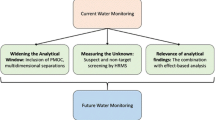
Abstract
Dissolved organic matter (DOM) especially anthropogenic compounds in sewage systems affects their ultimate fate in the environment which is challenging to ascertain the heterogenic nature of the compound and causes co-occurring effects in most aquatic samples. So, our study have focused on current approaches to the chemical and structural characterization of DOM with the detailed classification of individual compounds such as the molecular levels of volatile organic, inorganic materials, drugs and endocrine disrupting compounds. Analytical techniques for example high performance gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GCMS) with high-resolution liquid chromatography (HR-LCMS), X-ray diffraction (XRD) and three-dimensional fluorescence excitation emission matrix (3D-EEM) has resulted in advancing the parametric studies. In addition, the toxicological assessment of an aquatic organism (zebrafish as a model) has ensued in enlightening the risk of contaminated sources. The result of the research highlighted the efficacy of high-throughput approaches to assess the environmental impact of sewage water.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al Aukidy, M., Verlicchi, P., Jelic, A., Petrovic, M., & Barcelo, D. (2012). Monitoring release of pharmaceutical compounds: occurrence and environmental risk assessment of two WWTP effluents and their receiving bodies in the Po Valley, Italy. Science of the Total Environment, 438, 15–25.
Anbumani, S., & Mohankumar, M. N. (2012). Gamma radiation induced micronuclei and erythrocyte cellular abnormalities in the fish Catla catla. Aquatic Toxicology, 122, 125–132.
Anyakora, C., Ogbeche, A., Palmer, P., Coker, H., Ukpo, G., & Ogah, C. (2005). GC/MS analysis of polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons in sediment samples from the Niger Delta region. Chemosphere, 60(7), 990–997.
Baddi, G. A., Hafidi, M., Cegarra, J., Alburquerque, J. A., Gonzalvez, J., Gilard, V., & Revel, J.-C. (2004). Characterization of fulvic acids by elemental and spectroscopic (FTIR and 13C-NMR) analyses during composting of olive mill wastes plus straw. Bioresource Technology, 93(3), 285–290.
Baghoth, S., Sharma, S., & Amy, G. (2011). Tracking natural organic matter (NOM) in a drinking water treatment plant using fluorescence excitation–emission matrices and PARAFAC. Water Research, 45(2), 797–809.
Bambino, K., & Chu, J. (2017). Zebrafish in toxicology and environmental health. Current Topics in Developmental Biology, 124, 331–367.
Baynes, A., Green, C., Nicol, E., Beresford, N., Kanda, R., Henshaw, A., Churchley, J., & Jobling, S. (2012). Additional treatment of wastewater reduces endocrine disruption in wild fish. A comparative study of tertiary and advanced treatments. Environmental Science & Technology, 46(10), 5565–5573.
Carstea, E. M., Baker, A., Bieroza, M., Reynolds, D. M., & Bridgeman, J. (2014). Characterisation of dissolved organic matter fluorescence properties by PARAFAC analysis and thermal quenching. Water Research, 61, 152–161.
Chang, X., Meyer, M. T., Liu, X., Zhao, Q., Chen, H., Chen, J.-A., Qiu, Z., Yang, L., Cao, J., & Shu, W. (2010). Determination of antibiotics in sewage from hospitals, nursery and slaughter house, wastewater treatment plant and source water in Chongqing region of Three Gorge Reservoir in China. Environmental Pollution, 158(5), 1444–1450.
Chen, W., Westerhoff, P., Leenheer, J. A., & Booksh, K. (2003). Fluorescence excitation−emission matrix regional integration to quantify spectra for dissolved organic matter. Environmental Science & Technology, 37(24), 5701–5710.
D’Costa, A., Shyama, S., & Kumar, M. P. (2017). Bioaccumulation of trace metals and total petroleum and genotoxicity responses in an edible fish population as indicators of marine pollution. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 142, 22–28.
Eriksson, E., Auffarth, K., Henze, M., & Ledin, A. (2002). Characteristics of grey wastewater. Urban Water, 4(1), 85–104.
Fenech, M. (2007). Cytokinesis-block micronucleus cytome assay. Nature Protocols, 2(5), 1084–1104.
Fent, K., Weston, A. A., & Caminada, D. (2006). Ecotoxicology of human pharmaceuticals. Aquatic Toxicology, 76(2), 122–159.
Frenzilli, G., Nigro, M., & Lyons, B. (2009). The comet assay for the evaluation of genotoxic impact in aquatic environments. Mutation research/reviews in mutation Research, 681(1), 80–92.
