Abstract
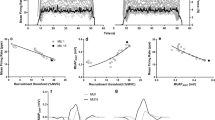
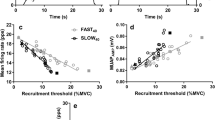
Despite ample evidence that females are weaker and possess smaller muscle cross-sectional areas (CSAs) compared to males, it remains unclear if there are sex-related differences in the properties of motor units (MU). Eleven males (age 22 ± 3 years) and 12 females (age 21 ± 1 years) performed isometric trapezoid muscle actions at 10% and 70% of maximal voluntary contraction (MVC). Surface electromyography signals were recorded and decomposed into MU action potential (AP) waveforms and firing instances. Average MUAP amplitudes (MUAPAMPS), mean firing rates (MFRs), initial firing rates (IFRs), and recruitment thresholds (RT) were calculated for the 10% MVC, while MUAPAMPS, IFRs, and MFRs were regressed against RT for the 70% MVC. Ultrasonography was used to measure CSA of the first dorsal interosseous (FDI). Males had greater CSAs (p < 0.001; males 2.34 ± 0.28 cm2, females 1.82 ± 0.18 cm2) and MVC strength (p < 0.001; males 25.9 ± 5.5 N, females 16.44 ± 2.5 N). No differences existed for MUAPAMPS, IFRs, MFRs, or RTs (p > 0.05) during the 10% MVC. For the 70% MVC, the y-intercepts from the MUAPAMPS vs. RT relationships were greater (p < 0.05) for the males (males − 0.19 ± 0.53 mV; females − 0.78 ± 0.75 mV), while the inverse was true for the MFR vs. RT relationships (males 31.55 ± 6.92 pps, females 38.65 ± 6.71 pps) with no differences (p > 0.05) in the slopes. Therefore, smaller CSAs and weaker MVCs are likely the result of smaller higher-threshold MUs for females.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bigland B, Lippold OCJ (1954) Motor unit activity in the voluntary contraction of human muscle. J Physiol 125:322–335. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005161
Burke RE, Levine DN, Tsairis P, Zajac FE (1973) Physiological types and histochemical profiles in motor units of the cat gastrocnemius. J Physiol 234:723–748. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010369
Canepari M, Pellegrino MA, D’Antona G, Bottinelli R (2010) Skeletal muscle fibre diversity and the underlying mechanisms. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/j.1748-1716.2010.02118.x. Accessed 14 Feb 2019
Carpentier A, Duchateau J, Hainaut K (2001) Motor unit behaviour and contractile changes during fatigue in the human first dorsal interosseus. J Physiol 534:903–912. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7793.2001.00903.x
Carroll CC, Gallagher PM, Seidle ME, Trappe SW (2005) Skeletal muscle characteristics of people with multiple sclerosis. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 86:224–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmr.2004.03.035
Clamann HP (1970) Activity of single motor units during isometric tension. Neurology 20:254. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.20.3.254
Contessa P, Luca CJD (2012) Neural control of muscle force: indications from a simulation model. J Neurophysiol 109:1548–1570. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.00237.2012
Dasgupta A, Simpson JA (1962) Relation between firing frequency of motor units and muscle tension in the human. Electromyography 2:117–128
De Luca CJ, Contessa P (2012) Hierarchical control of motor units in voluntary contractions. J Neurophysiol 107:178–195. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.00961.2010
De Luca CJ, Contessa P (2015) Biomechanical benefits of the onion-skin motor unit control scheme. J Biomech 48:195–203
De Luca CJ, Erim Z (1994) Common drive of motor units in regulation of muscle force. Trends Neurosci 17:299–305
De Luca CJ, Hostage EC (2010) Relationship between firing rate and recruitment threshold of motoneurons in voluntary isometric contractions. J Neurophysiol 104:1034–1046. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.01018.2009
De Luca CJ, Adam A, Wotiz R et al (2006) Decomposition of surface EMG signals. J Neurophysiol 96:1646–1657. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.00009.2006
Farina D, Holobar A, Gazzoni M et al (2009) Adjustments differ among low-threshold motor units during intermittent, isometric contractions. J Neurophysiol 101:350–359. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.90968.2008
