Abstract
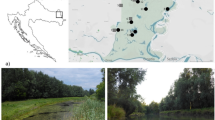
There is a strong link between habitat loss, fragmentation of natural vegetation, and reduction of biodiversity in aquatic systems. The objective of this study was to evaluate the influence of different landscape scales on the community of Ephemeroptera, Plecoptera, and Trichoptera in Atlantic Forest rivers. We sought to understand how aquatic communities are affected by different habitat structures and anthropogenic changes in different spatial scales (in radii of 30, 50, 100, 150, and 200 m). Seven points were established where eight sample campaigns were carried out between 2015 and 2016. The analyses indicate the types of land use, with forest cover being of greatest expressiveness, as determinants in the structure and diversity of the Ephemeroptera, Plecoptera, and Trichoptera community. When evaluating the effect of the scales, for the basin evaluated, it was detected that the 30 and 50 m buffers were the most representative. These buffers suggest that the configuration and composition of landscape, especially the forest cover class, have a strong influence on the composition of the aquatic entomofauna in the region. The results confirm the importance of studies at local scales regarding the relation of the landscape for Ephemeroptera, Plecoptera, and Trichoptera biodiversity in view of the particular relationship of these orders with the riparian forest for its various functions. It is concluded that riparian forests in the 30 and 50 m scales should not be modified; otherwise, aquatic biodiversity will be compromised.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allan, J. D. (1995). Stream ecology: Structure and function of running waters. London.
Allan, J. D. (2004). Landscapes and riverscapes: the influence of lan use ons stream ecosystems. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, 35, 257–284.
Barbour, M. T., Gerritsen, J., Griffith, G. E., Frydenborg, R., Mccarron, E., White, J. S., & Bastian, M. L. (1996). A framework for biological criteria for Florida streams using benthic macroinvertebrates. Journal of the North American Benthological Society, 15, 185–211.
Bateman, H. L., Stromberg, J. C., Banville, M. J., Makings, E., Scott, B. D., Suchy, A., & Wolkis, D. (2015). Novel water sources restore plant and animal communities along an urban river. Ecohydrololgy, 8, 792–811.
Bilton, D. T., Freeland, J. R., & Okamura, B. (2001). Dispersal in freshwater invertebrates. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 32, 159–181.
Bispo, P. C., Oliveira, L. G., Crisci-Bispo, V. L., & Souza, K. G. (2004). Environmental factors influencing distribution and abundance of trichopteran larvae in central Brazilian mountain streams. Studies on Neotropical Fauna and Environment, 39, 233–237.
Bispo, P. C., Oliveira, L. G., Bini, L. M., & Souza, K. G. (2006). Ephemeroptera, Plecoptera and Trichoptera from riffles in mountain streams of Central Brazil: environmental factors influencing the distribution and abundance of immatures. Brazilian Journal of Biology, 66, 611–622.
Boeder, M., & Chang, H. (2008). Multi-scale analysis of oxygen demand trends in an urbanizing Oregon watershed, USA. Journal of Environmental Management, 87, 567–581.
Brancalion, P. H. S., Garcia, L. C., Loyola, R., Rodrigues, R. R., Pillar, V. D., & Lewinsohn, T. M. (2016). A critical analysis of the native vegetation protection law of Brazil (2012): updates and ongoing initiatives. Natureza & Conservação, 14, 1–15.
Brasil. (2006). O corredor central da mata atlântica: uma nova escala de conservação da biodiversidade. Ministério do Meio Ambiente. Brasília, DF.
Brasil. (2012). Lei 12.651, de 25 de maio de 2012. Dispõe sobre a proteção da vegetação nativa e dá outras providências. Diário Oficial da União. Brasília, DF.
Briers, R. A., Cariss, H. M., & Gee, J. H. R. (2002). Dispersal of adult stoneflies (Plecoptera) from upland streams draining catchments with contrasting land-use. Archiv für Hydrobiologie, 155, 627–644.
Chase, J. M., & Bengtsson, J. (2010). Increasing spatio-temporal scales: metacommunity ecology. In H. A. Verhorf & P. J. Morin (Eds.), Community ecology: Processes, models and applications (pp. 57–68). Oxford: Oxford Univ. Press.
Constanza, R., D’Arge, R., De Groot, R., Farberk, S., Grasso, M., Hannon, B., Limburg, K., Naeem, S., O’Neill, R. V., Paruelo, J., Raskin, R. G., & Sutonk, P. (1997). The value of the world’s ecosystem services and natural capital. Nature, 387, 253–260.
