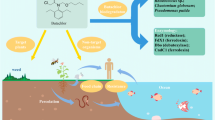
Abstract
Butachlor is a chloroacetamide pre-emergence herbicide, with a half-life of 1.6 to 29 days. It is a suspected carcinogen, genotoxin, neurotoxin and persists in the environment having toxic effect on living systems. Butachlor degrading bacterial strain A16 was isolated from coal tar contaminated soil, which showed 99.38% similarity with Bacillus altitudinis 41KF2bT as revealed by 16S rRNA analysis. B. altitudinis strain A16 utilised butachlor as a sole source of carbon and degraded 90% of 50 mg L−1 butachlor in 5 days at a rate constant and half-life (t1/2) of 0.02 h−1 and 34.65 h, respectively, following the first-order reaction kinetics. Five metabolites (N-(butoxymethyl)-N-(2-chloroethyl)-2,6-diethylaniline, (N-(butoxymethyl)-2-chloro-N-(2-ethylphenyl) acetamide, N-(butoxymethyl)-2,6-diethyl-N-propylaniline, 2-chloro-N-(2,6-diethylphenyl) acetamide and 2,6-diethylaniline) were produced during the breakdown of butachlor by B. altitudinis A16 as identified by GC–MS analysis, which are further mineralized to carbon dioxide and water. A metabolic pathway is proposed and compared with other bacteria. The findings have immense beneficial application since such microbes can be used on large scale for faster soil bioremediation and minimizing negative impact of pesticide butachlor on health and environment.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang S, Li H, Lin C (2013) Physiological, biochemical and growth responses of Italian ryegrass to butachlor exposure. Pestic Biochem Phys 106(1–2):21–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pestbp.2013.03.007
Abigail MEA, Samuel SM, Ramalingam C (2015) Addressing the environmental impacts of butachlor and the available remediation strategies: a systematic review. Int J Environ Sci Technol 12(12):4025–4036. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-015-0866-2
Gao Y, Jin L, Shi H, Chu Z (2015) Characterization of a novel butachlor biodegradation pathway and cloning of the debutoxylase (Dbo) gene responsible for debutoxylation of butachlor in Bacillus sp. hys-1. J Agric Food Chem 63(38):8381–8390. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.5b03326
Singh J, Nandabalan YK (2018) Prospecting Ammoniphilus sp. JF isolated from agricultural fields for butachlor degradation. 3 Biotech 8(3):164. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-018-1165-7
Alla MN, Badawi AM, Hassan NM, El-Bastawisy ZM, Badran EG (2008) Effect of metribuzin, butachlor and chlorimuron-ethyl on amino acid and protein formation in wheat and maize seedlings. Pestic Biochem Phys 90(1):8–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pestbp.2007.07.003
Verma JP, Jaiswal DK, Sagar R (2014) Pesticide relevance and their microbial degradation: a-state-of-art. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 13(4):429–466. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11157-014-9341-7
National Center for Biotechnology Information (2019) PubChem Database. Butachlor, CID=31677, https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Butachlor. Accessed 22 Oct 2019
Dwivedi S, Singh BR, Al-Khedhairy AA, Alarifi S, Musarrat J (2010) Isolation and characterization of butachlor-catabolizing bacterial strain Stenotrophomonas acidaminiphila JS-1 from soil and assessment of its biodegradation potential. Lett Appl Microbiol 51(1):54–60. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1472-765X.2010.02854.x
Dwivedi S, Saquib Q, Al-Khedhairy AA, Musarrat J (2012) Butachlor induced dissipation of mitochondrial membrane potential, oxidative DNA damage and necrosis in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Toxicology 302(1):77–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2012.07.014
Chang J, Liu S, Zhou S, Wang M, Zhu G (2013) Effects of butachlor on reproduction and hormone levels in adult zebrafish (Danio rerio). Exp Toxicol Pathol 65(1–2):205–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etp.2011.08.007
Liu WY, Wang CY, Wang TS, Fellers GM, Lai BC, Kam YC (2011) Impacts of the herbicide butachlor on the larvae of a paddy field breeding frog (Fejervarya limnocharis) in subtropical Taiwan. Ecotoxicology 20(2):377–384. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-010-0589-6
Muthukaruppan G, Janardhanan S, Vijayalakshmi G (2005) Sublethal toxicity of the herbicide butachlor on the earthworm Perionyx sansibaricus and its histological changes (5 pp). J Soils Sediments 5(2):82–86. https://doi.org/10.1065/jss2004.09.111
Kaur R, Goyal D (2019) Toxicity and degradation of the insecticide monocrotophos. Environ Chem Lett 17(3):1299–1324. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-019-00884-y
Chen Q, Zhang J, Wang CH et al (2014) Novosphingobium chloroacetimidivorans sp. nov., a chloroacetamide herbicide–degrading bacterium isolated from activated sludge. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64(8):2573–2578. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.062950-0
Mohanty SS, Jena HM (2019) Evaluation of butachlor biodegradation efficacy of Serratia ureilytica strain AS1: a statistical optimization approach. Int J Environ Sci Technol 16(10):5807–5816. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-1958-6
Mohanty SS, Jena HM (2018) Process optimization of butachlor bioremediation by Enterobacter cloacae using Plackett Burman design and response surface methodology. Process Saf Environ 119:198–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2018.08.009
