Abstract
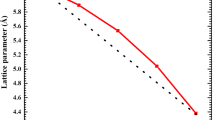
The structural stability and optoelectronic properties of the ternary Ba1−xBexS alloys along with the pure binary compounds BaS and BeS in the rock-salt (B1) and zinc-blende (B3) phases were investigated by the density functional theory (DFT) within the full-potential linearized augmented plane wave (FP-LAPW) method implemented in the Wien2k package. The generalized gradient approximation of Wu and Cohen (WC-GGA) was used for the exchange-correlation potential (Vxc) to compute the equilibrium structural parameters, lattice constant (a), and bulk modulus (B). In addition to the GGA approach, the modified Becke-Johnson potential of Tran and Blaha (TB-mBJ) scheme coupled with the spin-orbit interaction was used to calculate the band gap energies. Results reveal that BaS, Ba0.75Be0.25S, and Ba0.5Be0.5S compounds are stable in the rock-salt phase, while Ba0.25Be0.75S and BeS are found to be stable in the zinc-blende phase. The computed results for the band structures and optical constants are compared with other available theoretical calculations and experimental measurements.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lin GQ, Gong H, Wu P (2005) Electronic properties of barium chalcogenides from first-principles calculations: tailoring wide-band-gap II-VI semiconductors. Phys Rev B 71(8):085203–085208. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.71.085203
Bouhemadou A, Khenata R, Zegrar F, Sahnoun M, Baltache H, Reshak AH (2006) Ab initio study of structural, electronic, elastic and high pressure properties of barium chalcogenides. Comput Mater Sci 38:263–270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.commatsci.2006.03.001
Drablia S, Meradji H, Ghemid S, Nouet G, El Haj Hassan F (2009) First principles investigation of barium chalcogenide ternary alloys. Comput Mater Sci 46:376–382. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.commatsci.2009.03.013
Heng KL, Chua SJ, Wu P (2000) Prediction of semiconductor material properties by the properties of their constituent chemical elements. Chem Mater 12(6):1648–1653. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm9906194
Yamaoka S, Shimomura O, Nakazawa H, Fukunaga O (1980) Pressure-induced phase transformation in BaS. Solid State Commun 33(1):87–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/0038-1098(80)90702-4
Grzybowski TA, Ruoff AL (1983) High-pressure phase transition in BaSe. Phys Rev B 27(10):6502–6503. https://doi.org/10.1103/physrevb.27.6502
Grzybowski TA, Ruoff AL (1984) Band-overlap metallization of BaTe. Phys Rev Lett 53(5):489–492. https://doi.org/10.1103/physrevlett.53.489
Ruoff AL, Grzybowski TA (1985) Solid state physics under pressure. In: Minomura S (ed) Terra Scientic, Tokyo
Weir ST, Vohra YK, Ruoff AL (1987) Pressure-induced metallization of BaSe. Phys Rev B 35(2):874–876. https://doi.org/10.1103/physrevb.35.874
Weir ST, Vohra YK, Ruoff AL (1986) High-pressure phase transitions and the equations of state of BaS and BaO. Phys Rev B Condens Matter 33(6):4221–4226. https://doi.org/10.1103/physrevb.33.4221
Kaneko Y, Morimoto K, Koda T (1982) Optical properties of alkaline earth chalcogenides. J Phys Soc Jpn 51:2247–2254. https://doi.org/10.1143/JPSJ.51.2247
Narayana C, Nesamony VJ, Ruoff AL (1997) Phase transformation of BeS and equation-of-state studies to 96 GPa. Phys Rev B 56:14338. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.56.14338
Yim WM, Dismakes JB, Stofko EJ, Paff RJ (1972) Synthesis and some properties of BeTe, BeSe and BeS. J Phys Chem Solids 33(2):501–505. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-3697(72)90032-7
Waag A, Litz T, Fischer F, Lugauer HJ, Baron T, Schiill K, Zehnder U, Gerhard T, Lunza U, Keim M, Reuschera G, Landwehr G (1998) Novel beryllium containing II-VI compounds: basic properties and potential applications. J Cryst Growth 184/185:l–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-0248(98)80283-2
Zollweg RJ (1958) Optical absorption and photoemission of barium and strontium oxides, sulfides, selenides, and tellurides. Phys Rev 111(1):113–119. https://doi.org/10.1103/physrev.111.113
Kaneko Y, Morimoto K, Koda T (1983) Optical properties of alkaline-earth chalcogenides. II. Vacuum ultraviolet reflection spectra in the synchrotron radiation region of 4–40 eV. J Phys Soc Jpn. 52(12):4385–4396. https://doi.org/10.1143/jpsj.52.4385
Khenata R, Sahnoun M, Baltache H, Rérat M, Rached D, Driz M, Bouhafs B (2006) Structural, electronic, elastic and high-pressure properties of some alkaline-earth chalcogenides: an ab initio study. Phys B: Cond Matt 371(1):12–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2005.08.046