Gros, M., Petrovic, M., Ginebreda, A., & Barcelo, D. (2010). Removal of pharmaceuticals during wastewater treatment and environmental risk assessment using hazard indexes. Environment International, 36(1), 15–26.
Haberkamp, J., Ruhl, A. S., Ernst, M., & Jekel, M. (2007). Impact of coagulation and adsorption on DOC fractions of secondary effluent and resulting fouling behaviour in ultrafiltration. Water Research, 41(17), 3794–3802.
Hirsch, R., Ternes, T., Haberer, K., & Kratz, K.-L. (1999). Occurrence of antibiotics in the aquatic environment. Science of the Total Environment, 225(1–2), 109–118.
Huang, M.-H., Li, Y.-M., & Gu, G.-W. (2010). Chemical composition of organic matters in domestic wastewater. Desalination, 262(1–3), 36–42.
Huang, H., Xiao, D., Liu, J., Hou, L., & Ding, L. (2015). Recovery and removal of nutrients from swine wastewater by using a novel integrated reactor for struvite decomposition and recycling. Scientific Reports, 5, 10183.
Huang, C., Luo, M.-T., Chen, X.-F., Xiong, L., Li, X.-M., & Chen, X.-D. (2017). Recent advances and industrial viewpoint for biological treatment of wastewaters by oleaginous microorganisms. Bioresource Technology, 232, 398–407.
Karahan, O., Dogruel, S., Dulekgurgen, E., & Orhon, D. (2008). COD fractionation of tannery wastewaters—particle size distribution, biodegradability and modeling. Water Research, 42(4–5), 1083–1092.
Karthikeyan, S., Anandan, C., Subramanian, J., & Sekaran, G. (2013). Characterization of iron impregnated polyacrylamide catalyst and its application to the treatment of municipal wastewater. RSC Advances, 3(35), 15044–15057.
Kasprzyk-Hordern, B., Dinsdale, R. M., & Guwy, A. J. (2009). The removal of pharmaceuticals, personal care products, endocrine disruptors and illicit drugs during wastewater treatment and its impact on the quality of receiving waters. Water Research, 43(2), 363–380.
Khanam, T., Ata, S. W., Nur, W., & Rashedi, A. (2016). Particle size measurement in waste water influent and effluent using particle size analyzer and quantitative image analysis technique. Advanced Materials Research. Trans Tech Publ., 571–575.
Konca, K., Lankoff, A., Banasik, A., Lisowska, H., Kuszewski, T., Gozdz, S., Koza, Z., & Wojcik, A. (2003). A cross-platform public domain PC image-analysis program for the comet assay. Mutation Research/Genetic Toxicology and Environmental Mutagenesis, 534(1–2), 15–20.
Kumar, M. S., Pandita, N. S., & Pal, A. K. (2012). LC-MS/MS as a tool for identification of bioactive compounds in marine sponge Spongosorites halichondriodes (Dendy 1905). Toxicon, 60(6), 1135–1147.
Larsson, D. J., de Pedro, C., & Paxeus, N. (2007). Effluent from drug manufactures contains extremely high levels of pharmaceuticals. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 148(3), 751–755.
Li, W.-T., Chen, S.-Y., Xu, Z.-X., Li, Y., Shuang, C.-D., & Li, A.-M. (2014). Characterization of dissolved organic matter in municipal wastewater using fluorescence PARAFAC analysis and chromatography multi-excitation/emission scan: a comparative study. Environmental Science & Technology, 48(5), 2603–2609.
Li, J., Luo, C., Song, M., Dai, Q., Jiang, L., Zhang, D., & Zhang, G. (2017). Biodegradation of phenanthrene in polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-contaminated wastewater revealed by coupling cultivation-dependent and-independent approaches. Environmental Science & Technology, 51(6), 3391–3401.
Martin, J., Camacho-Munoz, D., Santos, J., Aparicio, I., & Alonso, E. (2012). Occurrence of pharmaceutical compounds in wastewater and sludge from wastewater treatment plants: removal and ecotoxicological impact of wastewater discharges and sludge disposal. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 239, 40–47.
Miege, C., Choubert, J., Ribeiro, L., Eusèbe, M., & Coquery, M. (2009). Fate of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in wastewater treatment plants-conception of a database and first results. Environmental Pollution, 157(5), 1721–1726.
Nakada, N., Tanishima, T., Shinohara, H., Kiri, K., & Takada, H. (2006). Pharmaceutical chemicals and endocrine disrupters in municipal wastewater in Tokyo and their removal during activated sludge treatment. Water Research, 40(17), 3297–3303.
Nebbioso, A., & Piccolo, A. (2013). Molecular characterization of dissolved organic matter (DOM): a critical review. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 405(1), 109–124.