Khanna P, Goyal D, Khanna S (2012) Characterization of pyrene utilizing Bacillus spp. from crude oil contaminated soil. Braz J Microbiol 43(2):606–617. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1517-83822012000200024
Haq AU, Saeed M, Usman M, Muneer M, Adeel S, Abbas S, Iqbal A (2019) Removal of butachlor from aqueous solution using cantaloupe seed shell powder: kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic studies. Int J Environ Sci Technol 16(10):6029–6042. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-1992-4
Xu C, Ding J, Qiu J, Ma Y (2013) Biodegradation of acetochlor by a newly isolated Achromobacter sp. strain D-12. J Environ Sci Health B 48(11):960–966. https://doi.org/10.1080/03601234.2013.816601
Kim OS, Cho YJ, Lee K et al (2012) Introducing EzTaxon-e: a prokaryotic 16S rRNA gene sequence database with phylotypes that represent uncultured species. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62(3):716–721. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.038075-0
Kumar S, Stecher G, Li M, Knyaz C, Tamura K (2018) MEGA X: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol Biol Evol 35(6):1547–1549. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msy096
Liu HM, Cao L, Lu P et al (2012) Biodegradation of butachlor by Rhodococcus sp. strain B1 and purification of its hydrolase (ChlH) responsible for N-dealkylation of chloroacetamide herbicides. J Agric Food Chem 60(50):2238–12244. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf303936j
Kim NH, Kim DU, Kim I, Ka JO (2013) Syntrophic biodegradation of butachlor by Mycobacterium sp. J7A and Sphingobium sp. J7B isolated from rice paddy soil. FEMS Microbiol Lett 344(2):114–120. https://doi.org/10.1111/1574-6968.12163
Agnihotri S, Sillu D, Sharma G, Arya RK (2018) Photocatalytic and antibacterial potential of silver nanoparticles derived from pineapple waste: process optimization and modeling kinetics for dye removal. Appl Nanosci 8(8):2077–2092. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-018-0883-9
Shivaji S, Chaturvedi P, Suresh K (2006) Bacillus aerius sp. nov., Bacillus aerophilus sp. nov., Bacillus stratosphericus sp. nov. and Bacillus altitudinis sp. nov., isolated from cryogenic tubes used for collecting air samples from high altitudes. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56(7):1465–1473. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.64029-0
Zhang J, Zheng JW, Liang B et al (2011) Biodegradation of chloroacetamide herbicides by Paracoccus sp. FLY-8 in vitro. J Agric Food Chem 59(9):4614–4621. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf104695g
Zheng J, Li R, Zhu J, Zhang J, He J, Li S, Jiang J (2012) Degradation of the chloroacetamide herbicide butachlor by Catellibacterium caeni sp. nov. DCA-1T. Int Biodeter Biodegr 73:16–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2012.06.003
García-Alcántara JA, Maqueda-Gálvez AP, Téllez-Jurado A, Hernández-Martínez R, Lizardi-Jiménez MA (2016) Maya crude-oil degradation by a Bacillus licheniformis consortium isolated from a Mexican thermal source using a bubble column bioreactor. Water Air Soil Pollut 227(11):413. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-3121-7
Surhio MA, Talpur FN, Nizamani SM et al (2017) Effective bioremediation of endocrine-disrupting phthalate esters, mediated by Bacillus strains. Water Air Soil Pollut 228(10):386. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-017-3567-2
Suyamud B, Inthorn D, Panyapinyopol B, Thiravetyan P (2018) Biodegradation of bisphenol A by a newly isolated Bacillus megaterium strain ISO-2 from a polycarbonate industrial wastewater. Water Air Soil Pollut 229(11):348. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-018-3983-y
Yu YL, Chen YX, Luo YM, Pan XD, He YF, Wong MH (2003) Rapid degradation of butachlor in wheat rhizosphere soil. Chemosphere 50(6):771–774. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-6535(02)00218-7
Yang C, Wang M, Li J (2012) Influence of rhizosphere microbial ecophysiological parameters from different plant species on butachlor degradation in a riparian soil. J Environ Qual 41(3):716–723. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq2011.0223
Chen K, Chen Q, Wang GX et al (2015) Sphingomonas chloroacetimidivorans sp. nov., a chloroacetamide herbicide-degrading bacterium isolated from activated sludge. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 108(3):703–710. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-015-0526-z
Chu CW, Chen Q, Wang CH et al (2016) Roseomonas chloroacetimidivorans sp. nov., a chloroacetamide herbicide-degrading bacterium isolated from activated sludge. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 109(5):611–618. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-016-0664-y
Acknowledgement
The authors would like to thank the Director, Thapar Institute of Engineering & Technology (Deemed to be University), Patiala, for infrastructural support and to DST-SERB (Science and Engineering Research Board, Department of Science and Technology, Government of India) for financial support vide Grant EMR/2016/002524.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RK conducted the experiments. RK and DG contributed equally towards the manuscript editing and its submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaur, R., Goyal, D. Biodegradation of Butachlor by Bacillus altitudinis and Identification of Metabolites. Curr Microbiol 77, 2602–2612 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-020-02031-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-020-02031-1