Cortezzi, S. S., Bispo, P. C., Paciencia, G. P., & Leite, R. C. (2009). Influência da ação antrópica sobre a fauna de macroinvertebrados aquáticos em riachos de uma região de cerrado do sudoeste do Estado de São Paulo. Iheringia Série Zoologia, 99, 36–43.
Costa, C., Ide, S., & Simonka, C. E. (2006). Insetos Imaturos. Metamorfose e Identificação. Holos. Ribeirão Preto.
Crisci-Bispo, V. L., Bispo, P. C., & Froehlich, C. G. (2007). Ephemeroptera, Plecoptera e Trichoptera assemblages in two Atlantic rainforest streams, Southeastern Brazil. Revista Brasileira de Zoologia, 24, 312–318.
Crook, D. A., Lowe, W. H., Allendorf, F. W., Erós, T., Finn, D. S., Gillanders, B. M., Hadwen, W. L., Harrod, C., Hermoso, V., Jennings, S., Kilada, R. W., Nagelkerken, I., Hansen, M. M., Page, T. J., Riginos, C., Fry, B., & Hughes, J. M. (2015). Human effects on ecological connectivity in aquatic ecosystems: Integrating scientific approaches to support management and mitigation. The Science of the Total Environment, 534, 52–64.
Delong, M. D., & Brusven, M. A. (1998). Macroinvertebrate community structure along the longitudinal gradient of an agriculturally impacted stream. Environmental Management, 22, 445–457.
Dias, A. C., & Pott, A. (2013). A influência da mata ciliar na qualidade das águas do córrego Bom Jardim, Brasilândia, /MS: estudos iniciais. Periódico Eletrônico: IX Fórum Ambiental da Alta Paulista, 9, 01–16.
Ding, J., Jiang, Y., Liu, Q., Hou, Z., Liao, J., Fu, L., & Peng, Q. (2016). Influences of the land use pattern on water quality in low-order streams of the Dongjiang River basin, China: a multi-scale analysis. Science of the Total Environment, 551-552, 205–216.
Domínguez, E., & Fernandéz, H. R. (2009). Macroinvertebrados bentônicos sudamericanos: sistemática y biologia (1st ed.). Tucumán: Fund Miguel Lillo.
Domínguez, E., Molineri, C., Pescador, M. L., Hubbard, M. D., & Nieto, C. (2006). Ephemeroptera of South American, Aquatic Biodiversity of Latin America (ABLA series, vol 2), Pensoft Publishers, Sofia-Moscow.
Feld, C. K., & Hering, D. (2007). Community structure or function: effects of environmental stress on benthic macroinvertebrates at different spatial scales. Freshwater Biology, 52, 1380–1399.
Figueiredo, R. O., Markewitz, D., Davidson, E. A., Schuler, A. E., Watrin, O. S., & Silva, P. (2010). Land-use effects on the chemical attributes of low-order streams in the eastern Amazon. Journal of Geophysical Research, 15, 1–14.
Fritzsons, E., Mantovani, L. E., & Rizzi, N. E. (2004). Aplicação de índices de paisagem às florestas ciliares na Bacia do Alto Capivari - Região Cárstica Curitibana. Revista Floresta, 24, 3–11.
Froehlich, C. G. (2011). Checklist of Plecoptera from São Paulo State, Brazil. Biota Neotropica, 11, 602–606.
Genito, D., Gburek, W. J., & Sharpley, A. N. (2002). Response of stream macro invertebrates to agricultural land cover in a small watershed. Journal of Freshwater Ecology, 17, 109–119.
Gregory, S. V., Swanson, F. J., Mckee, W. A., Kenneth, W., Swanson, J., & Cummins, K. W. (2010). An ecosystem perspective of riparian zones focus on links between land and water. Bioscience, 41, 540–551.
Gundersen, P., Lauren, A., Finer, L., Ring, E., Koivusalo, H., Satersdal, M., Weslien, J., Sigurdsson, B. D., Hogbom, L., Lainde, J., & Hansen, K. (2010). Environmental services provided from riparian forests in the Nordic countries. AMBIO, 39, 555–566.
Harding, J. S., Benfield, E. F., Bolstad, P. V., Helfman, G. S., & Jondes, E. B. D. (1998). Stream biodiversity: the ghost of land use past. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 95, 14843–14847.
Herlihy, A. T., Gerth, W. J., Li, J., & Banks, J. L. (2005). Macroinvertebrate community response to natural and forest harvest gradients in western Oregon headwater streams. Freshwater Biology, 50, 905–919.
Houlahan, J. E., & Findlay, C. S. (2004). Estimating the critical distance at which adjacent land-use degrades wetland water and sediment quality. Landscape Ecology, 19, 677–690.
