Abstract
Background
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) exon 19 deletions (19dels) appear in a large number of variants, which has not been distinguished in previously published trials despite differences in deletion and insertion locations.
Objective
The aim of this study was to investigate the therapeutic response of patients with different EGFR exon 19dels to first-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) and the mechanisms by which their tumors acquire resistance to these TKIs.
Patients and Methods
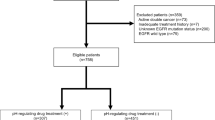
The clinical outcomes of 195 patients harboring EGFR exon 19dels and receiving first-generation EGFR TKIs between July 2011 and June 2019 were retrospectively analyzed.
Results
A total of twenty EGFR exon 19dels variants were identified. The patients were divided into three groups according to the first residue of the deletion, including E746, L747, and other residues (T751 or S752). The median progression-free survival (PFS) of patients treated with EGFR TKIs was significantly different between groups (p < 0.001). Patients harboring EGFR exon 19dels starting at T751 or S752 had the shortest median PFS (2.9 months), followed by those with E746 (11.4 months) and those with L747 (17.2 months). Analyzing 140 patients who had progressed on therapy, EGFR exon 19dels beginning at T751 or S752 were associated with a low incidence of the T790M mutation (16.7%).
Conclusions
Deletion location and type variants (with or without an insertion and/or a substitution) might affect first-generation TKI efficacy, and different EGFR exon 19dels should be considered when making decisions on which EGFR TKI should be used.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang YL, Yuan JQ, Wang KF, et al. The prevalence of EGFR mutation in patients with non-small cell lung cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Oncotarget. 2016;7(48):78985–993. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.12587.
Okayama H, Kohno T, Ishii Y, et al. Identification of gene upregulated in ALK-positive and EGFR/KRAS/ALK-negative lung adenocarcinomas. Cancer Res. 2012;72(1):100–11. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-1403.
Meng H, Guo X, Sun D, et al. Genomic profiling of driver gene mutation in Chinese patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Front Genet. 2019;10:1008. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2019.01008.
Douillard JY, Ostoros G, Cobo M, et al. First-line gefitinib in Caucasian EGFR mutation-positive NSCLC patients: a phase IV, open-label, single-arm study. Br J Cancer. 2014;110(1):55–62. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2013.721.
Choi YW, Jeon SY, Jeong GS, et al. EGFR exon 19 deletion is associated with favorable overall survival after first-line gefitinib therapy in advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients. Am J Clin Oncol. 2018;41(4):385–90. https://doi.org/10.1097/COC.0000000000000282.
Mok TS, Wu YL, Thongprasert S, et al. Gefitinib or carboplatin-paclitaxel in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(10):947–57. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa0810699.
Rosell R, Carcereny E, Gervais R, et al. Erlotinib versus standard chemotherapy as first-line treatment for European patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (EURTAC): a multicenter, open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012;13(3):239–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(11)70393-X.
Mitsudomi T, Morita S, Yatabe Y, et al. Gefitinib versus cisplatin plus docetaxel in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring mutation of the epidermal growth factor receptor (WJTOG3405): an open label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2010;11(2):121–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(09)70364-X.
Zhou C, Wu YL, Chen G, et al. Erlotinib versus chemotherapy as first-line treatment for patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (OPTIMAL, CTONG-0802): a multicenter, open-label, randomised phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2011;12(8):735–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(11)70184-X.
Shi YK, Wang L, Han BH, et al. First-line icotinib versus cisplatin/pemetrexed plus pemetrexed therapy for patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive lung adenocarcinoma (CONVINCE): a phase 3, open-label, randomised study. Ann Oncol. 2017;28(10):2443–50. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdx359.
Sequist LV, Yang JC, Yamamoto N, et al. Phase III study of afatinib or cisplatin plus pemetrexed in patients with metastatic lung adenocarcinoma with EGFR mutation. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31(27):3327–34. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2012.44.2806.
