Abstract
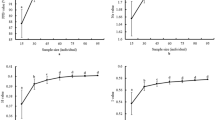
The conservation of seed germplasm is one of the most important ways to maintain the genetic variability of genetic resources, such as rice (Oryza sativa L.) and bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). These two species are fundamental for the food security and agribusiness of many countries, including Brazil. The efficient use of germplasm depends on the maintenance of the germination potential and the genetic integrity of conserved accessions. The objective of the present study was to analyze the genetic integrity of rice and bean accessions that have been maintained in long term conservation conditions. Six and four samples of two rice and bean accessions, respectively, were analyzed. Each sample was added to the collection in different years. First count, germination and germination speed index tests were carried out to evaluate the physiological quality of the seeds samples. Cytogenetic tests and comet assay were performed to evaluate the genetic integrity of the different samples. Significant differences were not observed among the samples of the two species in the cytogenetic tests. Eight of the 10 samples analyzed maintained high physiological quality after prolonged storage and presented acceptable levels of DNA damage (> 20%) in the comet assay. Evidences of DNA repair were detected in one sample. Data showed comet assay has potential to evaluate genetic integrity and DNA repair system in long term conserved seeds.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barbosa L (2007) Feijão com arroz e arroz com feijão: o Brasil no prato dos brasileiros. Horiz Antropol 28:87–116
Black M, Bewley JD, Halmer P (2006) The Encyclopedia of Seeds: Science. Technology and Uses, CABI, Wallingford
Bortolotto RP, de Menezes NL, Garcia DC, Mattioni NM (2008) Comportamento de hidratação e qualidade fisiológica das sementes de arroz. Bragantia 67:991–996
Brasil, (2009) Regras para análise de sementes/Ministério da Agricultura. Pecuária e Abastecimento, Mapa/ACS, Brasília
Collins AR, Dobson VL, Dušinská M, Kennedy G, Štětina R (1997) The comet assay: what can it really tell us? Mutat Res 375:183–193
Dantas AF, Lopes RM, Fascineli ML, José SCBR, Pádua JG, Gimenes MA, Grisolia CK (2018) Comet and cytogenetic tests as tools for evaluating genomic instability in seeds of Oryza sativa L. and Phaseolus vulgaris L. from gene banks. Genet Mol Biol 41:145–153
Dantas AF, Fascineli ML, José SCBR, Pádua JG, Gimenes MA, Grisolia CK (2019) Loss of genetic integrity in artificially aged seed lots of rice (Oryza sativa L.) and common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Mutat Res Gen Tox En 846:403080
de Oliveira Mdo SP, dos Santos JB, Amorim EP, Ferreira DF (2010) Variabilidade genética entre acessos de açaizeiro utilizando marcadores microssatélites. Ciênc Agrotec 34:1253–1260
Dehon G, Catoire L, Duez P, Bogaerts P, Dubois J (2008) Validation of an automatic comet assay analysis system integrating the curve fitting of combined comet intensity profiles. Mutat Res 650:87–95
Donà M, Balestrazzi A, Mondoni A, Rossi G, Ventura L, Buttafava A, Macovei A, Sabatini ME, Valassi A, Carbonera D (2013) DNA profiling, telomere analysis and antioxidant properties as tools for monitoring ex situ seed longevity. Ann Bot 111:987–998
El-Maarouf-Bouteau H, Mazuy C, Corbineau F, Bailly C (2011) DNA alteration and programmed cell death during ageing of sunflower seed. J Exp Bot 62:5003–5011
Fao, (2014) Genebank Standards for Plant Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Rome
Fleming MB, Hill LM, Walters C (2019) The kinetics of ageing in dry-stored seeds: a comparison of viability loss and RNA degradation in unique legacy seed collections. Ann Bot 123:1133–1146
Fontes BPD, Davide LC, Davide AC (2001) Fisiologia e citogenética de sementes envelhecidas de Araucaria angustifolia. Ciênc Agrotec 25:346–355
Fu YB, Ahmed Z, Diederichsen A (2015) Towards a better monitoring of seed ageing under ex situ seed conservation. Conserv Physiol 3:1–16
Gajski G, Gerić M, Oreščanin V, Garaj-Vrhovac V (2013) Cytogenetic status of healthy children assessed with the alkaline comet assay and the cytokinesis-block micronucleus cytome assay. Mutat Res 750:55–62
Garm C, Moreno-Villanueva M, Bürkle A, Petersen I, Bohr VA, Christensen K, Stevnsner T (2013) Age and gender effects on DNA strand break repair in peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Aging Cell 12:58–66
Heuser VD, de Andrade VM, Peres A, Braga LMG de M, Chies JAB (2008) Influence of age and sex on the spontaneous DNA damage detected by Micronucleus test and Comet assay in mice peripheral blood cells. Cell Biol Int 32:1223–1229
IBPGR (1991) Elsevier's Dictionary of Plant Genetic Resources. Elsevier Science Publishers B.V, Amsterdam
Khan MM, Iqbal MJ, Abbas M, Usman M (2003) Effect of Ageing on Viability, Vigour and Chromosomal Damage in Pea (Pisum Sativum L.) Seeds. Pak J Agr Sci 40:50–54
