Abstract
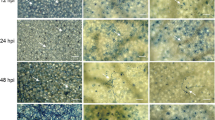
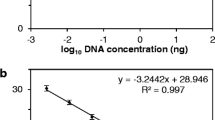
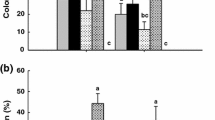
Barley, host to the wheat and rye attacking forms of the stem rust pathogen, Puccinia graminis (Pg), is considered inherently more resistant to Pg than wheat. To investigate whether this enhanced basal defence is associated with early infection or colonisation processes, adult plants of selected barley and wheat entries were inoculated with Pg f. sp. tritici (Pgt) races BNGSC and PTKST, and Pg f. sp. secalis (Pgs) isolate UVPgs1. Flag leaf sheaths on the last stem internode were sampled for analysis. Using scanning electron microscopy and epidermal stripping, early Pg infection structure development was compared between barley and wheat. Sub-stomatal vesicle appearance and production of haustorial mother cells were similar at 24 and 48 h post inoculation (hpi), respectively. Significant variation occurred among host entries (P ≤ 0.01) for colony size and fungal biomass at 120 hpi. Differences between the Pgt races and the Pgs isolate as well as the host entry-Pg isolate interaction proved insignificant (P ≥ 0.05). The period between 120 and 240 hpi may hold some explanation for the perceived lower stem rust receptivity in barley, since a steep increase in accumulated fungal biomass observed in the susceptible wheat Line 37 − 07 was not seen in the susceptible barley entries at the same time interval.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arora D, Gross T, Brueggeman R (2013) Allele characterization of genes required for rpg4-mediated wheat stem rust resistance identifies Rpg5 as the R gene. Phytopathology 103:1153–1161
Arthaud J, Guyot L, Malencon G (1966) Comparative biometric studies of the formae speciales of black rust (Puccinia graminis Pers.) living on the wild grasses of the Moroccan Atlas. In: Proceedings of the Cereal Rusts Conference, Cambridge, 1964, pp 204–206
Atienza SG, Jafary H, Niks RE (2004) Accumulation of genes for susceptibility to rust fungi for which barley is nearly a non-host results in two barley lines with extreme multiple susceptibility. Planta 220:71–79
Bender CM, Prins R, Pretorius ZA (2016) Development of a greenhouse screening method for adult plant response in wheat to stem rust. Plant Dis 100(1):627–633
Boshoff WHP, Bender CM, Pretorius ZA (2019) Reaction of South African rye, triticale and barley forage cultivars to stem and leaf rust. SA J Plant Soil 36(2):77–82
Boshoff WHP, Pretorius ZA, Van Niekerk BD, Komen JS (2002) First report of virulence in Puccinia graminis f. sp. tritici to wheat stem rust resistance genes Sr8b and Sr38 in South Africa. Plant Dis 86(8):922
Brown JKM, Hovmøller MS (2002) Aerial dispersal of pathogens on the global and continental scales and its impact on plant disease. Science 297:537–541
Brueggeman R, Druka A, Nirmala J, Cavileer T, Drader T, Rostoks N, Mirlohi A, Bennypaul H, Gill U, Kudrna D, Whitelaw C, Kilian A, Han F, Sun Y, Gill K, Steffenson B, Kleinhofs A (2008) The stem rust resistance gene Rpg5 encodes a protein with nucleotide binding site, leucine-rich, and protein kinase domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:14970–14975
Brueggeman R, Rostoks N, Kudrna D, Kilian A, Han F, Chen J, Druka A, Steffenson B, Kleinhofs A (2002) The barley stem rust-resistance gene Rpg1 is a novel disease-resistance gene with homology to receptor kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:9328–9333
Brueggeman R, Steffenson BJ, Kleinhofs A (2009) The rpg4/Rpg5 stem rust resistance locus in barley; resistance genes and cytoskeleton dynamics. Cell Cycle 8:977–981
Case AJ (2017) Genetics, sources, and mapping of stem rust resistance in barley. PhD Thesis, University of Minnesota, St. Paul
Chomczynski P, Sacchi N (1987) Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem 162(1):156–159
Coram TE, Settles ML, Chen X (2008) Transcriptome analysis of high-temperature adult-plant resistance conditioned by Yr39 during the wheat–Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici interaction. Mol Plant Pathol 9(4):479–493
Coutinho TA, Rijkenberg FHJ, Van Asch MAJ (1993) Development of infection structures by Hemileia vastatrix in resistant and susceptible selections of Coffea and in Phaseolus vulgaris. Can J Bot 71:1001–1008
Dean R, Van Kan JAL, Pretorius ZA, Hammond-Kosack K, Di Pietro A, Spanu P, Rudd JJ, Dickman M, Kahmann R, Ellis J, Foster GD (2012) The top 10 fungal pathogens in molecular plant pathology. Mol Plant Pathol 13:414–430