Hughes, S. J. (2006). Temporal and spatial distribution patterns of larval trichoptera in Madeiran streams. Hydrobiologia, 553, 27–41.
Hynes, H. B. N. (1976). Biology of Plecoptera. Annual Review of Entomology, 21, 135–153.
Iwata, T., Nakano, S., & Inoue, M. (2003). Impacts of past riparian deforestation on stream communities in a tropical rain forest in Borneo. Ecological Applications, 13, 461–473.
Jackson, J. K., & Resh, V. H. (1989). Distribution and abundance of adult aquatic insects in the forest adjacent to a Northern California Stream. Environmental Entomology, 18, 278–283.
Jeanmougin, M., Leprieur, F., Lois, G., & Clergeau, P. (2014). Fine-scale urbanization affects Odonata species diversity in ponds of a megacity (Paris, France). Acta Oecologica, 59, 26–34.
Johnson, R. D., Goedkoop, W., & Sandin, L. (2004). Spatial scale and ecological relationships between the macroinvertebrate communities of stony habitats of streams and lakes. Freshwater Biology, 9, 1179–1194.
Jones, E. B. D., Helfman, G. S., Harper, J. O., & Bolstad, P. V. (1999). Effects of riparian forest removal on fish assemblages in Southern Appalachian streams. Conservation Biology, 13, 1454–1465.
Lee, S. W., Hwang, S. J., Lee, S. B., Hwang, H. S., & Sung, H. C. (2009). Landscape ecological approach to the relationships of land use patterns in watersheds to water quality characteristics. Landscape and Urban Planning, 92, 80–89.
Lenat, D. R., & Crawford, J. K. (1994). Effects of land use on water quality and aquatic biota of three North Carolina Piedmont streams. Hydrobiologia, 294, 185–199.
Liu, J., Zhang, H., Chen, Y., Wu, H., & Xiong, Z. (2003). Nutrients in the Changjiang and its tributaries. Biogeochemistry, 62, 1–18.
Merrit, R. W., & Cummins, K. W. (1996). An introduction to the aquatic insects of North America (4rd ed.). Dubuque: Kendall/Hunt Publishing Co.
Metcalfe, J. L. (1989). Biological water quality assessment of running waters based on macroinvertebrates communities: history and present status in Europe. Environmental Pollution, 60, 101–139.
Moreno, P., & Callisto, M. (2006). Benthic macroinvertebrates in the watershed of an urban reservoir in southeastern Brazil. Hydrobiologia, 560, 311–321.
Müller, K. (1982). The colonization cycle of freshwater insects. Oecologia, 52, 202–207.
Nessimian, J. L., Venticinque, E. M., Zuanon, J., De Marco Jr, P., Gordo, M., Fidelis, L., Batista, J. D., & Juen, L. (2008). Land use, habitat integrity, and aquatic insect assemblages in Central Amazonian streams. Hydrobiologia, 614, 117–131.
Ohira, M., Tsunoda, H., Nishida, K., Mitsuo, Y., & Senga, Y. (2015). Niche processes and conservation implications of fish community assembly in a rice irrigation system. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems, 25, 322–335.
PESC (2019). Parque Estadual da Serra do Conduru. Plano de Manejo. Publishing. http://www.parquedoconduru.org/index.php/o-parque/plano-de-manejo. Accessed 09 September 2019.
Petersen, I., Masters, Z., Hildrew, A. G., & Oormerod, S. J. (2004). Dispersal of adult aquatic insects in catchments of differing land use. Journal of Applied Ecology, 41, 934–950.
Piana, P. A., Gubiani, E. A., & Gomes, L. C. A. (2014). Modified metapopulation model to predict colonisation and extinction rates in fragmented aquatic systems. Ecological Engineering, 73, 26–30.
Poff, N. L. (1997). Landscape filters and species traits: towards mechanistic understanding and prediction in stream ecology. Journal of the North American Benthological Society, 16, 391–409.
R Core Team. (2015). R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing. Vienna, Austria. URL: http://www.R-project.org/.
Riley, R. H., Townsend, C. R., Niyogi, D. K., Arbuckle, C. A., & Peacock, K. A. (2003). Headwater stream response to grassland agricultural development. New Zealand Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research, 37, 389–403.
Riva-Murray, K., Bode, R. W., Phillips, P. J., & Wall, G. L. (2002). Impact source determination with biomonitoring data in New York state: concordance with environmental data. Northeastern Naturalist, 9, 127–162.
