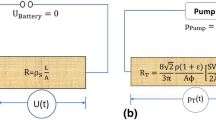
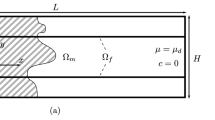
Abstract
We investigate viscous fluid flows and concurrent fluid-driven deformations in porous media. The hydro-mechanically (H-M) coupled pore-network model (PNM) is developed, which combines the two-dimensional square-lattice PNM and block-spring model. The single-/two-phase flows into saturated deformable porous media are simulated through iterative two-way coupling method in H-M coupled PNM. A comparison between simulations and laboratory observations on flow patterns, solid deformation behaviors, and pressure responses ensures the validity of our H-M coupled PNM in both single-/two-phase flows. Parametric studies using the validated model examine the effects of mechanical coupling, stiffness of solid particles, the viscosity of invading fluids, injection flow rate, and degree of disorder during immiscible viscous fluid injection. The viscous fluid-driven deformation increases the pore throat size and hence reduces the injection pressure. In particular, the viscosity of invading fluid significantly alters the patterns of fluid propagation and solid deformation, along with a transition from the viscous fingering to the stable displacement with increasing viscosity. Moreover, the structural disorder in porous networks magnifies the irregular flow pattern, the pressure fluctuation associated with Haines jumps, and the poromechanical deformation. The particle-level force analysis delineates two distinct regimes: fluid invasion with no deformation and drag-driven deformation, which depends on the balance between the seepage drag force and the skeletal force. The presented results contribute to a better understanding of the H-M coupled fluid flows during the injection of viscous fluids into disordered-deformable porous media.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aker, E., JØrgen MÅlØy, K., Hansen, A., Batrouni, G.G.: A two-dimensional network simulator for two-phase flow in porous media. Transp. Porous Media 32(2), 163–186 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1006510106194
Atrazhev, V.V., Astakhova, T.Y., Dmitriev, D.V., Erikhman, N.S., Sultanov, V.I., Patterson, T., Burlatsky, S.F.: The model of stress distribution in polymer electrolyte membrane. J. Electrochem. Soc. 160(10), F1129–F1137 (2013)
Badillo, G.M., Segura, L.A., Laurindo, J.B.: Theoretical and experimental aspects of vacuum impregnation of porous media using transparent etched networks. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 37(9), 1219–1226 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmultiphaseflow.2011.06.002
Blunt, M.J.: Flow in porous media—pore-network models and multiphase flow. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 6(3), 197–207 (2001)
Budday, S., Nay, R., de Rooij, R., Steinmann, P., Wyrobek, T., Ovaert, T.C., Kuhl, E.: Mechanical properties of gray and white matter brain tissue by indentation. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 46, 318–330 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmbbm.2015.02.024
Chang, C., Kneafsey, T.J., Zhou, Q., Oostrom, M., Ju, Y.: Scaling the impacts of pore-scale characteristics on unstable supercritical CO2-water drainage using a complete capillary number. Int. J. Greenhouse Gas Control 86, 11–21 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijggc.2019.04.010
Cui, G., Liu, M., Dai, W., Gan, Y.: Pore-scale modelling of gravity-driven drainage in disordered porous media. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 114, 19–27 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmultiphaseflow.2019.02.001
Fatt, I.: The network model of porous media. (1956)
Franceschini, G., Bigoni, D., Regitnig, P., Holzapfel, G.A.: Brain tissue deforms similarly to filled elastomers and follows consolidation theory. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 54(12), 2592–2620 (2006)
Haines, W.B.: Studies in the physical properties of soil. V. The hysteresis effect in capillary properties, and the modes of moisture distribution associated therewith. J. Agric. Sci. 20(1), 97–116 (1930). https://doi.org/10.1017/s002185960008864x
Han, G., Kwon, T.-H., Lee, J.Y., Jung, J.: Fines migration and pore clogging induced by single- and two-phase fluid flows in porous media: from the perspectives of particle detachment and particle-level forces. Geomech. Energy Environ. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gete.2019.100131
Holtzman, R., Juanes, R.: Crossover from fingering to fracturing in deformable disordered media. Phys. Rev. E 82(4), 046305 (2010)
Holtzman, R., Juanes, R.: Thermodynamic and hydrodynamic constraints on overpressure caused by hydrate dissociation: a pore-scale model. Res. Lett., Geophys (2011). https://doi.org/10.1029/2011gl047937
Hosseini Zadeh, A., Jeon, M.K., Kwon, T.H., Kim, S.: Study of poroelastic deformation in soft elastic granular materials during repetitive fluid injection. In: Paper presented at the 53rd U.S. Rock Mechanics/Geomechanics Symposium, New York City, New York (2019)
Johnson, K.L.: Contact Mechanics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1987)
Kharaghani, A., Metzger, T., Tsotsas, E.: A proposal for discrete modeling of mechanical effects during drying, combining pore networks with DEM. AIChE J. 57(4), 872–885 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1002/aic.12318
Lee, D., Ryu, S.: A Validation study of the repeatability and accuracy of atomic force microscopy indentation using polyacrylamide gels and colloidal probes. J. Biomech. Eng. doi 10(1115/1), 4035536 (2017)
