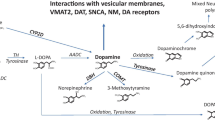
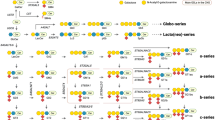
Abstract
Neuronal homeostasis depends on both simple and complex sugars (the glycoconjugates), and derangement of their metabolism is liable to impair neural function and lead to neurodegeneration. Glucose levels boost glycation phenomena, a wide series of non-enzymatic reactions that give rise to various intermediates and end-products that are potentially dangerous in neurons. Glycoconjugates, including glycoproteins, glycolipids, and glycosaminoglycans, contribute to the constitution of the unique features of neuron membranes and extracellular matrix in the nervous system. Glycosylation defects are indeed frequently associated with nervous system disturbances and neurodegeneration. Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by motor and non-motor symptoms associated with the loss of dopaminergic neurons in the pars compacta of the substantia nigra. Neurons present intracytoplasmic inclusions of α-synuclein aggregates involved in the disease pathogenesis together with the impairment of the autophagy-lysosome function, oxidative stress, and defective traffic and turnover of membrane components. In the present review, we selected relevant recent contributions concerning the direct involvement of glycation and glycosylation in α-synuclein stability, impaired autophagy and lysosomal function in PD, focusing on potential models of PD pathogenesis provided by genetic variants of glycosphingolipid processing enzymes, especially glucocerebrosidase (GBA). Moreover, we collected data aimed at defining the glycomic profile of PD patients as a tool to help in diagnosis and patient subtyping, as well as those pointing to sugar-related compounds with potential therapeutic applications in PD.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wihan J, Grosch J, Kalinichenko LS, Müller CP, Winkler J, Kohl Z (2019) Layer-specific axonal degeneration of serotonergic fibers in the prefrontal cortex of aged A53T α-synuclein–expressing mice. Neurobiol Aging 80:29–37
Deusser J, Schmidt S, Ettle B, Plötz S, Huber S, Müller CP, Masliah E, Winkler J et al (2015) Serotonergic dysfunction in the A53T alpha-synuclein mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem 135(3):589–597
Kohl Z, Ben Abdallah N, Vogelgsang J, Tischer L, Deusser J, Amato D, Anderson S, Müller CP et al (2016) Severely impaired hippocampal neurogenesis associates with an early serotonergic deficit in a BAC α-synuclein transgenic rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Dis 85:206–217
Nuber S, Rajsombath M, Minakaki G, Winkler J, Müller CP, Ericsson M, Caldarone B, Dettmer U et al (2018) Abrogating native α-Synuclein tetramers in mice causes a L-Dopa-responsive motor syndrome closely resembling Parkinson’s disease. Neuron 100(1):75–90 e5
Balestrino R, Schapira AHV (2020) Parkinson disease. Eur J Neurol 27(1):27–42
Schnaar RL, Gerardy-Schahn R, Hildebrandt H (2014) Sialic acids in the brain: Gangliosides and polysialic acid in nervous system development, stability, disease, and regeneration. Physiol Rev 94(2):461–518
Heindryckx F, Li JP (2018) Role of proteoglycans in neuro-inflammation and central nervous system fibrosis. Matrix Biol 68–69:589–601
Iqbal S, Ghanimi Fard M, Everest-Dass A, Packer NH, Parker LM (2019) Understanding cellular glycan surfaces in the central nervous system. Biochem Soc Trans 47(1):89–100
Lauc G, Vojta A, Zoldos V (2014) Epigenetic regulation of glycosylation is the quantum mechanics of biology. Biochim Biophys Acta 1840(1):65–70
Trinchera M, Zulueta A, Caretti A, Dall'Olio F (2014) Control of glycosylation-related genes by DNA methylation: the intriguing case of the B3GALT5 gene and its distinct promoters. Biology (Basel) 3(3):484–497
Zulueta A, Caretti A, Signorelli P, Dall'olio F, Trinchera M (2014) Transcriptional control of the B3GALT5 gene by a retroviral promoter and methylation of distant regulatory elements. FASEB J 28(2):946–955
Varki A (2017) Biological roles of glycans. Glycobiology 27(1):3–49