Derevnina L, Fetch T, Singh D, Brueggeman R, Dong C, Park RF (2014) Analysis of stem rust resistance in Australian barley cultivars. Plant Dis 98:1485–1493
Dickinson S (1969) Studies in the physiology of obligate parasitism. VI. Directed growth. J Phytopathol 66:38–49
Glauert AM (1974) Fixation, dehydration and embedding of biological specimens. In: Glauert AM (ed) Practical methods in electron microscopy, vol 3. North Holland Publishing Company, Amsterdam
Hughes FL, Rijkenberg FHJ (1985) Scanning electron microscopy of early infection in the uredial stage of Puccinia sorghi in Zea mays. Plant Pathol 34:61–68
Jafary H, Szabo LJ, Niks RE (2006) Innate non-host immunity in barley to different heterologous rust fungi is controlled by sets of resistance genes with different and overlapping specificities. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 19:1270–1279
Jin Y, Singh RP, Ward RW, Wanyera R, Kinyua M, Njau P, Fetch T, Pretorius ZA, Yahyaoui A (2007) Characterization of seedling infection types and adult plant infection responses of monogenic Sr gene lines to race TTKS of Puccinia graminis f. sp. tritici. Plant Dis 91:1096–1099
Jin Y, Steffenson BJ, Miller JD (1994) Inheritance of resistance to pathotypes QCC and MCC of Puccinia graminis f. sp. tritici in barley line Q21861 and temperature effects on the expression of resistance. Phytopathology 84:452–455
Jin Y, Szabo LJ, Pretorius ZA, Singh RP, Ward R, Fetch T (2008) Detection of virulence to resistance gene Sr24 within race TTKS of Puccinia graminis f. sp. tritici. Plant Dis 92:923–926
Jin Y, Szabo LJ, Rouse MN, Fetch T, Pretorius ZA, Wanyera R, Njau P (2009) Detection of virulence to resistance gene Sr36 within the TTKS race lineage of Puccinia graminis f. sp. tritici. Plant Dis 93:367–370
Johnson T (1934) A tropic response in germ tubes of urediospores of Puccinia graminis tritici. Phytopathology 24:80–82
Keiper FJ, Hayden MJ, Park RF, Wellings CR (2003) Molecular genetic variability of Australian isolates of five cereal rust pathogens. Mycol Res 107:545556
Knott DR (1989) The wheat rust pathogens. In: Knott DR (ed) The wheat rusts; breeding for resistance. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, pp 1–37
Mamo BE, Brueggeman RS, Smith KP, Steffenson BJ (2015) Genetic characterization of resistance to wheat stem rust race TTKSK in landrace and wild barley accessions identifies the rpg4/Rpg5 locus. Phytopathology 105:99–109
Martens JW, Dunsmore KM, Harder DE (1989) Incidence and virulence of Puccinia graminis in Canada on wheat and barley in 1988. Can J Plant Pathol 11:424–430
McIntosh RA, Wellings CR, Park RF (1995) Wheat rusts: An atlas of resistance genes. CSIRO, Canberra
McVey DV, Long DL, Roberts JJ (2002) Races of Puccinia graminis in the United States during 1997 and 1998. Plant Dis 86:568–572
Niks RE (1986) Variation of mycelial morphology between species and formae speciales of rust fungi of cereals and grasses. Can J Bot 64:29762983
Nirmala J, Dahl S, Steffenson BJ, Kannangara CG, von Wettstein D, Chen X, Kleinhofs A (2007) Proteolysis of the barley receptor-like protein kinase RPG1 by a proteasome pathway is correlated with Rpg1-mediated stem rust resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104(24):10276–10281
Park RF (2007) Stem rust of wheat in Australia. Aust J Agric Res 58:558–566
Park RF, Golegaonkar PG, Derevnina L, Sandhu KS, Karaoglu H, Elmansour HM, Dracatos PM, Singh D (2015) Leaf rust of cultivated barley: pathology and control. Annu Rev Phytopathol 53:565–589
Patterson F, Shands R, Dickson J (1957) Temperature and seasonal effects on seedling reactions of barley varieties to three races of Puccinia graminis f. sp. tritici. Phytopathology 47:395–402
Peterson PD (2001) Stem rust of wheat – from ancient enemy to modern foe. APS Press, St. Paul
Pretorius ZA, Ayliffe M, Bowden RL, Boyd LA, DePauw RM, Jin Y, Knox RE, McIntosh RA, Park RF, Prins R, Lagudah ES (2017) Advances in control of wheat rusts. In: Langridge P (ed) Achieving sustainable cultivation of wheat Volume 1: Breeding, quality traits, pests and diseases. Burleigh Dodds Science Publishing, Cambridge, pp 295–343
Pretorius ZA, Jin Y, Bender CM, Herselman L, Prins R (2012) Seedling resistance to stem rust race Ug99 and marker analysis for Sr2, Sr24 and Sr31 in South African wheat cultivars and lines. Euphytica 186:15–23
Pretorius ZA, Singh RP, Wagoire WW, Payne TS (2000) Detection of virulence to wheat stem rust resistance gene Sr31 in Puccinia graminis f. sp. tritici in Uganda. Plant Dis 84:203
