Abstract
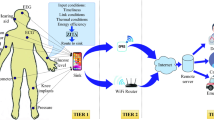
Recent technological advancements in miniaturization of sensor and wireless communication lead to development of Wireless Body Area Networks (WBAN). It is similar to Wireless Sensor Networks but mainly focuses on health care applications to monitor the health condition of patient continuously. It consists of implantable and wearable computing devices placed inside or outside the surface of human body for sensing and data communication. Due to continuous operation, the sensor node introduces electromagnetic radiations which causes damage to delicate human tissues as well as degrades the performance of the network. In addition, WBAN data are sensitive to delay and it is necessary to send critical patient data to the remote server in a timely manner to protect patient’s life. However, alternating the routing path of critical data leads to collision, packet loss, high power consumption, maximum delay and reduced network life time. In this paper, Optimum Path Optimum Temperature Routing Protocol is introduced to address the above issues. The proposed protocol chooses optimum routing path by determining the temperature of sensor nodes and by defining two threshold limits (minimum and maximum). It also considers the critical data signals to be sent when the temperature of node exceeds the admissible threshold limit. The obtained simulation results are compared with conventional routing protocols and was analyzed that the proposed protocol has decreased delay, minimum energy, reduced power, uniform temperature distribution and maximum lifetime of sensor node.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yang, X., Wang, L., & Zhang, Z. (2018). Wireless body area networks MAC protocol for energy efficiency and extending lifetime. IEEE Sensors Letters,2(1), 1–4.
Fernandes, D., Ferreira, A. G., Abrishambaf, R., Mendes, J., & Cabral, J. (2017). A low traffic overhead transmission power control for wireless body area networks. IEEE Sensors Journal,18(3), 1301–1313.
ul Huque, M. T. I., Munasinghe, K. S., & Jamalipour, A. (2014). Body node coordinator placement algorithms for wireless body area networks. IEEE Internet of Things Journal,2(1), 94–102.
Takahashi, D., Xiao, Y., Hu, F., Chen, J., & Sun, Y. (2008). Temperature-aware routing for telemedicine applications in embedded biomedical sensor networks. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking,2008, 26.
Schwiebert, L., Gupta, S. K., Auner, P. S. G., Abrams, G., Iezzi, R., & McAllister, P. (2002, June). A biomedical smart sensor for the visually impaired. In SENSORS, 2002 IEEE (Vol. 1, pp. 693–698). IEEE.
Tang, Q., Tummala, N., Gupta, S. K., & Schwiebert, L. (2005, June). TARA: thermal-aware routing algorithm for implanted sensor networks. In International Conference on Distributed Computing in Sensor Systems (pp. 206–217). Berlin: Springer.
Heinzelman, W. R., Chandrakasan, A., & Balakrishnan, H. (2000, January). Energy-efficient communication protocol for wireless microsensor networks. In Proceedings of the 33rd Annual Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences (p. 10). IEEE.
Bag, A., & Bassiouni, M. A. (2006, October). Energy efficient thermal aware routing algorithms for embedded biomedical sensor networks. In 2006 IEEE International Conference on Mobile Ad Hoc and Sensor Systems (pp. 604–609). IEEE.
Takahashi, D., Xiao, Y., & Hu, F. (2007). November. LTRT: Least total-route temperature routing for embedded biomedical sensor networks. In IEEE GLOBECOM 2007-IEEE Global Telecommunications Conference (pp. 641–645). IEEE.
Bag, A., & Bassiouni, M. A. (2008). February. Routing algorithm for network of homogeneous and id-less biomedical sensor nodes (RAIN). In 2008 IEEE Sensors Applications Symposium (pp. 68–73). IEEE.
Thirumoorthy, P., Kalyanasundaram, P., Maheswar, R., Jayarajan, P., Kanagachidambaresan, G. R., & Amiri, I. S. (2019). Time-critical energy minimization protocol using PQM (TCEM-PQM) for wireless body sensor network. The Journal of Supercomputing. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-019-03042-x.
Bag, A., & Bassiouni, M. A. (2008). Hotspot preventing routing algorithm for delay-sensitive applications of in vivo biomedical sensor networks. Information Fusion,9(3), 389–398.
Ahourai, F., Tabandeh, M., Jahed, M., & Moradi, S. (2009, April). A thermal-aware shortest hop routing algorithm for in vivo biomedical sensor networks. In 2009 Sixth International Conference on Information Technology: New Generations (pp. 1612–1613). IEEE.
Jayarajan, P., Kanagachidambaresan, G. R., Sundararajan, T. V. P., Sakthipandi, K., Maheswar, R., & Karthikeyan, A. (2018). An energy-aware buffer management (EABM) routing protocol for WSN. The Journal of Supercomputing, 65(3), 1–13.