Moll T, Shaw PJ, Cooper-Knock J (2019) Disrupted glycosylation of lipids and proteins is a cause of neurodegeneration. Brain. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awz358
Ng BG, Freeze HH (2018) Perspectives on glycosylation and its congenital disorders. Trends Genet 34(6):466–476
Trinchera M, Parini R, Indellicato R, Domenighini R, Dall’Olio F (2018) Diseases of ganglioside biosynthesis: An expanding group of congenital disorders of glycosylation. Mol Genet Metab 124(4):230–237
Schneider JS (1998) GM1 ganglioside in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci 845:363–373
Ba XH (2016) Therapeutic effects of GM1 on Parkinson’s disease in rats and its mechanism. Int J Neurosci 126(2):163–167
Ryu JK, Shin WH, Kim J, Joe EH, Lee YB, Cho KG, Oh YJ, Kim SU et al (2002) Trisialoganglioside GT1b induces in vivo degeneration of nigral dopaminergic neurons: role of microglia. Glia 38(1):15–23
Zappia M, Crescibene L, Bosco D, Arabia G, Nicoletti G, Bagala A, Bastone L, Napoli ID et al (2002) Anti-GM1 ganglioside antibodies in Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neurol Scand 106(1):54–57
Bhuiyan RH, Ohmi Y, Ohkawa Y, Zhang P, Takano M, Hashimoto N, Okajima T, Furukawa K (2019) Loss of enzyme activity in mutated B4GALNT1 gene products in patients with hereditary spastic paraplegia results in relatively mild neurological disorders: Similarity with phenotypes of B4galnt1 knockout mice. Neuroscience 397:94–106
Wu G, Lu ZH, Kulkarni N, Ledeen RW (2012) Deficiency of ganglioside GM1 correlates with Parkinson's disease in mice and humans. J Neurosci Res 90(10):1997–2008
Perissinotto F, Rondelli V, Parisse P, Tormena N, Zunino A, Almasy L, Merkel DG, Bottyan L et al (2019) GM1 Ganglioside role in the interaction of alpha-synuclein with lipid membranes: Morphology and structure. Biophys Chem 255:106272
Schneider JS (2018) Altered expression of genes involved in ganglioside biosynthesis in substantia nigra neurons in Parkinson’s disease. PLoS One 13(6):e0199189
Seyfried TN, Choi H, Chevalier A, Hogan D, Akgoc Z, Schneider JS (2018) Sex-related abnormalities in substantia nigra lipids in Parkinson’s disease. ASN Neuro 10:1759091418781889
Ma L, Song J, Sun X, Ding W, Fan K, Qi M, Xu Y, Zhang W (2019) Role of microtubule-associated protein 6 glycosylated with gal-(beta-1,3)-GalNAc in Parkinson’s disease. Aging (Albany NY) 11(13):4597–4610
Hoshi K, Matsumoto Y, Ito H, Saito K, Honda T, Yamaguchi Y, Hashimoto Y (2017) A unique glycan-isoform of transferrin in cerebrospinal fluid: A potential diagnostic marker for neurological diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj 1861(10):2473–2478
Varadi C, Nehez K, Hornyak O, Viskolcz B, Bones J (2019) Serum N-Glycosylation in Parkinson’s disease: a novel approach for potential alterations. Molecules 24(12):E2220
Russell AC, Simurina M, Garcia MT, Novokmet M, Wang Y, Rudan I, Campbell H, Lauc G et al (2017) The N-glycosylation of immunoglobulin G as a novel biomarker of Parkinson’s disease. Glycobiology 27(5):501–510
Birol M, Wojcik SP, Miranker AD, Rhoades E (2019) Identification of N-linked glycans as specific mediators of neuronal uptake of acetylated alpha-synuclein. PLoS Biol 17(6):e3000318
Kulathingal J, Ko LW, Cusack B, Yen SH (2009) Proteomic profiling of phosphoproteins and glycoproteins responsive to wild-type alpha-synuclein accumulation and aggregation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1794(2):211–224
Afonso-Oramas D, Cruz-Muros I, Alvarez dela Rosa D, Abreu P, Giraldez T, Castro-Hernandez J, Salas-Hernandez J, Lanciego JL et al (2009) Dopamine transporter glycosylation correlates with the vulnerability of midbrain dopaminergic cells in Parkinson's disease. Neurobiol Dis 36(3):494–508
Walimbe T, Panitch A (2019) Proteoglycans in biomedicine: resurgence of an underexploited class of ECM molecules. Front Pharmacol 10:1661
Liu IH, Uversky VN, Munishkina LA, Fink AL, Halfter W, Cole GJ (2005) Agrin binds alpha-synuclein and modulates alpha-synuclein fibrillation. Glycobiology 15(12):1320–1331