Soria JC, Ohe Y, Vansteenkiste J, et al. Osimertinib in untreated EGFR-mutation advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(2):113–25. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1713137.
Lee CK, Wu YL, Ding PN, et al. Impact of specific epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation and clinical characteristics on outcomes after treatment with EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors versus chemotherapy in EGFR-mutation lung cancer: a meta-analysis. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33(17):1958–65. http://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2014.58.1736.
Goto K, Nishio M, Yamamoto N, et al. A prospective, phase III, open-label study (JO22903) of first-line erlotinib in Japanese patients with epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation-positive advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Lung Cancer. 2013;82(1):109–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2013.07.003.
Zhang Y, Sheng J, Kang S, et al. Patients with exon 19 deletion were associated with longer progression-free survival compared to those with L858R mutation after first-line EGFR-TKIs for advanced non-small cell lung cancer: a meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2014;9(9):e107161. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0107161.
Care KD, Garton AJ, Romero MS, et al. Kinetic analysis of epidermal growth factor receptor somatic mutant proteins shows increased sensitivity to the epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, erlotinib. Cancer Res. 2006;66(16):8163–71. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-0453.
Rossi S, Toschi L, Finocchiaro G, et al. Impact of exon 19 deletion subtypes in EGFR-mutation metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer treated with first-line tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Clin Lung Cancer. 2019;20(2):82–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cllc.2018.10.009.
Su J, Zhong W, Zhang X, et al. Molecular characteristics and clinical outcomes of EGFR 19 indel subtypes to EGFR TKIs in NSCLC patients. Oncotarget. 2017;8(67):111246–257. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.22768.
Kuiper JL, Heideman DA, Thunnissen E, et al. Incidence of T790M mutation in(sequential) rebiopsies in EGFR-mutated NSCLC-patients. Lung Cancer. 2014;85(1):19–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2014.03.016.
Socinski MA, Villaruz LC, Ross J. Understanding mechanisms of resistance in the epithelial growth factor receptor in non-small cell lung cancer and the role of biopsy at progression. Oncologist. 2017;22(1):3–11. https://doi.org/10.1634/theoncologist.2016-0285.
Li W, Ren S, Li J, et al. T790M mutation is associated with better efficacy of treatment beyond progression with EGFR-TKI in advanced NSCLC patients. Lung Cancer. 2014;84(3):295–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2014.03.011.
Chung KP, Wu SG, Wu JY.et al. Clinical outcomes in non-small cell lung cancers harboring different exon 19 deletions in EGFR. Clin Cancer Res. 2012;18(12):3407–7. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-2353.
Kaneda T, Hata A, Tomioka H, et al. Possible different EGFR-TKI efficacy among exon 19 deletional locations in EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2014;86(2):213–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2014.09.014.
Zhou Q, et al. ARTEMIS (CTONG 1509): Phase III study of bevacizumab with or without erlotinib in untreated Chinese patients with advanced EGFR-mutated NSCLC. Ann Oncol. 2019;30(suppl_5):v602–60. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdz260.
Ramalingam SS, Vansteenkiste J, Planchard D, et al. Overall survival with osimertinib in untreated EGFR-mutated advanced NSCLC. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(1):41–50. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1913662.
Acknowledgements
We would like to take the opportunity to thank the patients, their families, and all of the research members.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Funding
This work was supported by a grant from the Beijing Hope Run Sepcial Funding of Cancer Foundation of the People’s Republic of China(LC2019L04).
Conflicts of interest
Haiyan Xu, Weihua Li, Guangjian Yang, Junling Li, Lu Yang, Fei Xu, Yaning Yang, Jianming Ying, and Yan Wang declare that they have no conflicts of interest that might be relevant to the contents of this manuscript.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, H., Li, W., Yang, G. et al. Heterogeneous Response to First-Generation Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancers with Different EGFR Exon 19 Mutations. Targ Oncol 15, 357–364 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11523-020-00722-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11523-020-00722-0