Kranner I, Birtić S, Anderson KM, Pritchard HW (2006) Glutathione half-cell reduction potential: A universal stress marker and modulator of programmed cell death? Free Radic Biol Med 40:2155–2165
Kranner I, Chen H, Pritchard HW, Pearce SR, Birtic S (2011) Inter-nucleosomal DNA fragmentation and loss of RNA integrity during seed ageing. Plant Growth Regul 63:63–72
Krishnan P, Ramakrishnan B, Reddy KR, Reddy VR (2011) High-Temperature Effects on Rice Growth, Yield, and Grain Quality. In: Sparks D (ed) Advances in Agronomy. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 87–206
Løhr M, Jensen A, Eriksen L, Grønbæk M, Loft S, Møller P (2015) Association between age and repair of oxidatively damaged DNA in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Mutagenesis 30:695–700
Lovell DP, Omori T (2008) Statistical issues in the use of the comet assay. Mutagenesis 23:171–182
Maguirre JD (1962) Speed of germination - aid seedling emergence and vigor. Crop Sci 2:176–177
Marim BG, da Silva DJH, Carneiro PCS, Miranda GV, Mattedi AP, Caliman FRB (2009) Variabilidade genética e importância relativa de caracteres em acessos de germoplasma de tomateiro. Pesq Agropec Bras 44:1283–1290
Menezes VO, Lopes SJ, Tedesco SB, Henning FA, Zen HD, Mertz LM (2014) Cytogenetic analysis of wheat seeds submitted to artificial aging stress. J Seed Sci 36:71–78
Piperakis SM, Kontogianni K, Karanastasi G, Iakovidou-Kritsi Z, Piperakis MM (2009) The use of comet assay in measuring DNA damage and repair efficiency in child, adult, and old age populations. Cell Biol Toxicol 25:65–71
Rajjou L, Debeaujon I (2008) Seed longevity: Survival and maintenance of high germination ability of dry seeds. C R Biol 331:796–805
Rank J (2003) The method Allium anaphase-telophase chromossome aberration assay. Ekologija 1:38–42
Ruiz M, Martín I, de la Cuadra C (1999) Cereal seed viability after 10 years of storage in active and base germplasm collections. Field Crops Res 64:229–236
Singh NP, Muller CH, Berger RE (2003) Effects of age on DNA double-strand breaks and apoptosis in human sperm. Fertil Steril 80:1420–1430
Singh AK, Bashir T, Sailer C, Gurumoorthy V, Ramakrishnan AM, Dhanapal S, Grossniklaus U, Baskar R (2015) Parental Age Affects Somatic Mutation Rates in the Progeny of Flowering Plants. Plant Physiol 168:247–257
Smiderle OJ, Miguel MH, Carvalho MV, Cícero SM (2008) Tratamento de Sementes de Feijão com Micronutrientes Embebição e Qualidade Fisiológica. Agro@mbiente On-line 2:22–27
Soares JP, Silva AM, Fonseca S, Oliveira MM, Peixoto F, Gaivão I, Mota MP (2015) How can age and lifestyle variables affect DNA damage, repair capacity and endogenous biomarkers of oxidative stress? Exp Gerontol 62:45–52
Swain U, Rao KS (2011) Study of DNA damage via the comet assay and base excision repair activities in rat brain neurons and astrocytes during aging. Mech Ageing Dev 132:374–381
Velegzhaninov I, Mezenceva V, Shostal O, Baranova A, Moskalev A (2015) Age dynamics of DNA damage and CpG methylation in the peripheral blood leukocytes of mice. Mutat Res 775:38–42
Ventura L, Donà M, Macovei A, Carbonera D, Buttafava A, Mondoni A, Rossi G, Balestrazzi A (2012) Understanding the molecular pathways associated with seed vigor. Plant Physiol Biochem 60:196–206
Vieira EA, JdeF F, Silva MS, Fukuda WMG, Faleiro FG (2008) Variabilidade genética do banco de germoplasma de mandioca da Embrapa cerrados acessada por meio de descritores morfológicos. Científica 36:56–67
Walsh DGF, Waldren S, Martin JR (2003) Monitoring seed viability of fifteen species after storage in the irish threatened plant genebank. Biol Environ 103B:59–67
Wen W, Taba S, Shah T, Tovar VHC, Yan J (2011) Detection of genetic integrity of conserved maize (Zea mays L.) germplasm in genebanks using SNP markers. Genet Resour Crop Evol 58:189–207
Wrasse CF, de Menezes NL, Marchesan E, Villela FA, Bortolotto RP (2009) Testes de vigor para sementes de arroz e sua relação com o comportamento de hidratação de sementes e a emergência de plântulas. Científica 37:107–114
Acknowledgements
This project was supported by Embrapa Genetic Resources & Biotechnology, National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq) (Grant Numbers 158940/2015–6), Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel (CAPES) and University of Brasília (UnB). We gratefully acknowledge the contribution of the Dr. Paulo Hideo Nakano Rangel and late Dr. Jaison Pereira de Oliveira for the samples analyzed in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dantas, A.F., Fascineli, M.L., José, S.C.B.R. et al. Analysis of the genetic integrity of rice (Oryza sativa L.) and bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) accessions stored in gene banks. Genet Resour Crop Evol 67, 1999–2007 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-020-00955-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-020-00955-y