Abstract
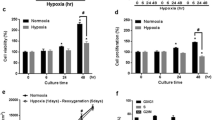
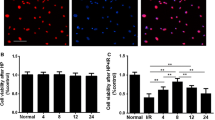
Activation of pro-inflammatory microglia is an important mechanism of the cerebral ischemia–reperfusion (I/R)-induced neuronal injury and dysfunction. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) together with their paracrine factors demonstrated curative potential in immune disorders and inflammatory diseases, as well as in ischemic diseases. However, it remains unclear whether conditioned medium from MSCs could effectively regulate the activation and polarization of microglia exposed to I/R stimulation. In this study, we investigated the effects of conditioned medium from bone marrow MSCs (BMSCs-CM) on I/R-stimulated microglia and the potential mechanism involved, as well as the way to obtain more effective BMSCs-CM. First, cell model of oxygen–glucose deprivation/reoxygenation (OGD/R) was established in microglia to mimic the I/R. BMSCs-CM from different culture conditions (normoxic: 21% O2; hypoxic: 1% O2; hypoxia preconditioning: preconditioning with 1% O2 for 24 h) was used to treat the microglia. Our results showed that BMSCs-CM effectively promoted the survival and alleviated the injury of microglia. Moreover, in microglia exposed to OGD/R, BMSCs-CM inhibited significantly the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6), CD86 and inducible nitric oxide synthase, whereas upregulated the levels of anti-inflammatory cytokine (IL-10), CD206 and Arginase-1. These results suggested that BMSCs-CM promoted the polarization of anti-inflammatory microglia. In particular, BMSCs-CM from cultures with hypoxia preconditioning was more effective in alleviating cell injury and promoting anti-inflammatory microglia polarization than BMSCs-CM from normoxic cultures and from hypoxic cultures. Furthermore, inhibition of exosomes secretion could largely mitigate these effects of BMSCs-CM. In conclusion, our results suggested that hypoxia preconditioning of BMSCs could enhance the efficacy of BMSCs-CM in alleviating OGD/R-induced injury and in promoting the anti-inflammatory polarization of microglia, and these beneficial effects of BMSCs-CM owed substantially to exosomes.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggarwal S, Pittenger MF (2005) Human mesenchymal stem cells modulate allogeneic immune cell responses. Blood 105(4):1815–1822. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2004-04-1559
Benjamin EJ, Muntner P, Alonso A, Bittencourt MS, Callaway CW, Carson AP, Chamberlain AM, Chang AR, Cheng S, Das SR, Delling FN, Djousse L, Elkind M, Ferguson JF, Fornage M, Jordan LC, Khan SS, Kissela BM, Knutson KL, Kwan TW, Lackland DT, Lewis TT, Lichtman JH, Longenecker CT, Loop MS, Lutsey PL, Martin SS, Matsushita K, Moran AE, Mussolino ME, O'Flaherty M, Pandey A, Perak AM, Rosamond WD, Roth GA, Sampson U, Satou GM, Schroeder EB, Shah SH, Spartano NL, Stokes A, Tirschwell DL, Tsao CW, Turakhia MP, VanWagner LB, Wilkins JT, Wong SS, Virani SS (2019) Heart disease and stroke statistics-2019 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 139(10):e56–e528. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000000659
Bernardo ME, Fibbe WE (2013) Mesenchymal stromal cells: sensors and switchers of inflammation. Cell Stem Cell 13(4):392–402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stem.2013.09.006
Chen J, Yang Y, Shen L, Ding W, Chen X, Wu E, Cai K, Wang G (2017) Hypoxic preconditioning augments the therapeutic efficacy of bone marrow stromal cells in a rat ischemic stroke model. Cell Mol Neurobiol 37(9):1115–1129. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-016-0445-1
Chu X, Cao L, Yu Z, Xin D, Li T, Ma W, Zhou X, Chen W, Liu D, Wang Z (2019) Hydrogen-rich saline promotes microglia M2 polarization and complement-mediated synapse loss to restore behavioral deficits following hypoxia-ischemic in neonatal mice via AMPK activation. J Neuroinflamm 16(1):104. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-019-1488-2
Crain JM, Nikodemova M, Watters JJ (2013) Microglia express distinct M1 and M2 phenotypic markers in the postnatal and adult central nervous system in male and female mice. J Neurosci Res 91(9):1143–1151. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.23242
Crotti A, Ransohoff RM (2016) Microglial physiology and pathophysiology: insights from genome-wide transcriptional profiling. Immunity 44(3):505–515. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2016.02.013
Cui C, Cui Y, Gao J, Li R, Jiang X, Tian Y, Wang K, Cui J (2017) Intraparenchymal treatment with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-conditioned medium exerts neuroprotection following intracerebral hemorrhage. Mol Med Rep 15(4):2374–2382. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2017.6223
