Abstract
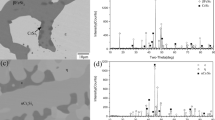
In this work, 700 and 850 °C isothermal sections of the Fe-Cr-Sn ternary system were experimentally determined by means of optical microscopy, scanning electron microscopy combined with energy dispersive spectrometry, and X-ray diffraction. At 700 °C, the existence of four binary compounds, FeSn, FeSn2, Fe3Sn2, and σ-FeCr were confirmed. Four three-phase regions were identified in the isothermal section of this system at 700 °C, and the maximum solubility of Cr in FeSn and Fe3Sn2 at 700 °C is 10.7 and 15.6 at%, respectively. At 850 °C, the existence of binary compound Fe5Sn3 phase was confirmed, and a three-phase equilibria of Fe5Sn3, α-(Fe,Cr), and liquid was determined. The maximum solubility of Cr in Fe5Sn3 at 850 °C is 5.8 at%.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Vercammen, B. Blanpain, B.C.D. Cooman, and P. Wollants, Cold Rolling Behaviour of an Austenitic Fe-30Mn-3Al-3Si TWIP-Steel: The Importance of Deformation Twinning, Acta Mater., 2003, 52(7), p 2005-2012. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2003.12.040
Y.F. Gong, H.S. Kim, S.K. Kim, and B.C.D. Cooman, Selective Oxidation and Sub-Surface Phase Transformation During Austenitic Annealing of TWIP Steels, Mater. Sci. Forum, 2010, 654–656, p 258-261. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.654-656.258
Y.F. Gong and B.C.D. Cooman, Selective Oxidation and Sub-surface Phase Transformation of TWIP Steel During Continuous Annealing, Steel Res. Int., 2011, 82, p 1310-1318. https://doi.org/10.1002/srin.201100122
Ş. Nevin Balo and F. Yakuphanoglu, The Effects of Cr on Isothermal Oxidation Behavior of Fe–30Mn–6Si Alloy, Thermochim. Acta, 2013, 560, p 43-46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tca.2013.03.005
H. Liu, F. Li, W. Shi, S. Swaminsthan, Y. He, M. Rohwerder, and L. Li, Challenges in Hot-Dip Galvanizing of High Strength Dual Phase Steel: Surface Selective Oxidation and Mechanical Property Degradation, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2012, 206, p 3428-3436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2012.02.001
L. Cho and B.C.D. Cooman, Selective Oxidation of TWIP Steel During Continuous Annealing, Mater. Charact., 2012, 83, p 391-397. https://doi.org/10.1002/srin.201100296
L. Cho, M.S. Kim, Y.H. Kim, and B.C.D. Cooman, Influence of Gas Atmosphere Dew Point on the Selective Oxidation and the Reactive Wetting During Hot Dip Galvanizing of CMnSi TRIP Steel, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2013, 44A, p 362-371. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-012-1392-1
L. Cho, M.S. Kim, Y.H. Kim, and B.C.D. Cooman, Influence of Minor Alloying Elements on Selective Oxidation and Reactive Wetting of CMnSi TRIP Steel During Hot Dip Galvanizing, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2014, 45, p 4484-4498. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-014-2394-y
Y. Kim, J. Lee, K.S. Shin et al., Effect of Dew Point on the Formation of Surface Oxides of Twinning-Induced Plasticity Steel, Mater. Charact., 2014, 89, p 138-145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2014.01.012
Y. Kim, J. Lee, K.S. Shin, S.H. Jeon, K.G. Chin, and J. Lee, The Influence of the Dew Point on the Wettability of Twinning-Induced-Plasticity Steels by Liquid Zn–0.23-wt% Al, Corros. Sci., 2014, 8, p 364-371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2014.04.034
I. Cvijović, I. Arezanović, and M. Piegel, Influence of H2–N2, Mosphere Composition and Annealing Duration on the Selective Surface Oxidation of Low-Carbon Steels, Corros. Sci., 2005, 48, p 980-993. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2005.02.022
M. Pourmajidian and J.R. Mcdermid, On the Reactive Wetting of a Medium-Mn Advanced High-Strength Steel During Continuous Galvanizing, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2018, 357, p 418-426. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2018.10.028
B.F.O. Costa, G.L. Caër, S. Begin-Colin, P.J. Mendes, and N.A. Campos, Characterization of Mechanically Alloyed Fe–Cr–Sn Alloys, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 1999, 92–93, p 395-400. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0924-0136(99)00158-2
