Abstract
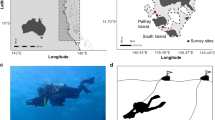
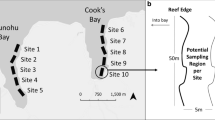
Population irruptions of crown-of-thorns starfish (Acanthaster spp.) contribute greatly to the degradation of coral reefs throughout the Indo-Pacific. Effective management of these population irruptions is limited, in part, by incomplete knowledge of their early life history. Importantly, there are very limited data on the distribution and abundance of newly settled crown-of-thorns starfish (0 + starfish, in their first year since settlement). Extensive sampling was conducted around the circumference of three distinct mid-shelf reefs (at 1–18 m depths) in the central Great Barrier Reef (GBR), during active population irruptions, in May–June 2017, to quantify the occurrence and densities of settlement-stage starfish (2–65 mm diameter) and relate patterns of abundance to distinct habitat features at the scale of individual reefs. Overall, 140 settlement-stage starfish were detected across 1242 quadrats (1 m2). Settlement-stage starfish were recorded from 31 out of 42 sites (73.8%) at mean densities of 0–0.77 starfish m−2. Both estimated densities and the likelihood of occurrence of settlement-stage starfish within quadrats increased overall with the proportion of coral rubble (and dead intact corals), were greatest at intermediate depths (8–14 m), but decreased with the proportion of live hard coral. At the scale of individual reefs, settlement-stage starfish occurred most frequently in south-western and northern fore reef habitats. Our results suggest that settlement and/or early post-settlement survival of crown-of-thorns starfish is greatest in relatively shallow waters of obliquely exposed fore reef habitats where there is high cover of coral rubble. The specific occurrence of these habitat types (within spur and groove systems and rubble slips) provides an opportunity to concentrate searches and increase effective sampling of settlement-stage starfish, though these habitats are relatively widespread and unlikely to constrain the population replenishment or population irruptions of crown-of-thorns starfish on the GBR.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babcock RC, Dambacher JM, Morello EB, Plagányi ÉE, Hayes KR, Sweatman HPA, Pratchett MS (2016a) Assessing different causes of crown-of-thorns starfish outbreaks and appropriate responses for management on the Great Barrier Reef. PLoS One 11:e0169048
Babcock RC, Milton DA, Pratchett MS (2016b) Relationships between size and reproductive output in the crown-of-thorns starfish. Mar Biol 163:3–9
Baird AH, Pratchett MS, Hoey AS, Herdiana Y, Campbell SJ (2013) Acanthaster planci is a major cause of coral mortality in Indonesia. Coral Reefs 32:803–812
Barker MF, Nichols D (1983) Reproduction, recruitment and juvenile ecology of the starfish, Asterias rubens and Marthasterias glacialis. J Mar Biol Ass UK 63:745–765
Black KP, Moran PJ (1991) Influence of hydrodynamics on the passive dispersal and initial recruitment of larvae of Acanthaster planci (Echinodermata: Asteroidea) on the Great Barrier Reef. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 69:55–65
Brooks ME, Kristensen K, van Benthem KJ, Magnusson A, Berg CW, Nielsen A, Skaug HJ, Mächler M, Bolker BM (2017) glmmTMB balances speed and flexibility among packages for zero-inflated generalized linear mixed modeling. The R Journal 9:378–400
Buston PM, Elith J (2011) Determinants of reproductive success in dominant pairs of clownfish: a boosted regression tree analysis. J Anim Ecol 80:528–538
Caballes CF, Pratchett MS, Kerr AM, Rivera-Posada JA (2016) The role of maternal nutrition on oocyte size and quality, with respect to early larval development in the coral-eating starfish. Acanthaster planci. PLoS One 11:e0158007
Cowan ZL, Dworjanyn SA, Caballes CF, Pratchett MS (2016a) Predation on crown-of-thorns starfish larvae by damselfishes. Coral Reefs 35:1253–1262
Cowan Z-L, Dworjanyn S, Caballes C, Pratchett M (2016b) Benthic predators influence microhabitat preferences and settlement success of crown-of-thorns starfish (Acanthaster cf. solaris). Diversity 8:27