Fahmy SR, Soliman AM, El AM, Elhamid SA, Mohsen H (2017) Therapeutic efficacy of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells transplantation against renal ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Tissue Cell 49(3):369–375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tice.2017.04.006
Fumagalli S, Perego C, Pischiutta F, Zanier ER, De Simoni MG (2015) The ischemic environment drives microglia and macrophage function. Front Neurol 6:81. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2015.00081
Garcia JM, Stillings SA, Leclerc JL, Phillips H, Edwards NJ, Robicsek SA, Hoh BL, Blackburn S, Dore S (2017) Role of interleukin-10 in acute brain injuries. Front Neurol 8:244. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2017.00244
Harrell CR, Fellabaum C, Jovicic N, Djonov V, Arsenijevic N, Volarevic V (2019) Molecular mechanisms responsible for therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cell-derived secretome. Cells 8:5. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8050467
Hladik D, H I, Oestreicher U, Beckers J, Matjanovski M, Bao X, Scherthan H, Atkinson MJ, Rosemann M (2019) Long-term culture of mesenchymal stem cells impairs ATM-dependent recognition of DNA breaks and increases genetic instability. Stem Cell Res Ther 10(1):218. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-019-1334-6
Holtman IR, Raj DD, Miller JA, Schaafsma W, Yin Z, Brouwer N, Wes PD, Moller T, Orre M, Kamphuis W, Hol EM, Boddeke EW, Eggen BJ (2015) Induction of a common microglia gene expression signature by aging and neurodegenerative conditions: a co-expression meta-analysis. Acta Neuropathol Commun 3:31. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40478-015-0203-5
Hu X, Leak RK, Shi Y, Suenaga J, Gao Y, Zheng P, Chen J (2015) Microglial and macrophage polarization—new prospects for brain repair. Nat Rev Neurol 11(1):56–64. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneurol.2014.207
Hu X, Li P, Guo Y, Wang H, Leak RK, Chen S, Gao Y, Chen J (2012) Microglia/macrophage polarization dynamics reveal novel mechanism of injury expansion after focal cerebral ischemia. Stroke 43(11):3063–3070. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.112.659656
Hummitzsch L, Zitta K, Berndt R, Wong YL, Rusch R, Hess K, Wedel T, Gruenewald M, Cremer J, Steinfath M, Albrecht M (2019) Remote ischemic preconditioning attenuates intestinal mucosal damage: insight from a rat model of ischemia–reperfusion injury. J Transl Med 17(1):136. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-019-1885-4
Jeong JO, Han JW, Kim JM, Cho HJ, Park C, Lee N, Kim DW, Yoon YS (2011) Malignant tumor formation after transplantation of short-term cultured bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in experimental myocardial infarction and diabetic neuropathy. Circ Res 108(11):1340–1347. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.110.239848
Jiang W, Xu J (2020) Immune modulation by mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Prolif 53(1):e12712. https://doi.org/10.1111/cpr.12712
Jin X, Yamashita T (2016) Microglia in central nervous system repair after injury. J Biochem 159(5):491–496. https://doi.org/10.1093/jb/mvw009
Jolivel V, Bicker F, Biname F, Ploen R, Keller S, Gollan R, Jurek B, Birkenstock J, Poisa-Beiro L, Bruttger J, Opitz V, Thal SC, Waisman A, Bauerle T, Schafer MK, Zipp F, Schmidt M (2015) Perivascular microglia promote blood vessel disintegration in the ischemic penumbra. Acta Neuropathol 129(2):279–295. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-014-1372-1
Jun EK, Zhang Q, Yoon BS, Moon JH, Lee G, Park G, Kang PJ, Lee JH, Kim A, You S (2014) Hypoxic conditioned medium from human amniotic fluid-derived mesenchymal stem cells accelerates skin wound healing through TGF-beta/SMAD2 and PI3K/Akt pathways. Int J Mol Sci 15(1):605–628. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms15010605
Li Q, Barres BA (2018) Microglia and macrophages in brain homeostasis and disease. Nat Rev Immunol 18(4):225–242. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri.2017.125
Li W, Ren G, Huang Y, Su J, Han Y, Li J, Chen X, Cao K, Chen Q, Shou P, Zhang L, Yuan ZR, Roberts AI, Shi S, Le AD, Shi Y (2012) Mesenchymal stem cells: a double-edged sword in regulating immune responses. Cell Death Differ 19(9):1505–1513. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2012.26