Philips, L. A., Ruffner, D. B., Cheong, F. C., Blusewicz, J. M., Kasimbeg, P., Waisi, B., McCutcheon, J. R., & Grier, D. G. (2017). Holographic characterization of contaminants in water: differentiation of suspended particles in heterogeneous dispersions. Water Research, 122, 431–439.
Qiao, M., Ying, G.-G., Singer, A. C., & Zhu, Y.-G. (2018). Review of antibiotic resistance in China and its environment. Environment International, 110, 160–172.
Repeta, D. J., Quan, T. M., Aluwihare, L. I., & Accardi, A. (2002). Chemical characterization of high molecular weight dissolved organic matter in fresh and marine waters. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 66(6), 955–962.
Roth, G. A., Neu-Baker, N. M., & Brenner, S. A. (2015). SEM analysis of particle size during conventional treatment of CMP process wastewater. Science of the Total Environment, 508, 1–6.
Schaider, L. A., Rodgers, K. M., & Rudel, R. A. (2017). Review of organic wastewater compound concentrations and removal in onsite wastewater treatment systems. Environmental Science & Technology, 51(13), 7304–7317.
Shiba, N. C., & Ntuli, F. (2017). Extraction and precipitation of phosphorus from sewage sludge. Waste Management, 60, 191–200.
Shu, Y., Tang, C., Hu, X., Jiang, L., Hu, X., & Zhao, Y. (2018). H3PO4-activated cattail carbon production and application in chromium removal from aqueous solution: process optimization and removal mechanism. Water, 10(6), 754.
Siu, W., Cao, J., Jack, R., Wu, R., Richardson, B., Xu, L., & Lam, P. (2004). Application of the comet and micronucleus assays to the detection of B [a] P genotoxicity in haemocytes of the green-lipped mussel (Perna viridis). Aquatic Toxicology, 66(4), 381–392.
Smoczynski, L., Ratnaweera, H., Kosobucka, M., Smoczynski, M., Pieczulis-Smoczynska, K., & Cretescu, I. (2016). Size of aggregates formed during coagulation and electrocoagulation of synthetic wastewater. Journal of Environmental Protection and Ecology, 17(3), 1160–1170.
Sophonsiri, C., & Morgenroth, E. (2004). Chemical composition associated with different particle size fractions in municipal, industrial, and agricultural wastewaters. Chemosphere, 55(5), 691–703.
Srut, M., Stambuk, A., Bourdineaud, J.-P., & Klobucar, G. I. (2015). Zebrafish genome instability after exposure to model genotoxicants. Ecotoxicology, 24(4), 887–902.
Tagg, A. S., Sapp, M., Harrison, J. P., & Ojeda, J. S. J. (2015). Identification and quantification of microplastics in wastewater using focal plane array-based reflectance micro-FT-IR imaging. Analytical Chemistry, 87(12), 6032–6040.
Tang, C., Shu, Y., Zhang, R., Li, X., Song, J., Li, B., Zhang, Y., & Ou, D. (2017). Comparison of the removal and adsorption mechanisms of cadmium and lead from aqueous solution by activated carbons prepared from Typha angustifolia and Salix matsudana. RSC Advances, 7(26), 16092–16103.
Yamamoto, H., Nakamura, Y., Moriguchi, S., Nakamura, Y., Honda, Y., Tamura, I., Hirata, Y., Hayashi, A., & Sekizawa, J. (2009). Persistence and partitioning of eight selected pharmaceuticals in the aquatic environment: laboratory photolysis, biodegradation, and sorption experiments. Water Research, 43(2), 351–362.
Yang, Y., Hu, M., Zhou, D., Fan, W., Wang, X., & Huo, M. (2017). Bioremoval of Cu2+ from CMP wastewater by a novel copper-resistant bacterium Cupriavidus gilardii CR3: characteristics and mechanisms. RSC Advances, 7(30), 18793–18802.
Zeng, J., Gao, J.-M., Chen, Y.-P., Yan, P., Dong, Y., Shen, Y., Guo, J.-S., Zeng, N., & Zhang, P. (2016). Composition and aggregation of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) in hyperhaline and municipal wastewater treatment plants. Scientific Reports, 6, 26721.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Department of Science and Technology Promotion of University Research and Scientific Excellence (DST-PURSE; DST Sanction Order No SR/FT/LS-113/2009) for providing confocal microscopy images, and Centre of Excellence in Life Science, Bharathidasan University, Trichy.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 44 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vimala, R.T.V., Lija Escaline, J., Murugan, K. et al. Evolving high-throughput approaches to assess the environmental risk of sewage water at molecular level: comprehensive study. Environ Monit Assess 192, 377 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-08258-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-08258-6