14
Hu XJ, Liu XB, Gong MH, Luan M, Zheng YL, Wu GL, Shentu JZ, Zhang L (2014) Development and validation of liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for quantification of a potential anticancer triterpene saponin from seeds of Nigella glandulifera in rat plasma: application to a pharmacokinetic study. J Chromatogr B Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci 967:156–161
Hu XJ, Lin MH, Zhu W, Zheng YL, Zhang Q, Wu GL, Qiu YQ (2020) Potential Cytotoxicity, Pharmacokinetics, and Excretion Properties of Sapindoside B from the Seeds of Nigella sativa var. hispidula. Planta Med 86:356–363
İbrahim K, Mehmet A, Şerife G, Krishnendu A (2018) Effects of fludioxonil, propolis and black seed oil application on the postharvest quality of “wonderful” pomegranate. PLOS ONE 13(5):e0198411
Imran M, Rauf A, Khan IA, Shahbaz M, Qaisrani TB, Fatmawati S, Abu-Izneid T, Imran A, Rahman KU, Gondal TA (2018) Thymoquinone: a novel strategy to combat cancer: a review. Biomed Pharmacother 106:390–402
Jakaria M, Cho DY, Ezazul Haque M, Karthivashan G, Kim IS, Ganesan P, Choi DK (2018) Neuropharmacological Potential and Delivery Prospects of Thymoquinone for Neurological Disorders. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2018:1–17
Jeong YH, Hyun JW, Kim VLT, Kim DH, Kim HS (2013) Kalopanaxsaponin A exerts anti-inflammatory effects in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated microglia via inhibition of JNK and NF-κB/AP-1 pathways. Biomol Ther (Seoul) 21:332–337
Khonche A, Huseini HF, Gholamian M, Mohtashami R, Nabati F, Kianbakht S (2019) Standardized Nigella sativa seed oil ameliorates hepatic steatosis, aminotransferase and lipid levels in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a randomized, double-blind and placebo-controlled clinical trial. J Ethnopharmacol 234:106–111
Kooti W, Hasanzadeh-Noohi Z, Sharafi-Ahvazi N, Asadi-Samani M, Ashtary-Larky D (2016) Phytochemistry, pharmacology, and therapeutic uses of black seed (Nigella sativa). Chin J Nat Med 14:732–745
Li Y, Shan MZ, Yan MJ, Yao HK, Wang YC, Gu B, Zhu ZB, Li HC (2019) Anticandidal activity of kalopanaxsaponin A: effect on proliferation, cell morphology, and key virulence attributes of Candida albicans. Front Microbiol 10:2844
Liu XX, Aisa HA, Xin XL (2017) A new fatty acid ester from Nigella sativa var. hispidula Boiss showing potent anti-protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B activity Nat Prod Res 33:472–476
Liu YM, Liu QH, Chen BQ (2011) A new flavonol glycoside from the seeds of Nigella glandulifera. Nat Prod Res 25:1334–1338
Liu YM, Yang JS, Liu QH (2004) A new alkaloid and its artificial derivative with an indazole ring from Nigella glandulifera. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 52:454–455
Liu YM, Sun L, Liu QH, Lu SR, Chen BQ (2013) Dolabellane-type diterpene alkaloids from Nigella glandulifera. Biochem Syst Ecol 49:43–46
Maimaitiyiming D, Amanguli, Yan L, Kurbantay N, Wu GZ, Shan LL, Omarniyaz Z, Yang T, Tian S, Upur H, Aikemu A (2015) The impact of the uighur medicine seeds of Nigella glandulifera Freyn (SNF) on antitumor and antioxidant activity in a S180 and EAC mouse tumor model. 2015 International Conference on Mechatronics, Electronic, Industrial and Control Engineering (MEIC-15), Advances in Engineering Research, Atlantis Press; 2015. https://doi.org/10.2991/meic-15.2015.232
Maimaitiyiming D, Kamilijiang M, Xiaerfuding X, Hui SW, Abudureyimu M, Hajinisha, Aikemu A (2017) Protective effects of traditional Uighur medicine-seeds of Nigella glandulifera Freyn extracts against CCl4-induced acute hepatic injury in mice. Pak J Pharm Sci 30:1567–1571
Man SL, Gao WY, Zhang YJ, Huang LQ, Liu CX (2010) Chemical study and medical application of saponins as anti-cancer agents. Fitoterapia 81:703–714
Mollazadeh H, Mahdian D, Hosseinzadeh H (2019) Medicinal plants in treatment of hypertriglyceridemia: A review based on their mechanisms and effectiveness. Phytomedicine 53:43–52
Mostofa AGM, Kamal HM, Debasish B, Shahdaat BSM (2017) Thymoquinone as a potential adjuvant therapy for cancer treatment: evidence from preclinical studies. Front Pharm 8:295
Mouwakeh A, Kincses A, Nové M, Mosolygó T, Mohácsi-Farkas C, Kiskó G, Spengler G (2019) Nigella sativa essential oil and its bioactive compounds as resistance modifiers against Staphylococcus aureus. Phytother Res 33:1010–1018
Nguyen D, La LH, Lee HB, Kim D, Shin J, Kim E (2007) Isolation of dioctyl phthalate with high depigmenting effect from Chinese herb Nigella glandulifera Freyn. J Biotechnol 131:S43–S43
Nguyen DH, Lee JE, Kim EK (2011) Identification of depigmenting components from Nigella glandulifera Freyn. Korean J Chem Eng 28:1070–1073
Ong WY, Wu YJ, Farooqui T, Farooqui AA (2018) Qi Fu Yin-a Ming dynasty prescription for the treatment of dementia. Mol Neurobiol 55:7389–7400
Park H, Kwon S, Lee J, Lee K, Miyamoto K, Lee K (2001) Kalopanaxsaponin A is a basic saponin structure for the anti-tumor activity of hederagenin monodesmosides. Planta Med 67:118–121