Li X, Xie X, Yu Z, Chen Y, Qu G, Yu H, Luo B, Lei Y, Li Y (2019) Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived conditioned medium protects cardiomyocytes from hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced injury through Notch2/mTOR/autophagy signaling. J Cell Physiol 234(10):18906–18916. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.28530
Liang QJ, Jiang M, Wang XH, Le LL, Xiang M, Sun N, Meng D, Chen SF (2015) Pre-existing interleukin 10 in cerebral arteries attenuates subsequent brain injury caused by ischemia/reperfusion. IUBMB Life 67(9):710–719. https://doi.org/10.1002/iub.1429
Liesz A, Bauer A, Hoheisel JD, Veltkamp R (2014) Intracerebral interleukin-10 injection modulates post-ischemic neuroinflammation: an experimental microarray study. Neurosci Lett 579:18–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2014.07.003
Lin QM, Tang XH, Lin SR, Chen BD, Chen F (2020) Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation attenuates overexpression of inflammatory mediators in rat brain after cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Neural Regen Res 15(2):324–331. https://doi.org/10.4103/1673-5374.265563
Liu L, Gao J, Yuan Y, Chang Q, Liao Y, Lu F (2013) Hypoxia preconditioned human adipose derived mesenchymal stem cells enhance angiogenic potential via secretion of increased VEGF and bFGF. Cell Biol Int 37(6):551–560. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbin.10097
Liu Z, Li Y, Zhang RL, Cui Y, Chopp M (2011) Bone marrow stromal cells promote skilled motor recovery and enhance contralesional axonal connections after ischemic stroke in adult mice. Stroke 42(3):740–744. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.110.607226
Long Q, Upadhya D, Hattiangady B, Kim DK, An SY, Shuai B, Prockop DJ, Shetty AK (2017) Intranasal MSC-derived A1-exosomes ease inflammation, and prevent abnormal neurogenesis and memory dysfunction after status epilepticus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 114(17):E3536–E3545. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1703920114
Ma Y, Wang J, Wang Y, Yang GY (2017) The biphasic function of microglia in ischemic stroke. Prog Neurobiol 157:247–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2016.01.005
Masuda T, Croom D, Hida H, Kirov SA (2011) Capillary blood flow around microglial somata determines dynamics of microglial processes in ischemic conditions. Glia 59(11):1744–1753. https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.21220
McDonough A, Noor S, Lee RV, Dodge RR, Strosnider JS, Shen J, Davidson S, Moller T, Garden GA, Weinstein JR (2020) Ischemic preconditioning induces cortical microglial proliferation and a transcriptomic program of robust cell cycle activation. Glia 68(1):76–94. https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.23701
Perego C, Fumagalli S, De Simoni MG (2011) Temporal pattern of expression and colocalization of microglia/macrophage phenotype markers following brain ischemic injury in mice. J Neuroinflamm 8:174. https://doi.org/10.1186/1742-2094-8-174
Petrovic-Djergovic D, Goonewardena SN, Pinsky DJ (2016) Inflammatory disequilibrium in stroke. Circ Res 119(1):142–158. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.308022
Poh L, Kang SW, Baik SH, Ng G, She DT, Balaganapathy P, Dheen ST, Magnus T, Gelderblom M, Sobey CG, Koo EH, Fann DY, Arumugam TV (2019) Evidence that NLRC4 inflammasome mediates apoptotic and pyroptotic microglial death following ischemic stroke. Brain Behav Immun 75:34–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2018.09.001
Qin C, Zhou LQ, Ma XT, Hu ZW, Yang S, Chen M, Bosco DB, Wu LJ, Tian DS (2019) Dual functions of microglia in ischemic stroke. Neurosci Bull 35(5):921–933. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-019-00388-3
Ransohoff RM (2016) A polarizing question: do M1 and M2 microglia exist? Nat Neurosci 19(8):987–991. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.4338
Sisa C, Kholia S, Naylor J, Herrera SM, Bruno S, Deregibus MC, Camussi G, Inal JM, Lange S, Hristova M (2019) Mesenchymal stromal cell derived extracellular vesicles reduce hypoxia-ischaemia induced perinatal brain injury. Front Physiol 10:282. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2019.00282
Tian X, Liu H, Xiang F, Xu L, Dong Z (2019) Beta-caryophyllene protects against ischemic stroke by promoting polarization of microglia toward M2 phenotype via the TLR4 pathway. Life Sci 237:116915. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2019.116915
Wang C, Wang Q, Lou Y, Xu J, Feng Z, Chen Y, Tang Q, Zheng G, Zhang Z, Wu Y, Tian N, Zhou Y, Xu H, Zhang X (2018) Salidroside attenuates neuroinflammation and improves functional recovery after spinal cord injury through microglia polarization regulation. J Cell Mol Med 22(2):1148–1166. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.13368