Lenormand, R., Touboul, E., Zarcone, C.: Numerical models and experiments on immiscible displacements in porous media. J. Fluid Mech. 189, 165–187 (1988)
Lindquist, W.B., Venkatarangan, A.: Investigating 3D geometry of porous media from high resolution images. Phys. Chem. Earth Part A. 24(7), 593–599 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1464-1895(99)00085-X
MacMinn, C.W., Dufresne, E.R., Wettlaufer, J.S.: Fluid-driven deformation of a soft granular material. Phys. Rev. X 5(1), 011020 (2015)
Mahabadi, N., Jang, J.: The impact of fluid flow on force chains in granular media. Appl. Phys. Lett. 110(4), 041907 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4975065
Maier, R., Laidlaw, W.G.: Fluid percolation in bond-site size-correlated three-dimensional networks. Transp. Porous Media 5(4), 421–428 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01141994
Massonnet, D., Holzer, T., Vadon, H.: Land subsidence caused by the East Mesa Geothermal Field, California, observed using SAR interferometry. Geophys. Res. Lett. 24(8), 901–904 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1029/97gl00817
Pan, P., Wu, Z., Feng, X., Yan, F.: Geomechanical modeling of CO2 geological storage: a review. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 8(6), 936–947 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2016.10.002
Pandey, S.N., Chaudhuri, A., Kelkar, S.: A coupled thermo-hydro-mechanical modeling of fracture aperture alteration and reservoir deformation during heat extraction from a geothermal reservoir. Geothermics 65, 17–31 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geothermics.2016.08.006
Reeves, P.C., Celia, M.A.: A functional relationship between capillary pressure, saturation, and interfacial area as revealed by a pore-scale network model. Water Resour. Res. 32(8), 2345–2358 (1996)
Shin, H., Santamarina, J.C.: Desiccation cracks in saturated fine-grained soils: particle-level phenomena and effective-stress analysis. Géotechnique 61(11), 961–972 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.8.P.012
Silin, D., Tomutsa, L., Benson, S.M., Patzek, T.W.: Microtomography and pore-scale modeling of two-phase fluid distribution. Transp. Porous Media 86(2), 495–515 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-010-9636-2
Silin, D.B., Jin, G., Patzek, T.W.: Robust determination of the pore space morphology in sedimentary rocks. In: Paper presented at the SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, Denver, Colorado (2003)
Simms, P., Yanful, E.: A pore-network model for hydromechanical coupling in unsaturated compacted clayey soils. Can. Geotech. J. 42(2), 499–514 (2005)
Stan, C.A., Tang, S.K.Y., Whitesides, G.M.: Independent control of drop size and velocity in microfluidic flow-focusing generators using variable temperature and flow rate. Anal. Chem. 81(6), 2399–2402 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1021/ac8026542
Streit, J.E., Hillis, R.R.: Estimating fault stability and sustainable fluid pressures for underground storage of CO2 in porous rock. Energy 29(9), 1445–1456 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2004.03.078
Støverud, K.H., Darcis, M., Helmig, R., Hassanizadeh, S.M.: Modeling concentration distribution and deformation during convection-enhanced drug delivery into brain tissue. Transp. Porous Media 92(1), 119–143 (2012)
Suh, H.S., Kang, D.H., Jang, J., Kim, K.Y., Yun, T.S.: Capillary pressure at irregularly shaped pore throats: implications for water retention characteristics. Adv. Water Resour. 110, 51–58 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2017.09.025
Vogel, H.-J., Tölke, J., Schulz, V.P., Krafczyk, M., Roth, K.: Comparison of a Lattice-Boltzmann model, a full-morphology model, and a pore network model for determining capillary pressure-saturation relationships. Vadose Zone J. 4(2), 380–388 (2005). https://doi.org/10.2136/vzj2004.0114
Wang, Z., Chauhan, K., Pereira, J.-M., Gan, Y.: Disorder characterization of porous media and its effect on fluid displacement. Phys. Rev. Fluids 4(3), 034305 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevFluids.4.034305
Zhang, C., Oostrom, M., Wietsma, T.W., Grate, J.W., Warner, M.G.: Influence of viscous and capillary forces on immiscible fluid displacement: pore-scale experimental study in a water-wet micromodel demonstrating viscous and capillary fingering. Energy Fuels 25(8), 3493–3505 (2011)
Zheng, X., Mahabadi, N., Yun, T.S., Jang, J.: Effect of capillary and viscous force on CO2 saturation and invasion pattern in the microfluidic chip. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 122(3), 1634–1647 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/2016jb013908
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank three anonymous reviewers for providing valuable comments and suggests, which was very helpful to improve this manuscript. This research was supported by the Basic Research Laboratory Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the MSIT (NRF-2018R1A4A1025765) and by Korea Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport (MOLIT) as “Innovative Talent Education Program for Smart City.”
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jeon, MK., Kim, S., Hosseini Zadeh, A. et al. Study on Viscous Fluid Flow in Disordered-Deformable Porous Media Using Hydro-mechanically Coupled Pore-Network Modeling. Transp Porous Med 133, 207–227 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-020-01419-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-020-01419-8