Lehri-Boufala S, Ouidja MO, Barbier-Chassefiere V, Henault E, Raisman-Vozari R, Garrigue-Antar L, Papy-Garcia D, Morin C (2015) New roles of glycosaminoglycans in alpha-synuclein aggregation in a cellular model of Parkinson disease. PLoS One 10(1):e0116641
Mehra S, Ghosh D, Kumar R, Mondal M, Gadhe LG, Das S, Anoop A, Jha NN et al (2018) Glycosaminoglycans have variable effects on alpha-synuclein aggregation and differentially affect the activities of the resulting amyloid fibrils. J Biol Chem 293(34):12975–12991
Raghunathan R, Polinski NK, Klein JA, Hogan JD, Shao C, Khatri K, Leon D, McComb ME et al (2018) Glycomic and proteomic changes in aging brain Nigrostriatal pathway. Mol Cell Proteomics 17(9):1778–1787
Choudhary S, Save SN, Vavilala SL (2018) Unravelling the inhibitory activity of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii sulfated polysaccharides against alpha-Synuclein fibrillation. Sci Rep 8(1):5692
Panigrahi GP, Rane AR, Vavilala SL, Choudhary S (2019) Deciphering the anti-Parkinson’s activity of sulphated polysaccharides from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii on the alpha-Synuclein mutants A30P, A53T, E46K, E57K and E35K. J Biochem 166(6):463–474
Yang X, Qian K (2017) Protein O-GlcNAcylation: emerging mechanisms and functions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 18(7):452–465
Wani WY, Ouyang X, Benavides GA, Redmann M, Cofield SS, Shacka JJ, Chatham JC, Darley-Usmar V et al (2017) O-GlcNAc regulation of autophagy and alpha-synuclein homeostasis; implications for Parkinson’s disease. Mol Brain 10(1):32
Levine PM, Galesic A, Balana AT, Mahul-Mellier AL, Navarro MX, De Leon CA, Lashuel HA, Pratt MR (2019) Alpha-Synuclein O-GlcNAcylation alters aggregation and toxicity, revealing certain residues as potential inhibitors of Parkinson's disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 116(5):1511–1519
Sidransky E, Nalls MA, Aasly JO, Aharon-Peretz J, Annesi G, Barbosa ER, Bar-Shira A, Berg D et al (2009) Multicenter analysis of glucocerebrosidase mutations in Parkinson’s disease. N Engl J Med 361(17):1651–1661
Wong YC, Krainc D (2016) Lysosomal trafficking defects link Parkinson’s disease with Gaucher’s disease. Mov Disord 31(11):1610–1618
Riboldi GM, Di Fonzo AB (2019) GBA, Gaucher Disease, and Parkinson’s disease: from genetic to clinic to new therapeutic approaches. Cells 8(4):E364
Mullin S, Hughes D, Mehta A, Schapira AHV (2019) Neurological effects of glucocerebrosidase gene mutations. Eur J Neurol 26(3):388–e29
Platt FM, d'Azzo A, Davidson BL, Neufeld EF, Tifft CJ (2018) Lysosomal storage diseases. Nat Rev Dis Primers 4(1):27
Gegg ME, Schapira AHV (2018) The role of glucocerebrosidase in Parkinson disease pathogenesis. FEBS J 285(19):3591–3603
Papadopoulos VE, Nikolopoulou G, Antoniadou I, Karachaliou A, Arianoglou G, Emmanouilidou E, Sardi SP, Stefanis L et al (2018) Modulation of beta-glucocerebrosidase increases alpha-synuclein secretion and exosome release in mouse models of Parkinson’s disease. Hum Mol Genet 27(10):1696–1710
Lin G, Wang L, Marcogliese PC, Bellen HJ (2019) Sphingolipids in the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease and parkinsonism. Trends Endocrinol Metab 30(2):106–117
Indellicato R, Trinchera M (2019) The link between Gaucher disease and Parkinson’sdDisease sheds light on old and novel disorders of sphingolipid metabolism. Int J Mol Sci 20(13):E3304
Pchelina S, Baydakova G, Nikolaev M, Senkevich K, Emelyanov A, Kopytova A, Miliukhina I, Yakimovskii A et al (2018) Blood lysosphingolipids accumulation in patients with Parkinson’s disease with glucocerebrosidase 1 mutations. Mov Disord 33(8):1325–1330
Li H, Ham A, Ma TC, Kuo SH, Kanter E, Kim D, Ko HS, Quan Y et al (2019) Mitochondrial dysfunction and mitophagy defect triggered by heterozygous GBA mutations. Autophagy 15(1):113–130
Wilke M, Dornelles AD, Schuh AS, Vairo FP, Basgalupp SP, Siebert M, Nalin T, Piltcher OB et al (2019) Evaluation of the frequency of non-motor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease in adult patients with Gaucher disease type 1. Orphanet J Rare Dis 14(1):103