Tuncel E, Colakoglu K, Deligoz E, Ciftci YO (2009) A first-principles study on the structural, elastic, vibrational, and thermodynamical properties of BaX (X = S, Se, and Te). J Phys Chem Solids 70(2):371–378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2008.11.002
Drablia S, Meradji H, Ghemid S, Boukhris N, Bouhafs B, Nouet G (2009) Electronic and optical properties of BaO, BaS, BaSe, BaTe and BaPo compounds under hydrostatic pressure. Mod Phys Lett B 23(26):3065–3079. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0217984909021235
Pourghazi A, Dadsetani M (2005) Electronic and optical properties of BaTe, BaSe and BaS from first principles. Physica B 370(1–4):35–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2005.08.032
Gökoğlu G (2008) First principles study of barium chalcogenides. J Phys Chem Solids 69(11):2924–2927. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2008.08.012
El Haj Hassan F, Akbarzadeh H (2006) First-principles elastic and bonding properties of barium chalcogenides. Comput Mater Sci 38(2):362–368. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.commatsci.2005.09.012
Waag A, Fischer F, Lugauer HJ, Litz T, Gerhard T, Nürnberger J, Lunz U, Zehnder U, Ossau W, Landwehr G, Roos B, Richter H (1997) Beryllium chalcogenides for ZnSe-based light emitting devices. Mater Sci Eng B43(1–3):65–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0921-5107(96)01911-3
Luo H, Ghandehari K, Greene RG, Ruoff AL, Trail SS, DiSalvo FJ (1995) Phase transformation of BeSe and BeTe to the NiAs structure at high pressure. Phys Rev B 52(10):7058–7064. https://doi.org/10.1103/physrevb.52.7058
Pandey R, Sivaraman S (1991) Spectroscopic properties of defects in alkaline-earth sulfides. J Phys Chem Solids 52(1):211–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-3697(91)90066-9
Asano S, Yamashita N, Nakao Y (1978) Luminescence of the Pb2+-ion dimer center in CaS and CaSe phosphors. Phys Status Solidi B 89(2):663–673. https://doi.org/10.1002/pssb.2220890242
Wilmers K, Wethkamp T (1999) Ellipsometric studies of BexZn1−xSe between 3 eV and 25 eV. Phys Rev B 59(15):10071–10075. https://doi.org/10.1103/physrevb.59.10071
Kalpana G, Pari G, Mookerjee A, Bhattacharyya AK (1998) Ab initio electronic band structure calculations for beryllium chalcogenides. Int J Mod Phys B 12(19):1975–1984. https://doi.org/10.1142/s0217979298001149
Okoye CMI (2004) Structural, electronic, and optical properties of beryllium monochalcogenides. Eur Phys J B 39(1):5–17. https://doi.org/10.1140/epjb/e2004-00164-3
El Haj Hassan F, Akbarzadeh H (2006) Ground state properties and structural phase transition of beryllium chalcogenides. Comput Mater Sci 35(4):423–431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.commatsci.2005.02.010
Berghout A, Zaoui A, Hugel J (2006) Fundamental state quantities and high-pressure phase transition in beryllium chalcogenides. J Phys Condens Matter 18(46):10365–10375. https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-8984/18/46/005
Heciri D, Beldi L, Drablia S, Meradji H, Derradji NE, Belkhir H, Bouhafs B (2007) First-principles elastic constants and electronic structure of beryllium chalcogenides BeS, BeSe and BeTe. Comput Mater Sci 38(4):609–617. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.commatsci.2006.04.003
Munjal N, Sharma V, Sharma G, Vyas V, Sharma BK, Lowther JE (2011) Ab-initiostudy of the electronic and elastic properties of beryllium chalcogenides BeX (X=S, Se and Te). Phys Scr 84(3):035704. https://doi.org/10.1088/0031-8949/84/03/035704
Guo L, Hu G, Zhang S, Feng W, Zhang Z (2013) Structural, elastic, electronic and optical properties of beryllium chalcogenides BeX (X=S, Se, Te) with zinc-blende structure. J Alloys Compd 561:16–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.01.144
Yu Y, Liu D, Chen J, Ji J, Long J (2014) First-principles investigations on structural, electronic and elastic properties of BeSe under high pressure. Solid State Sci 28:35–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2013.12.009
Rai DP, Ghimire MP, Thapa RK (2014) A DFT study of BeX (X = S, se, Te) semiconductor: modified Becke Johnson (mBJ) potential. Semiconductors 48(11):1411–1422. https://doi.org/10.1134/s1063782614110244
Ji X, Yu Y, Ji J, Long J, Chen J, Liu D (2015) Theoretical studies of the pressure-induced phase transition and elastic properties of BeS. J Alloys Compd 623:304–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2014.10.151
Drablia S, Boukhris N, Boulechfar R, Meradji H, Ghemid S, Ahmed R, Bin Omran S, El Haj Hassan F, Khenata R (2017) Ab initio calculations of the structural, electronic, thermodynamic and thermal properties of BaSe1−xTex alloys. Phys Scr 92(10):105701–105709. https://doi.org/10.1088/1402-4896/aa842e
