Abstract
Objectives
To express a TAT-PBX1 fusion protein using a prokaryotic expression system and to explore potential effects of TAT-PBX1 in the proliferation and senescence of human hair follicle-derived mesenchymal stem cells.
Results
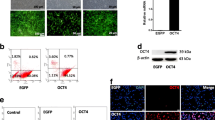
The TAT-PBX1 fusion was produced in inclusion bodies and heterogenously expressed in Rosetta (DE3) cells. Immunofluorescence staining showed that TAT-PBX1 fusion proteins were internalized by human hair follicle-derived mesenchymal stem cells. The growth rate of cells was increased after treatment with more than 5.0 μg/mL of TAT-PBX1. The rate of senescence-associated β-galactosidase positive cells was reduced in the 10.0 μg/mL TAT-PBX1 group (28%) than the 0 μg/mL control group (60%). Cells treated with the TAT-PBX1 fusion protein showed higher expression of p-AKT (1.22-fold that of the control), which indicates that TAT-PBX1 activated AKT pathway after cellular uptake.
Conclusions
The TAT-PBX1 fusion protein increased the proliferation of hair follicle mesenchymal stem cells and delayed their senescence by activating the AKT pathway following internalization by cells.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Athanasopoulos T, Munye MM, Yanez-Munoz RJ (2017) Nonintegrating gene therapy vectors. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am 31:753–770. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hoc.2017.06.007
Bai T et al (2017) Epidermal growth factor induces proliferation of hair follicle-derived mesenchymal stem cells through epidermal growth factor receptor-mediated activation of ERK and AKT signaling pathways associated with upregulation of cyclin D1 and downregulation of p16. Stem Cells Dev 26:113–122. https://doi.org/10.1089/scd.2016.0234
Chan KK et al (2009) KLF4 and PBX1 directly regulate NANOG expression in human embryonic stem cells. Stem cells (Dayton, Ohio) 27:2114–2125. https://doi.org/10.1002/stem.143
Han X, Liu D, Zhang Y, Li Y, Lu W, Chen J, Songyang Z (2013) Akt regulates TPP1 homodimerization and telomere protection. Aging Cell 12:1091–1099. https://doi.org/10.1111/acel.12137
He C, Ohnishi K (2017) Efficient renaturation of inclusion body proteins denatured by SDS. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 490:1250–1253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.07.003
Jiang Y et al (2019) PBX homeobox 1 enhances hair follicle mesenchymal stem cell proliferation and reprogramming through activation of the AKT/glycogen synthase kinase signaling pathway and suppression of apoptosis. Stem Cell Res Therapy 10:268. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-019-1382-y
Kadonosono T, Yamano A, Goto T, Tsubaki T, Niibori M, Kuchimaru T, Kizaka-Kondoh S (2015) Cell penetrating peptides improve tumor delivery of cargos through neuropilin-dependent extravasation. J Control Rel 201:14–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2015.01.011
Li C, Wang J (2013) Quantifying cell fate decisions for differentiation and reprogramming of a human stem cell network: landscape and biological paths. PLoS Comput Biol 9:e1003165–e1003165. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003165
Liu F et al (2019) NANOG attenuates hair follicle-derived mesenchymal stem cell senescence by upregulating PBX1 and activating AKT signaling. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2019:4286213. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/4286213
Lu Y et al (2019) OCT4 maintains self-renewal and reverses senescence in human hair follicle mesenchymal stem cells through the downregulation of p21 by DNA methyltransferases. Stem Cell Res Therapy 10:28. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-018-1120-x
Moens CB, Selleri L (2006) Hox cofactors in vertebrate development. Dev Biol 291:193–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2005.10.032
Nagahara H et al (1998) Transduction of full-length TAT fusion proteins into mammalian cells: TAT-p27Kip1 induces cell migration. Nat Med 4:1449–1452. https://doi.org/10.1038/4042
Patel SG et al (2019) Cell-penetrating peptide sequence and modification dependent uptake and subcellular distribution of green florescent protein in different cell lines. Sci Rep 9:6298. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-42456-8
Porowinska D, Wujak M, Roszek K, Komoszynski M (2013) [Prokaryotic expression systems] Postepy Higieny I Medycyny Doswiadczalnej (Online) 67:119–129
Singh SM, Panda AK (2005) Solubilization and refolding of bacterial inclusion body proteins. J Biosci Bioeng 99:303–310. https://doi.org/10.1263/jbb.99.303
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Jilin Province Science and Technology Development Plan [20190304044YY]; the Innovative special industry fund project in Jilin province [2018C049-2]; the Joint construction project between Jilin province and provincial colleges [SXGJQY2017-12]; and the China Natural National Science Foundation [81573067].
Supplementary information
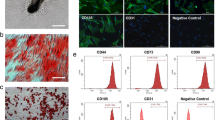
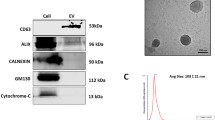
Supplementary Figure 1—Isolation and characterization of HF-MSCs.
Supplementary Figure 2—Reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction.
Supplementary Materials and Methods 1—Isolation and identification of hHF-MSCs.
Supplementary Materials and Methods 2—Promoter sequence of pNanog-Luc plasmid.
Supplementary Materials and Methods 3—Reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, B., Liu, F., Liu, Z. et al. Internalization of the TAT-PBX1 fusion protein significantly enhances the proliferation of human hair follicle-derived mesenchymal stem cells and delays their senescence. Biotechnol Lett 42, 1877–1885 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-020-02909-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-020-02909-x