Avenali M, Toffoli M, Mullin S, McNeil A, Hughes DA, Mehta A, Blandini F, Schapira AHV (2019) Evolution of prodromal parkinsonian features in a cohort of GBA mutation-positive individuals: a 6-year longitudinal study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 90(10):1091–1097
Huebecker M, Moloney EB, van der Spoel AC, Priestman DA, Isacson O, Hallett PJ, Platt FM (2019) Reduced sphingolipid hydrolase activities, substrate accumulation and ganglioside decline in Parkinson’s disease. Mol Neurodegener 14(1):40
Blandini F, Cilia R, Cerri S, Pezzoli G, Schapira AHV, Mullin S, Lanciego JL (2019) Glucocerebrosidase mutations and synucleinopathies: toward a model of precision medicine. Mov Disord 34(1):9–21
Paciotti S, Gatticchi L, Beccari T, Parnetti L (2019) Lysosomal enzyme activities as possible CSF biomarkers of synucleinopathies. Clin Chim Acta 495:13–24
Moren C, Juarez-Flores DL, Chau KY, Gegg M, Garrabou G, Gonzalez-Casacuberta I, Guitart-Mampel M, Tolosa E et al (2019) GBA mutation promotes early mitochondrial dysfunction in 3D neurosphere models. Aging (Albany NY) 11(22):10338–10355
Romero R, Ramanathan A, Yuen T, Bhowmik D, Mathew M, Munshi LB, Javaid S, Bloch M et al (2019) Mechanism of glucocerebrosidase activation and dysfunction in Gaucher disease unraveled by molecular dynamics and deep learning. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 116(11):5086–5095
Lerche S, Wurster I, Roeben B, Zimmermann M, Riebenbauer B, Deuschle C, Hauser AK, Schulte C et al (2019) Parkinson’s disease: Glucocerebrosidase 1 mutation severity is associated with CSF alpha-synuclein profiles. Mov Disord 35(3):495–499
Hertz E, Thornqvist M, Holmberg B, Machaczka M, Sidransky E, Svenningsson P (2019) First Clinicogenetic description of Parkinson’s disease related to GBA mutation S107L. Mov Disord Clin Pract 6(3):254–258
Velez-Pardo C, Lorenzo-Betancor O, Jimenez-Del-Rio M, Moreno S, Lopera F, Cornejo-Olivas M, Torres L, Inca-Martinez M et al (2019) The distribution and risk effect of GBA variants in a large cohort of PD patients from Colombia and Peru. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 63:204–208
Mahungu AC, Anderson DG, Rossouw AC, van Coller R, Carr JA, Ross OA, Bardien S (2019) Screening of the glucocerebrosidase (GBA) gene in south Africans of African ancestry with Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Aging
Ji S, Wang C, Qiao H, Gu Z, Gan-Or Z, Fon EA, Chan P (2020) Decreased penetrance of Parkinson’s disease in elderly carriers of Glucocerebrosidase gene L444P/R mutations: a community-based 10-year longitudinal study. Mov Disord 35:672–678
Lin CH, Chen PL, Tai CH, Lin HI, Chen CS, Chen ML, Wu RM (2019) A clinical and genetic study of early-onset and familial parkinsonism in Taiwan: an integrated approach combining gene dosage analysis and next-generation sequencing. Mov Disord 34(4):506–515
Simuni T, Brumm MC, Uribe L, Caspell-Garcia C, Coffey CS, Siderowf A, Alcalay RN, Trojanowski JQ et al (2020) Clinical and dopamine transporter imaging characteristics of leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) and glucosylceramidase beta (GBA) Parkinson’s disease participants in the Parkinson’s progression markers initiative: a dross-sectional study. Mov Disord. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.27989
Goldstein O, Gana-Weisz M, Cohen-Avinoam D, Shiner T, Thaler A, Cedarbaum JM, John S, Lalioti M et al (2019) Revisiting the non-Gaucher-GBA-E326K carrier state: Is it sufficient to increase Parkinson’s disease risk? Mol Genet Metab 128(4):470–475
Hsieh PC, Wang CC, Tsai CL, Yeh YM, Lee YS, Wu YR (2019) POLG R964C and GBA L444P mutations in familial Parkinson’s disease: case report and literature review. Brain Behav 9(5):e01281
Sanyal A, DeAndrade MP, Novis HS, Lin S, Chang J, Lengacher N, Tomlinson JJ, Tansey MG et al (2020) Lysosome and inflammatory defects in GBA1-mutant astrocytes are normalized by LRRK2 inhibition. Mov Disord. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.27994