Chelli S, Touam S, Hamioud L, Meradji H, Ghemid S, El Haj HF (2015) Ab-initio study of structural, elastic, electronic and thermodynamic properties of BaxSr1−xS ternary alloys. Mater Sci Pol 33(4):879–886. https://doi.org/10.1515/msp-2015-0108
Chelli S, Meradji H, Amara Korba S, Ghemid S, El Haj HF (2014) First principles calculations of structural, electronic, thermodynamic and thermal properties of BaxSr1−xTe ternary alloys. Int J Mod Phys B 28(4):1450041–1450058. https://doi.org/10.1142/s0217979214500416
Baaziz H, Charifi Z, El Haj Hassan F, Hashemifar SJ, Akbarzadeh H (2006) FP-LAPW investigations of Zn1–xBexS, Zn1–xBexSe and Zn1–xBexTe ternary alloys. Phys Status Solidi B 243(6):1296–1305. https://doi.org/10.1002/pssb.200541481
Bensaid D, Ameri M, Benseddik N, Mir A, Bouzouira NE, Benzoudji F (2014) Band gap engineering of Cd1-xBexSe alloys. Int J Met 2014:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/286393
Sabir B, Noor NA, Rashid M, Din FU, Ramay SM, Mahmood A (2018) Bandgap engineering to tune the optical properties of Bex Mg1−x X (X = S, Se, Te) alloys. Chin Phys B 27(1):016101–016110. https://doi.org/10.1088/1674-1056/27/1/016101
Madsen GKH, Blaha P, Schwarz K, Sjöstedt E, Nordström L (2001) Efficient linearization of the augmented plane-wave method. Phys Rev B 64:195134–195144. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.64.195134
Schwarz K, Blaha P, Madsen GKH (2002) Electronic structure calculations of solids using the Wien2k package for material sciences. Comput Phys Commun 147(1–2):71–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0010-4655(02)00206-0
Hohenberg P, Kohn W (1964) Inhomogeneous electron gas. Phys Rev 136(3B):B864–B871. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRev.136.B864
Kohn W, Sham LJ (1965) Self-consistent equations including exchange and correlation effects. Phys Rev 140(4A):A1133–A1138. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRev.140.A1133
Blaha P, Schwarz K, Madsen GKH, Kvasnicka D, Luitz J (2001) WIEN2K: an augmented plane wave plus local orbitals program for calculating crystal properties, Vienna
Wu Z, Cohen RE (2006) More accurate generalized gradient approximation for solids. Phys Rev B 73(23):235116–235122. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.73.235116
Tran F, Blaha P (2009) Accurate band gaps of semiconductors and insulators with semi local exchange-correlation potential. Phys Rev Lett 102(22):226401–226405. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.102.226401
Amimour B, Slimani M, Sifi C, Khémissi R, Meradji H, Ghemid S, Omran SB, Khenata R (2017) Computational investigations of the band structure and thermodynamic properties of calcium-doped BaS using the FP-LAPW approach. Chin J Phys 55(2):367–377. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjph.2017.02.002
Bhattacharjee R, Chattopadhyaya S (2017) Effects of barium (Ba) doping on structural, electronic and optical properties of binary strontium chalcogenide semiconductor compounds -a theoretical investigation using DFT based FP-LAPW approach. Mater Chem Phys 199:295–312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2017.06.057
Feng Z, Hu H, Cui S, Wang W (2009) Electronic structure calculations for BaSxSe1-x alloys. Physica B 404(16):2107–2110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2008.11.201
Ameri M, Touia A, Khachai H, Mahdjoub Z, Chekroun MZ, Slamani A (2012) Ab initio study of structural and electronic properties of barium chalcogenide alloys. Mater Sci Appl 3(9):612–618. https://doi.org/10.4236/msa.2012.39088
Benkaddour I, Khachai H, Chiker F, Benosman N, Benkaddour Y, Murtaza G, Omran SB, Khenata R (2015) Ab initio study of the structural, electronic, and thermal properties of BaS1−xTex alloy. Int J Thermophys 36:1640–1653. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-015-1908-1
Wang KL, Gao SP (2018) Phonon dispersions, band structures, and dielectric functions of BeO and BeS polymorphs. J Phys Chem Solids 118:242–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2018.03.013
Rached D, Rabah M, Benkhettou N, Khenata R, Soudini B, Douri YA, Baltache H (2006) First-principle study of structural, electronic and elastic properties of beryllium chalcogenides BeS, BeSe and BeTe. Comput Mater Sci 37(3):292–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.commatsci.2005.08.005
Laref S, Laref A (2012) Thermal properties of BeX (X = S, Se and Te) compounds from ab initio quasi-harmonic method. Comput Mater Sci 51(1):135–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.commatsci.2011.07.016