B.F.O. Costa, G.L. Caër, and N.A.D. Campos, On the Role of Tin Solubility in the Precipitation of the Sigma-Phase in Fe–Cr–Sn Alloys, Phys. Status Solidi A, 1997, 164, p 687-697. 10.1002/1521-396X(199712)164:2<687::AID-PSSA687>3.0.CO;2-S
B.F.O. Costa, G.L. Caër, and N.A.D. Campos, Study of Alpha–Sigma Phase Transformation in Mechanically Alloyed Fe–Cr–Sn Alloys, Phys. Status Solidi A, 2001, 183, p 235-250. 10.1002/1521-396X(200102)183:2<235::AID-PSSA235>3.0.CO;2-Z
E. Essuman, G.H. Meier, J. Żurek, M. Hänsel, and W.J. Quadakkers, The Effect of Water Vapor on Selective Oxidation of Fe–Cr Alloys, Oxid. Met., 2008, 69, p 143-162. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11085-007-9090-x
B.V.N. Rao and G. Thomas, Structure–Property Relations and the Design of Fe-4Cr-C Base Structural Steels for High Strength and Toughness, Metall. Trans. A, 1980, 11, p 441-457. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02654568
B.F.O. Costa, G.L. Caër, M.M. Amado, J.B. Sousa, and N.A. Campos, Magnetic Properties of Coarse-Grained and Nanocrystalline Fe–Cr–Sn Alloys, J. Alloys Compd., 2000, 308, p 0-55. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-8388(00)00914-2
D. Goll, R. Loeffler, and J. Herbst, Magnetic Properties of Hard Magnetic (Fe,Cr)3Sn2 Intermetallic Compound, Phys. Status Solidi (RRL), 2015, 9, p 603-606. https://doi.org/10.1002/pssr.201510243
H.D. Nüssler, O.V. Goldbeck, and P.J. Spencer, A Thermodynamic Assessment of the Iron-Tin System, Calphad, 1979, 3, p 19-26. https://doi.org/10.1016/0364-5916(79)90018-X
K.C.H. Kumar, P. Wollants, and L. Delaey, Thermodynamic Evaluation of Fe-Sn Phase Diagram, Calphad, 1996, 20, p 139-149. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0364-5916(96)00021-1
Y.C. Huang, W. Gierlotka, and S.W. Chen, Sn–Bi–Fe Thermodynamic Modeling and Sn–Bi/Fe Interfacial Reactions, Intermetallics, 2010, 18, p 984-991. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intermet.2010.01.026
J.O. Andersson and B. Sundman, Thermodynamic Properties of the CrFe System, Calphad, 1987, 11, p 83-92. https://doi.org/10.1016/0364-5916(87)90021-6
W. Xiong, M. Selleby, Q. Chen, J. Odqvist, and Y. Du, Phase Equilibria and Thermodynamic Properties in the Fe-Cr System, Crit. Rev. Solid State, 2010, 35, p 125-152. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408431003788472
J. Pérez and B. Sundman, Thermodynamic Assessment of the CR-SN Binary System, Calphad, 2001, 25, p 59-66
P. Lafaye, C. Toffolon-Masclet, J.C. Crivello, and J.M. Joubert, Thermodynamic Modelling of the Cr-Nb-Sn System, Calphad, 2017, 57, p 37-45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.calphad.2017.02.003
N. Bochvar, T. Dobatkina, O. Fabrichnaya, V. Ivanchenko, and D.M. Cupid, Aluminium-Chromium-Titanium. In Landolt-Boernstein New Series Ternary Alloy220 Systems: Phase diagrams, Crystallographic and Thermodynamic Data critically evaluated by MSIT, vol. 11. Belrin: Springer, 2009, p 72-108
A.M.V.D. Kraan and K.H.J. Buschow, The 57Fe Mössbauer Isomer Shift in Intermetallic Compounds of Iron, Physica B + C, 1986, 138, p 55-62. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-4363(86)90492-4
G.L. Caer, B. Malaman, G. Venturini, D. Fruchart, and B. Roques, A Mossbauer Study of FeSn2, J. Phys. F, 1985, 15, p 1813-1827. https://doi.org/10.1088/0305-4608/15/8/019
B. Malaman, B. Roques, A. Courtois, and J. Protas, Crystal Structure of the Fe3Sn2, Acta Crystallogr. B, 1976, 32, p 1348-1351
W.P. Allen and J.H. Perepezko, Solidification of Undercooled Sn-Sb Peritectic Alloys: Part I. Microstructural Evolution, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1991, 22, p 753-764. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02670298
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge financial support from the National Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 51671036, 51871030) and the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions. This work is also funded by the Education Department of Jiangsu Province (17KJA430001) and Qing Lan Project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Z., Liu, Y., Wu, C. et al. Experimental Investigation of the Phase Relationship of the Fe-Cr-Sn System. J. Phase Equilib. Diffus. 41, 234–242 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11669-020-00808-2
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11669-020-00808-2