Gustavsson N, Marote A, Pomeshchik Y, Russ K, Azevedo C, Chumarina M, Goldwurm S, Collin A et al (2019) Generation of an induced pluripotent stem cell line (CSC-46) from a patient with Parkinson’s disease carrying a novel p.R301C mutation in the GBA gene. Stem Cell Res 34:101373
Rodriguez-Traver E, Rodriguez C, Diaz-Guerra E, Arenas F, Arauzo-Bravo M, Orera M, Kulisevsky J, Moratalla R et al (2019) Generation of an integration-free iPSC line, ICCSICi005-a, derived from a Parkinson’s disease patient carrying the L444P mutation in the GBA1 gene. Stem Cell Res 40:101578
Baden P, Yu C, Deleidi M (2019) Insights into GBA Parkinson’s disease pathology and therapy with induced pluripotent stem cell model systems. Neurobiol Dis 127:1–12
Chung SJ, Jeon S, Yoo HS, Kim G, Oh JS, Kim JS, Evans AC, Sohn YH et al (2019) Detrimental effect of type 2 diabetes mellitus in a large case series of Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 64:54–59
Marques A, Dutheil F, Durand E, Rieu I, Mulliez A, Fantini ML, Boirie Y, Durif F (2018) Glucose dysregulation in Parkinson’s disease: too much glucose or not enough insulin? Parkinsonism Relat Disord 55:122–127
Konig A, Vicente Miranda H, Outeiro TF (2018) Alpha-synuclein glycation and the action of anti-diabetic agents in Parkinson’s disease. J Park Dis 8(1):33–43
Castellani R, Smith MA, Richey PL, Perry G (1996) Glycoxidation and oxidative stress in Parkinson disease and diffuse Lewy body disease. Brain Res 737(1–2):195–200
Guerrero E, Vasudevaraju P, Hegde ML, Britton GB, Rao KS (2013) Recent advances in alpha-synuclein functions, advanced glycation, and toxicity: implications for Parkinson’s disease. Mol Neurobiol 47(2):525–536
Trezzi JP, Galozzi S, Jaeger C, Barkovits K, Brockmann K, Maetzler W, Berg D, Marcus K et al (2017) Distinct metabolomic signature in cerebrospinal fluid in early Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 32(10):1401–1408
Biosa A, Sandrelli F, Beltramini M, Greggio E, Bubacco L, Bisaglia M (2017) Recent findings on the physiological function of DJ-1: beyond Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Dis 108:65–72
Sharma N, Rao SP, Kalivendi SV (2019) The deglycase activity of DJ-1 mitigates alpha-synuclein glycation and aggregation in dopaminergic cells: Role of oxidative stress mediated downregulation of DJ-1 in Parkinson’s disease. Free Radic Biol Med 135:28–37
Lee HJ, Yoon YS, Lee SJ (2018) Mechanism of neuroprotection by trehalose: controversy surrounding autophagy induction. Cell Death Dis 9(7):712
Hoffmann AC, Minakaki G, Menges S, Salvi R, Savitskiy S, Kazman A, Vicente Miranda H, Mielenz D et al (2019) Extracellular aggregated alpha synuclein primarily triggers lysosomal dysfunction in neural cells prevented by trehalose. Sci Rep 9(1):544
Varki A, Cummings RD, Aebi M, Packer NH, Seeberger PH, Esko JD, Stanley P, Hart G et al (2015) Symbol nomenclature for graphical representations of glycans. Glycobiology 25(12):1323–1324
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by “Aldo Ravelli” Center for Neurotechnology and Experimental Brain Therapeutics (to AM, PS, AC, RG, MT) and from the University of Insubria (to MT). AZ was supported by Fondazione Veronesi, Milan Italy. AM is a fellowship of “Aldo Ravelli” Center for Neurotechnology and Experimental Brain Therapeutics.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AZ and AM conducted the literature search, AC made the tables and figure, MT wrote the manuscript and supervised the project, and PS, AC, and RG critically revised the manuscript. All authors have seen and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
All authors have no disclosures.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zulueta, A., Mingione, A., Signorelli, P. et al. Simple and Complex Sugars in Parkinson’s Disease: a Bittersweet Taste. Mol Neurobiol 57, 2934–2943 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-020-01931-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-020-01931-4