Dabhi S, Mankad V, Prafulla KJ (2014) A first principles study of phase stability, bonding, electronic and lattice dynamical properties of beryllium chalcogenides at high pressure. J Alloys Compd 617:905–914. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2014.08.035
Ali R, Mohammad S, Ullah H, Khan SA, Uddin H, Khan M, Khan NU (2013) The structural, electronic and optical response of IIA–VIA compounds through the modified Becke–Johnson potential. Physica B 410(1):93–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2012.09.050
Zhang X, Ying C, Shi G, Li Z (2011) A first-principles study on the structural, lattice dynamical and thermodynamic properties of beryllium chalcogenides. Physica B 406(24):4666–4670. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2011.09.056
Khenata R, Bouhemadou A, Hichour M, Baltache H, Rached D, Rérat M (2006) Elastic and optical properties of BeS, BeSe and BeTe under pressure. Solid State Electron 50(7–8):1382–1388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sse.2006.06.019
Fluegel B, Francoeur S, Mascarenhas A, Tixier S, Young EC, Tiedje T (2006) Giant spin-orbit bowing in GaAs1−xBix. Phys Rev Lett 97:067205–067205. https://doi.org/10.1103/physrevlett.97.067205
Zhang Y, Mascarenhas A, Wang LW (2005) Similar and dissimilar aspects of III−V semiconductors containing Bi versus N. Phys Rev B Matt 71(15):155201–155205. https://doi.org/10.1103/physrevb.71.155201
Dalven R (1973) Empirical relation between energy gap and lattice constant in cubic semiconductors. Phys Rev B 8(12):6033–6034. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.8.6033
Carlsson AE, Wilkins JW (1984) Band-overlap metallization of BaS, BaSe, and BaTe. PhysRev B 29(10):5836–5839. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.29.5836
Fox M (2002) Optical properties of solids. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Ambrosch DA, Sofo JO (2006) Linear optical properties of solids within the full-potential linearized augmented planewave method. Comput Phys Commun 175(1):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpc.2006.03.005
Harbeke G (1972) In optical properties of solids. In: Abelès F (ed) North-Holland, Amsterdam
Lines ME (1990) Bond-orbital theory of linear and nonlinear electronic response in ionic crystals. I Linear response. Phys Rev B 41(6):3372–3382. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.41.3372
Drofenik M, Ažman A (1972) The dynamic ionic charge of NaCl type crystals CaS, SrS. BaS J Phys Chem Solids 33(3):761–763. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-3697(72)90087-X
Dadsetani M, Pourghazi A (2006) The dielectric constant of barium mono-chalcogenides and their improved band gap results. Opt Commun 266(2):562–564. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optcom.2006.05.018
Debnath B, Debbarma M, Ghosh D, Chanda S, Bhattacharjee R, Chattopadhyaya S (2019) Optoelectronic properties of CaxBa1-xX (X=S, Se and Te) alloys: a first principles investigation employing modified Becke-Johnson (mBJ) functional. Int. J. Mod Phys B 33:1950042–1950079. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0217979219500425
Sifi C, Meradji H, Silmani M, Labidi S, Ghemid S, Hanneche EB, El Haj HF (2009) First principle calculations of structural, electronic, thermodynamic and optical properties of Pb1−xCaxS, Pb1−xCaxSe and Pb1−xCaxTe ternary alloys. J Phys Condens Matter 21(19):195401–195050. https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-8984/21/19/195401
Hervé PJL, Vandamme LKJ (1995) Empirical temperature dependence of the refractive index of semiconductors. J Appl Phys 77(10):5476–5477. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.359248
Othman M, Kasap E, Korozlu N (2010) Ab-initio investigation of structural, electronic and optical properties of InxGa1-xAs, GaAs1-yPy ternary and InxGa1-xAs1-yPy quaternary semiconductor alloys. J Alloys Compd 496(1–2):226–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2009.12.109
Acknowledgments
Authors acknowledge the help of Prof. Hamad R. Jappor from the College of Education for Pure Sciences, University of Babylon, Iraq, for his careful reading of the paper.
Funding
The author S. Bin Omran acknowledges the financial support by the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Saud University for funding the work through the Research Group project number RG-1440-106.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gagui, S., Bendjeddou, H., Meradji, H. et al. Phase stability and optoelectronic characteristics of Ba1−xBexS: a DFT-based simulation. J Mol Model 26, 147 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-020-04370-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-020-04370-z