Javaid, N., Abbas, Z., Fareed, M. S., Khan, Z. A., & Alrajeh, N. (2013). M-ATTEMPT: A new energy-efficient routing protocol for wireless body area sensor networks. Procedia Computer Science,19, 224–231.
Monowar, M. M., Mehedi Hassan, M., Bajaber, F., Hamid, M. A., & Alamri, A. (2014). Thermal-aware multiconstrained intrabody QoS routing for wireless body area networks. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks,10(3), 676312.
Ahmad, A., Javaid, N., Qasim, U., Ishfaq, M., Khan, Z. A., & Alghamdi, T. A. (2014). RE-ATTEMPT: A new energy-efficient routing protocol for wireless body area sensor networks. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks,10(4), 464010.
Monowar, M., & Bajaber, F. (2015). On designing thermal-aware localized QoS routing protocol for in vivo sensor nodes in wireless body area networks. Sensors,15(6), 14016–14044.
Bhangwar, A. R., Kumar, P., Ahmed, A., & Channa, M. I. (2017). Trust and thermal aware routing protocol (TTRP) for wireless body area networks. Wireless Personal Communications,97(1), 349–364.
Yang, G., Wu, X. W., Li, Y., & Ye, Q. (2019). Energy efficient protocol for routing and scheduling in wireless body area networks. Wireless Networks, 26(2), 1–9.
Lu, T., Liu, G., & Chang, S. (2018). Energy-efficient data sensing and routing in unreliable energy-harvesting wireless sensor network. Wireless Networks,24(2), 611–625.
Banerjee, P. S., Mandal, S. N., De, D., & Maiti, B. (2019). iSleep: Thermal entropy aware intelligent sleep scheduling algorithm for wireless sensor network. Microsystem Technologies. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-019-04706-7.
Bhangwar, A. R., Ahmed, A., Khan, U. A., Saba, T., Almustafa, K., Haseeb, K., et al. (2019). WETRP: Weight based energy & temperature aware routing protocol for wireless body sensor networks. IEEE Access,7, 87987–87995.
Albukhary, R. A., & Bouabdallah, F. (2019). Time-variant balanced routing strategy for underwater wireless sensor networks. Wireless Networks,25(6), 3481–3495.
Jain, S., & Singh, A. (2018). Temperature-aware routing using secondary sink in wireless body area sensor network. International Journal of E-Health and Medical Communications (IJEHMC),9(2), 38–58.
Fu, X., Fortino, G., Pace, P., Aloi, G., & Li, W. (2020). Environment-fusion multipath routing protocol for wireless sensor networks. Information Fusion,53, 4–19.
Khan, R., Zakarya, M., Tan, Z., Usman, M., Jan, M. A., & Khan, M. (2019). PFARS: Enhancing throughput and lifetime of heterogeneous WSNs through power-aware fusion, aggregation, and routing scheme. International Journal of Communication Systems,32, e4144.
Kanagachidambaresan, G. R., Maheswar, R., Jayaparvathy, R., Thampi, S. M., & Mahima, V. (2019). Fail safe routing algorithm for green wireless nano body sensor network (GWNBSN). In Body Area Network Challenges and Solutions (pp. 131–149). Cham: Springer.
Mu, J., Liu, X., & Yi, X. (2019). Simplified energy-balanced alternative-aware routing algorithm for wireless body area networks. IEEE Access,7, 108295–108303.
Tang, Q., Tummala, N., Gupta, S. K., & Schwiebert, L. (2005). Communication scheduling to minimize thermal effects of implanted biosensor networks in homogeneous tissue. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering,52(7), 1285–1294.
Pennes, H. H. (1948). Analysis of tissue and arterial blood temperatures in the resting human forearm. Journal of Applied Physiology,1(2), 93–122.
Ahmed, G., Mahmood, D., & Islam, S. (2019). Thermal and energy aware routing in wireless body area networks. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks,15(6), 1550147719854974.
Maymand, L. Z., Ayatollahitafti, V., & Gandomi, A. (2017). Traffic control thermal-aware routing in body area networks. Journal of Soft Computing and Decision Support Systems,4(4), 17–22.
Hayajneh, T., Almashaqbeh, G., Ullah, S., & Vasilakos, A. V. (2014). A survey of wireless technologies coexistence in WBAN: Analysis and open research issues. Wireless Networks,20(8), 2165–2199.
Bradai, N., Charfi, E., Fourati, L. C., & Kamoun, L. (2016). Priority consideration in inter-WBAN data scheduling and aggregation for monitoring systems. Transactions on Emerging Telecommunications Technologies,27(4), 589–600.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Banuselvasaraswathy, B., Rathinasabapathy, V. Self-heat controlling energy efficient OPOT routing protocol for WBAN. Wireless Netw 26, 3781–3792 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-020-02303-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-020-02303-5