Park SK, Hwang YS, Park KK, Park HJ, Seo JY, Chung WY (2009) Kalopanaxsaponin A inhibits PMA-induced invasion by reducing matrix metalloproteinase-9 via PI3K/Akt- and PKCdelta-mediated signaling in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Carcinogenesis 30:1225–1233
Pelegrin S, Galtier F, Chalançon A, Gagnol JP, Barbanel AM, Pélissier Y, Larroque M, Lepape S, Faucanié M, Gabillaud I, Petit P, Chevassus H (2019) Effects of Nigella sativa seeds (black cumin) on insulin secretion and lipid profile: a pilot study in healthy volunteers. Br J Clin Pharm 85:1607–1611
Pharmacopoeia Commission of PRC (2015) Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China 2015 ed. China Medical Science Press, Beijing, China
Sayeed MSB, Shams T, Hossain SF, Rahman MR, Mostofa A, Kadir MF, Mahmood S, Asaduzzaman M (2014) Nigella sativa l seeds modulate mood, anxiety and cognition in healthy adolescent males. J Ethnopharmacol 152:156–162
Seflek HN, Kalkan S, Cuce G, Kilinc I, Sozen ME (2019) Effects of Nigella sativa oil on ovarian volume, oxidant systems, XIAP and NF-κB expression in an experimental model of diabetes. Biotech Histochem 94:325–333
Sun L, Liu YM, Chen BQ, Liu QH (2015) New phenolic compounds from the seeds of Nigella glandulifera and their inhibitory activities against human cancer cells. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 25:3864–3866
Sun LL, Luan M, Zhu W, Gao S, Zhang QL, Xu CJ, Lu XH, Xu XD, Tian JK, Zhang L (2013) Study on antitubercular constituents from the seeds of Nigella glandulifera. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 61:873–876
Tang D, Chen QB, Xin XL, Aisa HA (2017) Anti-diabetic effect of three new norditerpenoid alkaloids in vitro and potential mechanism via PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother 87:145–152
Tian J, Han C, Guo WH, Yin Y, Wang XB, Sun HB, Yao HQ, Yang Y, Wang C, Liu C, Yang MH, Kong LY (2017) Nigegladines A-C, three thymoquinone dimers from Nigella glandulifera. Org Lett 19:6348–6351
Tian Z, Liu YM, Chen SB, Yang JS, Xiao PG, Wang L, Wu E (2006) Cytotoxicity of two triterpenoids from Nigella glandulifera. Molecules 11:693–699
Wei Y, Ma T, Wang H, Xing J, Wang Y, Gu Z, Mu D, Yin Q, Cheng X, Wang C (2018) Extracts of compound Muniziqi granule suppressed uterus contraction and ameliorated oxytocin-induced primary dysmenorrhea. J Ethnopharmacol 223:33–40
Xin XL, Aisa HA, Wang HQ (2008a) Flavonoids and phenolic compounds from seeds of the Chinese plant Nigella glandulifera. Chem Nat Compd 44:368–369
Xin XL, Aisa HA, Xue HQ, Wang HQ (2008b) Triterpene saponins from seeds of the Chinese plant Nigella glandulifera. Chem Nat Compd 44:134–136
Xin X, Wang Q, Aisa HA, Wang H (2010) Antidiabetes properties of n-hexane and petroleum ether extracts from seeds of Nigella glandulifera Freyn. J Food Biochem 34:811–824
Xin X, Yang Y, Zhong J, Aisa HA, Wang H (2009) Preparative isolation and purification of isobenzofuranone derivatives and saponins from seeds of Nigella glandulifera Freyn by high-speed counter-current chromatography combined with gel filtration. J Chromatogr A 1216:4258–4262
Yimer EM, Tuem KB, Karim A, Ur-Rehman N, Anwar F (2019) Nigella sativa L. (Black Cumin): a promising natural remedy for wide range of illnesses. Evid Based Complement Altern Med 2019 2019:1528635
Yu F, Liu YM, Liu QH, Lei YJ (2012) Nigelactone, new phthalide glucoside from the seeds Nigella glandulifera. Heterocycles 85:3015–3019
Yu S, Kong X, Chen M, He X, Wu N, University GM (2016) Study on the protective effect of uygur medicine Nigellae Semenon on acute alcoholic liver injury mice and its inhibition on NF-кB signaling pathway. World Chin Med 11:1831–1834
Zhang Y, Ge D, Chen Q, He W, Han L, Wei H, Jia X, Wang T (2012) Flavonol glycosides, nigelflavonosides A-F from the whole plant of Nigella glandulifera (Ranunculaceae). J Nat Med 66:645–652
Zhao J, Xu F, Huang H, Gu Z, Wang L, Tan W, He J, Chen Y, Li C (2013) Evaluation on anti-Inflammatory, analgesic, antitumor, and antioxidant potential of total saponins from Nigella glandulifera seeds. Evid Based Complement Altern Med 827230:2013
Acknowledgements
The author is grateful to Mr YunQing Qiu from the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang University for funding.
Funding
This study was supported by the Key Technologies R&D Program of 13th Five-year Plan of China (2018ZX09301025002), Natural Science Foundation of Zhejing Province, China (Nos. LY16H280002 and LY19H280011), Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine of Zhejiang Province, China (No. 2018ZQ033) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81903849).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical standards
No experiments were conducted in this review paper, and all institutional ethical standards were followed.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, Y., Zhang, Q. & Hu, X. A comprehensive review of ethnopharmacological uses, phytochemistry, biological activities, and future prospects of Nigella glandulifera. Med Chem Res 29, 1168–1186 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-020-02558-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-020-02558-9