Weinstein JR, Koerner IP, Moller T (2010) Microglia in ischemic brain injury. Future Neurol 5(2):227–246. https://doi.org/10.2217/fnl.10.1
Wu LJ, Wu G, Akhavan SM, Baker A, Jia Y, Fahey FH, Luo HR, Feener EP, Clapham DE (2012) The voltage-gated proton channel Hv1 enhances brain damage from ischemic stroke. Nat Neurosci 15(4):565–573. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.3059
Xiao C, Wang K, Xu Y, Hu H, Zhang N, Wang Y, Zhong Z, Zhao J, Li Q, Zhu D, Ke C, Zhong S, Wu X, Yu H, Zhu W, Chen J, Zhang J, Wang J, Hu X (2018) Transplanted mesenchymal stem cells reduce autophagic flux in infarcted hearts via the exosomal transfer of miR-125b. Circ Res 123:564–578. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.118.312758
Xie Y, Jiang D, Xiao J, Fu C, Zhang Z, Ye Z, Zhang X (2018) Ischemic preconditioning attenuates ischemia/reperfusion-induced kidney injury by activating autophagy via the SGK1 signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis 9(3):338. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-018-0358-7
Xin H, Li Y, Cui Y, Yang JJ, Zhang ZG, Chopp M (2013) Systemic administration of exosomes released from mesenchymal stromal cells promote functional recovery and neurovascular plasticity after stroke in rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 33(11):1711–1715. https://doi.org/10.1038/jcbfm.2013.152
Xu W, Xu R, Li Z, Wang Y, Hu R (2019) Hypoxia changes chemotaxis behaviour of mesenchymal stem cells via HIF-1alpha signalling. J Cell Mol Med 23(3):1899–1907. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.14091
Yang J, Liu C, Du X, Liu M, Ji X, Du H, Zhao H (2018) Hypoxia inducible factor 1alpha plays a key role in remote ischemic preconditioning against stroke by modulating inflammatory responses in rats. J Am Heart Assoc. https://doi.org/10.1161/JAHA.117.007589
Zanier ER, Pischiutta F, Riganti L, Marchesi F, Turola E, Fumagalli S, Perego C, Parotto E, Vinci P, Veglianese P, D'Amico G, Verderio C, De Simoni MG (2014) Bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells drive protective M2 microglia polarization after brain trauma. Neurotherapeutics 11(3):679–695. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13311-014-0277-y
Zhang CS, Shao K, Liu CW, Li CJ, Yu BT (2019a) Hypoxic preconditioning BMSCs-exosomes inhibit cardiomyocyte apoptosis after acute myocardial infarction by upregulating microRNA-24. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 23(15):6691–6699. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201908_18560
Zhang Y, Ma L, Su Y, Su L, Lan X, Wu D, Han S, Li J, Kvederis L, Corey S, Borlongan CV, Ji X (2019b) Hypoxia conditioning enhances neuroprotective effects of aged human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived conditioned medium against cerebral ischemia in vitro. Brain Res 1725:146432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2019.146432
Zhang ZG, Buller B, Chopp M (2019c) Exosomes—beyond stem cells for restorative therapy in stroke and neurological injury. Nat Rev Neurol 15(4):193–203. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41582-018-0126-4
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81771707), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of China (Grant No. 2042018kf0235). The funders had no role in the study design, the data collection and analysis or the decision to publish.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YL and HY performed interpretation and drafted the manuscript. YL, YC, XH, YL and HY contributed to designing experiments and revising the manuscript. HY and ZX performed most of the experiments and data analysis. GQ performed the experiments of BV2 microglia culture and CCK-8 test. LL and HW performed culture and characterization of BMSCs. XL and XX performed the LDH and ROS analysis. YL and YL provided the experimental reagents and materials. All authors have read the manuscript and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethics Approval
All experimental animal procedures were approved by the Ethics Committee on Animal Care and Use of Wuhan University, Wuhan, China (Permit Number 20170303).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, H., Xu, Z., Qu, G. et al. Hypoxic Preconditioning Enhances the Efficacy of Mesenchymal Stem Cells-Derived Conditioned Medium in Switching Microglia toward Anti-inflammatory Polarization in Ischemia/Reperfusion. Cell Mol Neurobiol 41, 505–524 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-020-00868-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-020-00868-5