Fuglevand AJ, Winter DA, Patla AE, Stashuk D (1992) Detection of motor unit action potentials with surface electrodes: influence of electrode size and spacing. Biol Cybern 67:143–153. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00201021
Goldberg LJ, Derfler B (1977) Relationship among recruitment order, spike amplitude, and twitch tension of single motor units in human masseter muscle. J Neurophysiol 40:879–890. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.1977.40.4.879
Henneman E (1957) Relation between size of neurons and their susceptibility to discharge. Science 126:1345–1347
Herda TJ, Miller JD, Trevino MA et al (2016) The change in motor unit firing rates at de-recruitment relative to recruitment is correlated with type I myosin heavy chain isoform content of the vastus lateralis in vivo. Acta Physiol 216:454–463. https://doi.org/10.1111/apha.12624
Herda TJ, Trevino MA, Sterczala AJ et al (2019) Muscular strength and power is correlated with motor unit action potential amplitudes, but not myosin heavy chain isoforms in sedentary males and females. J Biomech 86:215–255
Holobar A, Farina D, Gazzoni M et al (2009) Estimating motor unit discharge patterns from high-density surface electromyogram. Clin Neurophysiol 120:551–562. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2008.10.160
Hu X, Rymer WZ, Suresh NL (2013a) Motor unit pool organization examined via spike-triggered averaging of the surface electromyogram. J Neurophysiol 110:1205–1220. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.00301.2012
Hu X, Rymer WZ, Suresh NL (2013b) Assessment of validity of a high-yield surface electromyogram decomposition. J Neuroeng Rehabil 10:99. https://doi.org/10.1186/1743-0003-10-99
Hubal MJ, Gordish-Dressman H, Thompson P et al (2006) Variability in muscle size and strength gain after unilateral resistance training. Yearb Sports Med 2006:149–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0162-0908(08)70354-4
Hunter SK (2016) Sex differences in fatigability of dynamic contractions: Sex differences in skeletal muscle fatigue. Exp Physiol 101:250–255. https://doi.org/10.1113/EP085370
Johnson MA, Polgar J, Weightman D, Appleton D (1973) Data on the distribution of fibre types in thirty-six human muscles: an autopsy study. J Neurol Sci 18:111–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-510X(73)90023-3
Kamen G, Sison SV, Du CC, Patten C (1995) Motor unit discharge behavior in older adults during maximal-effort contractions. J Appl Physiol 79:1908–1913. https://doi.org/10.1152/jappl.1995.79.6.1908
Martinez-Valdes E, Negro F, Falla D et al (2018) Surface electromyographic amplitude does not identify differences in neural drive to synergistic muscles. J Appl Physiol 124:1071–1079. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.01115.2017
Maughan RJ, Watson JS, Weir J (1983) Strength and cross-sectional area of human skeletal muscle. J Physiol (Lond) 338:37–49
McManus L, Hu X, Rymer WZ et al (2016) Muscle fatigue increases beta-band coherence between the firing times of simultaneously active motor units in the first dorsal interosseous muscle. J Neurophysiol 115:2830–2839. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.00097.2016
Miller AEJ, MacDougall JD, Tarnopolsky MA, Sale DG (1993) Gender differences in strength and muscle fiber characteristics. Eur J Appl Physiol 66:254–262. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00235103
Miller JD, Herda TJ, Trevino MA et al (2017a) Age-related differences in twitch properties and muscle activation of the first dorsal interosseous. Clin Neurophysiol 128:925–934. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2017.03.032
Miller JD, Herda TJ, Trevino MA et al (2017b) Time-related changes in firing rates are influenced by recruitment threshold and twitch force potentiation in the first dorsal interosseous: recruitment threshold, potentiation and motor unit firing rates. Exp Physiol 102:950–961. https://doi.org/10.1113/EP086262
Miller JD, Sterczala AJ, Trevino MA, Herda TJ (2018) Examination of muscle composition and motor unit behavior of the first dorsal interosseous of normal and overweight children. J Neurophysiol 119:1902–1911. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.00675.2017