Cowan ZL, Ling SD, Dworjanyn SA, Caballes CF, Pratchett MS (2017) Interspecific variation in potential importance of planktivorous damselfishes as predators of Acanthaster sp. eggs. Coral Reefs 36:653–661
Cowan ZL, Ling SD, Caballes CF, Dworjanyn SA, Pratchett MS (2020) Crown-of-thorns starfish larvae are vulnerable to predation even in the presence of alternative prey. Coral Reefs. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00338-019-01890-w
De’ath G (2007) Boosted trees for ecological modelling and prediction. Ecology 88:243–251
De’ath G, Fabricius KE, Sweatman H, Puotinen M (2012) The 27-year decline of coral cover on the Great Barrier Reef and its causes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:17995–17999
Deaker DJ, Agüera A, Lin H-A, Lawson C, Budden C, Dworjanyn SA, Mos B, Byrne M (2020) The hidden army: corallivorous crown-of-thorns seastars can spend years as herbivorous juveniles. Biol Lett 16:20190849
Doherty PJ, Davidson J (1988) Monitoring the distribution and abundance of juvenile Acanthaster planci. Proc 6th Int Coral Reef Symp Aust 2:131-136
Done TJ (1999) Coral community adaptability to environmental change at the scales of regions, reefs and reef zones. Am Zool 39:66–79
Duce S, Vila-Concejo A, Hamylton SM, Webster JM, Bruce E, Beaman RJ (2016) A morphometric assessment and classification of coral reef spur and groove morphology. Geomorphology 265:68–83
Ebert T (1983) Recruitment in echinoderms. In: Jangoux M, Lawrence JM (eds) Echinoderm studies 1. A. A. Balkema, Rotterdam, pp 169–203
Elith J, Leathwick JR, Hastie T (2008) A working guide to boosted regression trees. J Anim Ecol 77:802–813
Engelhardt U, Hartcher M, Cruise J, Engelhardt D, Russel M, Taylor N, Thomas G, Wiseman D (1999) Fine-scale surveys of crown-of-thorns starfish (Acanthaster planci) in the central Great Barrier Reef region. CRC Reef Research Centre. Technical Report No. 30, Townsville, 97 pp
Guillou M, Joly-Turquin G, Leyzour S, Pernet P, Dubois P (2012) Factors controlling juvenile growth and population structure of the starfish Asterias rubens in intertidal habitats: field and experimental approaches. J Mar Biol Ass UK 92:367–378
Habe T, Yamamoto G, Nagai A, Kosaka M, Ogura M, Sawamoto S, Ueno S, Yokochi H (1989) Studies on the conservation and management of coral reefs and the control of Acanthaster planci juveniles. Report of Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research, Ministry of Education, Science and Culture, Japan pp 158-186
Hijmans RJ, Phillips S, Leathwick J, Elith J (2017) dismo: Species distribution modeling. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=dismo
Hock K, Wolff NH, Condie SA, Anthony KRN, Mumby PJ (2014) Connectivity networks reveal the risks of crown-of-thorns starfish outbreaks on the Great Barrier Reef. J Appl Ecol 51:1188–1196
Hughes TP, Kerry JT, Álvarez-Noriega M, Álvarez-Romero JG, Anderson KD, Baird AH, Babcock RC, Beger M, Bellwood DR, Berkelmans R, Bridge TC, Butler IR, Byrne M, Cantin NE, Comeau S, Connolly SR, Cumming GS, Dalton SJ, Diaz-Pulido G, Eakin CM, Figueira WF, Gilmour JP, Harrison HB, Heron SF, Hoey AS, Hobbs J-PA, Hoogenboom MO, Kennedy EV, Kuo C-y, Lough JM, Lowe RJ, Liu G, McCulloch MT, Malcolm HA, McWilliam MJ, Pandolfi JM, Pears RJ, Pratchett MS, Schoepf V, Simpson T, Skirving WJ, Sommer B, Torda G, Wachenfeld DR, Willis BL, Wilson SK (2017) Global warming and recurrent mass bleaching of corals. Nature 543(7645):373–377
Hughes TP, Anderson KD, Connolly SR, Heron SF, Kerry JT, Lough JM, Baird AH, Baum JK, Berumen ML, Bridge TC, Claar DC, Eakin CM, Gilmour JP, Graham NAJ, Harrison H, Hobbs JPA, Hoey AS, Hoogenboom M, Lowe RJ, McCulloch MT, Pandolfi JM, Pratchett MS, Schoepf V, Torda G, Wilson SK (2018) Spatial and temporal patterns of mass bleaching of corals in the Anthropocene. Science 359(6371):80–83
Johnson CR, Sutton DC, Olson RR, Giddins R (1991) Settlement of crown-of-thorns starfish: role of bacteria on surfaces of coralline algae and a hypothesis for deep-water recruitment. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 71:143–162
Johnson C (1992) Settlement and recruitment of Acanthaster planci on the Great Barrier Reef: questions of process and scale. Aust J Mar Freshwater Res 43:611–627