Prins R, Dreisigacker S, Pretorius Z, van Schalkwyk H, Wessels E, Smit C, Bender C, Singh D, Boyd LA (2016) Stem rust resistance in a geographically diverse collection of spring wheat lines collected from across Africa. Front Plant Sci 7:973
Roelfs AP, Singh RP, Saari EE (1992) Rust diseases of wheat: concepts and methods of disease management. Centro International de Mejoramiento de Maiz y Trigo (CIMMYT), Mexico City
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: A laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2000) Molecular cloning: A laboratory manual. 3rd edition. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, New York, pp A8.19-8.21; 7.31–7.34
Scholtz JJ, Visser B (2013) Reference gene selection for qPCR gene expression analysis of rust-infected wheat. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 81:2225
Shands R (1939) Chevron, a barley variety resistant to stem rust and other diseases. Phytopathology 29:209–211
Singh RP, Hodson DP, Huerta-Espino J, Jin Y, Njau P, Wanyera R, Herrera-Foessel SA, Ward RW (2008) Will stem rust destroy the world’s wheat crop? Adv Agron 98:271–309
Singh RP, Hodson DP, Jin Y, Huerta-Espino J, Kinyua MG, Wanyera R, Njau P, Ward RW (2006) Current status, likely migration and strategies to mitigate the threat to wheat production from race Ug99 (TTKS) of stem rust pathogen. CAB Rev: Perspectives in Agriculture, Veterinary Science, Nutr Nat Resour 1:113
Singh RP, Hodson DP, Jin Y, Lagudah ES, Ayliffe MA, Bhavani S, Rouse MN, Pretorius ZA, Szabo LJ, Huerta-Espino J, Basnet BR, Lan C, Hovmøller MS (2015) Emergence and spread of new races of wheat stem rust fungus: continued threat to food security and prospects of genetic control. Phytopathology 105:872–884
Sood PN, Sackston WE (1970) Studies on sunflower rust. VI. Penetration and infection of sunflowers susceptible and resistant to Puccinia helianthi race 1. Can J Bot 48:2179–2181
Steffenson BJ (1992) Analysis of durable resistance to stem rust in barley. Euphytica 63:153–167
Steffenson BJ, Case AJ, Pretorius ZA, Coetzee V, Kloppers FJ, Zhou H, Chai Y, Wanyera R, Macharia G, Bhavani S, Grando S (2017) Vulnerability of barley to African pathotypes of Puccinia graminis f. sp. tritici and sources of resistance. Phytopathology 107:950–962
Steffenson BJ, Jin Y, Brueggeman RS, Kleinhofs A, Sun Y (2009) Resistance to stem rust race TTKSK maps to the rpg4/Rpg5 complex of chromosome 5H of barley. Phytopathology 99:1135–1141
Steffenson BJ, Olivera P, Roy JK, Jin Y, Smith KP, Muehlbauer GJ (2007) A walk on the wild side: Mining wild wheat and barley collections for rust resistance genes. Aust J Agric Res 58:532–544
Sun Y, Steffenson BJ (2005) Reaction of barley seedlings with different stem rust resistance genes to Puccinia graminis f. sp. tritici and Puccinia graminis f. sp. secalis. Can J Plant Pathol 27:80–89
Swertz CA (1994) Morphology of germlings of urediniospores and its value for the identification and classification of grass rust fungi. Stud Mycol 36:1–152
Wang X, Richards J, Gross T, Druka A, Kleinhofs A, Steffenson B, Acevedo M, Brueggeman R (2013) The rpg4-mediated resistance to wheat stem rust (Puccinia graminis) in barley (Hordeum vulgare) requires Rpg5, a second NBS-LRR gene, and an actin depolymerization factor. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 26:407–418
Wanyera R, Kinyua MG, Jin Y, Singh RP (2006) The spread of stem rust caused by Puccinia graminis f. sp. tritici with virulence on Sr31 in Eastern Africa. Plant Dis 90:113
Wynn WK (1976) Appressorium formation over stomata by the bean rust fungus: response to a surface contact stimulus. Phytopathology 66:136–146
Zadoks JC, Chang TT, Konzak CF (1974) A decimal code for the growth stages of cereals. Weed Res 14:415–421
Zurn JD, Dugyala S, Borowicz P, Brueggeman R, Acevedo M (2015) Unravelling the wheat stem rust infection process on barley genotypes through relative qPCR and fluorescence microscopy. Phytopathology 105:707–712
Acknowledgements
The South African Winter Cereal Trust, National Research Foundation (UID 96099) and University of Free State are thanked for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Online Resource 1
(PDF 263 kb)
Online Resource 2
(PDF 792 kb)
Online Resource 3
(PDF 423 kb)
Online Resource 4
(PDF 426 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maree, G.J., Castelyn, H.D., Bender, C.M. et al. Comparing infection and colonisation of Puccinia graminis in barley and wheat. Australasian Plant Pathol. 49, 431–445 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13313-020-00715-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13313-020-00715-7