Miller JD, Sterczala AJ, Trevino MA et al (2019) Motor unit action potential amplitudes and firing rates during repetitive muscle actions of the first dorsal interosseous in children and adults. Eur J Appl Physiol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-019-04090-0
Milner-Brown HS, Stein RB (1975) The relation between the surface electromyogram and muscular force. J Physiol 246:549–569. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010904
Milner-Brown HS, Stein RB, Yemm R (1973a) The orderly recruitment of human motor units during voluntary isometric contractions. J Physiol 230:359–370. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010192
Milner-Brown HS, Stein RB, Yemm R (1973b) Changes in firing rate of human motor units during linearly changing voluntary contractions. https://physoc.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010193. Accessed 14 Feb 2019
Monster AW, Chan H (1977) Isometric force production by motor units of extensor digitorum communis muscle in man. J Neurophysiol 40:1432–1443. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.1977.40.6.1432
Nawab SH, Chang S-S, De Luca CJ (2010) High-yield decomposition of surface EMG signals. Clin Neurophysiol 121:1602–1615. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2009.11.092
Peng Y-L, Tenan MS, Griffin L (2018) Hip position and sex differences in motor unit firing patterns of the vastus medialis and vastus medialis oblique in healthy individuals. J Appl Physiol 124:1438–1446. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.00702.2017
Rowan SL, Rygiel K, Purves-Smith FM et al (2012) Denervation causes fiber atrophy and myosin heavy chain co-expression in senescent skeletal muscle. PLoS ONE 7:e29082. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0029082
Simoneau J-A, Lortie G, Boulay MR et al (1985) Human skeletal muscle fiber type alteration with high-intensity intermittent training. Eur J Appl Physiol 54:250–253. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00426141
Staron RS, Hagerman FC, Hikida RS et al (2000) J Histochem Cytochem 48:623–629
Sterczala AJ, Herda TJ, Miller JD et al (2018) Age-related differences in the motor unit action potential size in relation to recruitment threshold. Clin Physiol Funct Imaging 38:610–616. https://doi.org/10.1111/cpf.12453
Tanji J, Kato M (1973) Recruitment of motor units in voluntary contraction of a finger muscle in man. Exp Neurol 40:759–770. https://doi.org/10.1016/0014-4886(73)90110-6
Tenan MS, Peng Y-L, Hackney AC, Griffin L (2013) Menstrual cycle mediates vastus medialis and vastus medialis oblique muscle activity. Med Sci Sports Exerc 45:2151–2157. https://doi.org/10.1249/MSS.0b013e318299a69d
Thomas CK, Ross BH, Stein RB (1986) Motor-unit recruitment in human first dorsal interosseous muscle for static contractions in three different directions. J Neurophysiol 55:1017–1029. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.1986.55.5.1017
Trevino MA, Herda TJ, Fry AC et al (2016) Influence of the contractile properties of muscle on motor unit firing rates during a moderate-intensity contraction in vivo. J Neurophysiol 116:552–562. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.01021.2015
Trevino MA, Sterczala AJ, Miller JD et al (2018) Sex-related differences in muscle size explained by amplitudes of higher-threshold motor unit action potentials and muscle fibre typing. Acta Physiol. https://doi.org/10.1111/apha.13151
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the graduate and undergraduate students who aided in the collection of data, as well as each of the subjects for their selfless participation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise.
Additional information
Communicated by John C. Rothwell.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Parra, M.E., Sterczala, A.J., Miller, J.D. et al. Sex-related differences in motor unit firing rates and action potential amplitudes of the first dorsal interosseous during high-, but not low-intensity contractions. Exp Brain Res 238, 1133–1144 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-020-05759-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-020-05759-1