Abstract
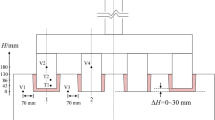
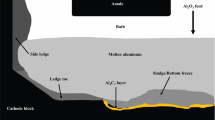
In China, a special anode design with a button in each stub hole is adopted by many smelters. To investigate the effects of the stub hole button on the anode, numerical simulations of the anode rodding process and the running process of the conventional anode without a stub hole button (design A) and the special design (design B) were conducted. In anode rodding, design B shows worse cooling capacity than design A, while the air gap of design B (0.39 mm to 0.94 mm) is larger than that of design A (0.3 mm to 0.45 mm). During the anode running process, the stub hole button could contact neither the cast iron nor the stub, and the anode voltage drop of design B is 26 mV larger than that of design A because the larger air gap deteriorates the cast iron–carbon contact. In conclusion, the stub hole button should be removed.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Molenaar, T. Kilpatrick, and A. Montalto, Light Metals (Warrendale: TMS, 2013), pp. 1359–1364.
A. Urrutia, J.D. Celentano, and R.D. Gunasegaram, Metals 7, 549 (2017).
D.R. Gunasegaram and D. Molenaar, Light Metals (Warrendale: TMS, 2014), pp. 1287–1292.
D. Richard, M. Fafard, R. Lacroix, P. Cléry, and Y. Maltais, Finite Elem. Anal. Des. 37, 287 (2001).
T. Li, W. Tao, Z. Wang, X. Liu, and J. Hou, Metals 8, 1026 (2018).
H. Chaouki, M. Baiteche, A. Jacques, E. Gosselin, H. Alamdari, and M. Fafard, Light Metals (Warrendale: TMS, 2017), pp. 1315–1323.
H. Li, X. Cao, and Y. Tian, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China (Chinese version) 22, 2960 (2012).
S. Wilkening and J. Côté, Light Metals (Warrendale: TMS, 2007), pp. 865–873.
S. Yang and W. Tao, Heat transfer, 4th ed. (Beijing: High Education Press, 2006), p. 438. (in Chinese).
B. Allard, S. Lacroix, J.-P. Noyel, and L. Rivoaland, Light Metals (Warrendale: TMS, 2009), pp. 1097–1102.
ANSYS Mechanical 17.2 User manual, ANSYS Inc.
Z. Lee, T. Kim, and Y. Choi, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 29, 1051 (1998).
O. Trempe, D. Larouche, D. Ziegler, M. Guillot, and M. Fafard, Light Metals (Warrendale: TMS, 2011), pp. 991–996.
T. Li, H. Chaouki, W. Tao, J. Hou, Z. Wang, M. Fafard, In Travaux No. 46, (Saint Colomban, QC, Canada: ICSOBA, 2017) pp. 803–814.
H. Fortin, N. Kandev, and M. Fafard, Finite Elem. Anal. Des. 52, 71 (2012).
H. Abbas, M. P. Taylor, M. Farid, J.JJ. Chen, in Light Metals 2009, (Warrendale, PA: TMS, 2009) pp. 551–556.
D.R. Gunasegaram and D. Molenaar, J. Cleaner Prod. 93, 174 (2015).
D. Richard, M.Sc. thesis, Laval University, Québec, QC, 2000.
N. Kandev and H. Fortin, Light Metals (Warrendale: TMS, 2011), pp. 1061–1066.
P. Goulet (2004) Modeling the thermo-electro-mechanical behavior of the contact interfaces of a Hall-Héroult cell. Ph.D. dissertation, Laval University, Quebec, Canada,
B. Zhang: Casting Handbook: Vol. 1 Cast Iron (in Chinese), 3rd ed. (Beijing: China Machine Press, 2013), pp. 15–60.
M.M.J. Behnam, P. Davami, and N. Varahram, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 528, 583 (2010).
S.K. Choudhary and A. Ghosh, ISIJ Int. 49, 1819 (2009).
H. Li, P. Tuo, S. Wang, J. Qian, X. Zhao, and J. Liu, Light Metals 4, 31 (2011).
D. Richard, P. Goulet, O. Trempe, M. Dupuis, and M. Fafard, Light Metals (Warrendale: TMS, 2009), pp. 1067–1072.
S. Beier, J.J.J. Chen, H. Fortin, and M. Fafard, Light Metals (Warrendale: TMS, 2011), pp. 979–984.
R. Friedrich, F. Hiltmann, A. Lützerath, R. Meier, M. Pfeffer, T. Reek, and O.V. Garcia, Light Metals (Warrendale: TMS, 2017), pp. 707–711.
Acknowledgements
The authors appreciate financial support provided by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51804071, 51434005, 51874086, 51804069, and 51529401) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Nos. N162502002, N2025024, N2025033).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, T., Tao, W., Chaouki, H. et al. Effects of Stub Hole Button on Anode of Aluminum Reduction Cell. JOM 72, 2426–2435 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-020-04162-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-020-04162-z