Rolls, R. J., Stewart-Koster, B., Ellison, T., Faggotter, S., & Roberts, D. T. (2014). Multiple factors determine the effect of anthropogenic barriers to connectivity on riverine fish. Biodiversity and Conservation, 23, 2201–2220.
Rosenberg, D. M., & Resh, V. H. (1993). Freshwater biomonitoring and benthic macroinvertebrates (Vol. 488). New York: Chapmanm & Hall.
Salles, F. F., Da-Silva, E. R., Serrão, J. E., & Francischetti, C. N. (2004). Baetidae (Ephemeroptera) na Região Sudeste do Brasil: novos registros e chave para os gêneros no estágio ninfal. Neotropical Entomology, 33, 725–735.
Samways, M. J., & Steytler, N. S. (1996). Dragonfly (Odonata) distribution patterns in urban and forest landscapes, and recommendations for riparian management. Biodiversity and Conservation, 78, 279–288.
Schroth, G., Faria, D., Araujo, M., Bede, L., Van Bael, S. A., Cassano, C. R., Oliveira, L. C., & Delabie, J. H. C. (2011). Conservation in tropical landscape mosaics: the case of the cacao landscape of southern Bahia, Brazil. Biodiversity and Conservation, 20, 1635–1654.
Shen, Z., Hou, X., Li, W., Aini, G., Chen, L., & Gong, Y. (2015). Impact of landscape pattern at multiple spatial scales on water quality: a case study in a typical urbanized watershed in China. Ecological Indicators, 48, 417–427.
Shi, P., Zhang, Y., Li, Z., Li, P., & Xu, G. (2017). Influence of land use and land cover patterns on seasonal water quality at multi-spatial scales. Catena, 151, 182–190.
Souza, A. F. E. (2000). Recursos hídricos e a ecologia de paisagem. São Paulo: Sabesp.
Spanghero, P. E. S. F., Meliani, P. F., & Mendes, J. S. (2015). Mapeamento hidrográfico de detalhes e análise morfométrica comparativa das Bacias dos Rios Tijuípe e Tijuipinho, Litoral Sul da Bahia. Caminhos de Geografia, 16, 101–117.
Tonkin, J. D., Stolls, S., Jahninf, S. C., & Haase, P. (2016). Contrasting metacommunity structure and beta diversity in an aquatic-floodplain system. Oikos, 125, 686–697.
Towsend, C. R., Harper, J. L., & Begon, M. (2000). Essentials of ecology (Vol. 552). Malden: Blackwell Science.
Tran, C. P., Bode, R., Smith, A., & Kleppel, G. (2010). Land use proximity as a basis for assessing stream water quality in New York state (USA). Ecological Indicators, 10, 727–733.
Vermonden, K., Velde, G., & Leuven, R. S. E. W. (2012). Key factors for biodiversity of surface waters in climate proof cities. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 64, 56–62.
Vinson, M. R., & Hawkins, C. P. (1998). Biodiversity of stream insects: variation at local, basin, and regional scales. Annual Review of Entomology, 43, 271–293.
Vinson, M. R., & Hawkins, C. P. (2003). Broad-scale geographical patterns in local stream insect genera richness. Ecography, 26, 751–767.
Vitousek, P. M., Mooney, H. A., Lubchenko, J., & Melillo, J. M. (1997). Human domination of earths ecosystems. Science, 277, 494–499.
Weigel, B. M., Wang, L., Rasmussen, P. W., Butcher, J. T., Stewart, P. M., Simon, T. P., & Wiley, M. J. (2003). Relative influence of variables at multiple spatial scales on stream macroinvertebrates in the Northern Lakes and Forest ecoregion, U.S.a. Freshwater Biology, 48, 1440–1461.
Whiles, M. R., Brock, B. L., Franien, A. C., & Dinsmore, S. C. (2000). Stream invertebrate communities, water quality, and land-use patterns in an agricultural drainage basin of northeastern Nebraska, USA. Environmental Management, 26, 563–576.
Acknowledgments
The authors also thank Prof. Dr. Marciel Elio Rodrigues for help with the statistical analysis.
Funding
This work was supported by FAPESB (Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado da Bahia).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors have been personally and actively involved on the design of the work, analysis, and interpretation of the data and on the preparation of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Consent for publication
This material has not been published in whole or in part elsewhere. The manuscript is not currently being considered for publication in another journal.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Souza, F.N., Mariano, R., Moreira, T. et al. Influence of the landscape in different scales on the EPT community (Ephemeroptera, Plecoptera and Trichoptera) in an Atlantic Forest region. Environ Monit Assess 192, 391 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-08318-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-08318-x