Johnson DB, Moran PJ, Baker VJ, Christie CA, Miller IR, Miller-Smith BA, Thompson AA (1992) An attempt to locate high density populations of juvenile crown-of-thorns starfish (Acanthaster planci) on the central Great Barrier Reef. Coral Reefs 11:122
Keesing JK, Halford AR (1992) Field measurement of survival rates of juvenile Acanthaster planci: techniques and preliminary results. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 85:107–114
Keesing JK, Wiedermeyer WL, Okaji K, Halford AR, Hall KC, Cartwright CM (1996) Mortality rates of juvenile starfish Acanthaster planci and Nardoa spp. measured on the Great Barrier Reef, Australia and in Okinawa. Japan. Oceanol Acta 19:441–448
Keesing JK, Halford AR, Hall KC (2018) Mortality rates of small juvenile crown-of-thorns starfish Acanthaster planci on the Great Barrier Reef: implications for population size and larval settlement thresholds for outbreaks. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 597:179–190
Laxton JH (1974) Aspects of the ecology of the coral-eating starfish Acanthaster planci. Biol J Linn Soc 6:19–45
Littler MM, Littler DS (2013) The nature of crustose coralline algae and their interactions on reefs. In: Lang MA, Marinelli RL, Roberts SJ, Taylor PR (eds) Research and discoveries: the revolution of science through Scuba. Smithsonian Institution Scholarly Press, Washington DC, pp 199–212
Leathwick JR, Elith J, Francis MP, Hastie T, Taylor P (2006) Variation in demersal fish species richness in the oceans surrounding New Zealand: an analysis using boosted regression trees. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 321:267–281
Loosanoff VL (1964) Variations in time and intensity of setting of the starfish, Asterias forbesi, in Long Island Sound during a twenty-five-year period. Biological Bulletin 126:423–439
MacNeil MA, Mellin C, Pratchett MS, Hoey J, Anthony KRN, Cheal AJ, Miller I, Sweatman H, Cowan ZL, Taylor S, Moon S, Fonnesbeck CJ (2016) Joint estimation of crown of thorns (Acanthaster planci) densities on the Great Barrier Reef. PeerJ 4:e2310
Mellin C, Matthews S, Anthony KRN, Brown SC, Caley MJ, Johns KA, Osborne K, Puotinen M, Thompson A, Wolff NH, Fordham DA, MacNeil MA (2019) Spatial resilience of the Great Barrier Reef under cumulative disturbance impacts. Glob Change Biol 25:2431–2445
Mead AD (1900) On the correlation between growth and food supply in starfish. Amer Nat 34:17–23
Moran PJ, Bradbury RH, Reichelt RE (1985) Mesoscale studies of the crown-of-thorns/coral interaction: A case history from the Great Barrier Reef. Proc Fifth Int Coral Reef Congress 5:321–326
Nauen CE (1978) The growth of the sea star, Asterias rubens, and its role as benthic predator in Kiel Bay. Kieler Meeresforschungen 4:68–81
Nauen CE, Böhm L (1979) Skeletal growth in the echinoderm Asterias rubens L. (Asteroidea, Echinodermata) estimated by 45Ca-labelling. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 38:261–269
Nichols D, Barker MF (1984) Growth of juvenile Asterias rubens L. (Echinodermata: Asteroidea) on an intertidal reef in southwestern Britain. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 78:157–165
Okaji, K. Feeding Ecology in the Early Life Stages of the Crown-of-Thorns Starfish, Acanthaster planci (L.). Ph.D. Thesis, James Cook University, Townsville, Australia, February 1996; p. 140
Pearson RG, Endean R (1969) A preliminary study of the coral predator Acanthaster planci (L.) (Asteroidea) on the Great Barrier Reef. Fisheries Notes, Queensland Department of Harbours and Marine. pp 1–38
Pratchett MS (2005) Dynamics of an outbreak population of Acanthaster planci at Lizard Island, northern Great Barrier Reef (1995–1999). Coral Reefs 24:453–462
Pratchett MS, Caballes CF, Rivera-Posada JA, Sweatman HPA (2014) Limits to understanding and managing outbreaks of crown-of-thorns starfish (Acanthaster spp.). Ocean Mar Biol Annu Rev 52:133–200
Pratchett M, Dworjanyn S, Mos B, Caballes C, Thompson C, Blowes S (2017a) Larval survivorship and settlement of crown-of-thorns starfish (Acanthaster cf. solaris) at varying cell densities. Diversity 9, 2
Pratchett MS, Cowan ZL, Nadler LE, Caballes CF, Hoey AS, Messmer V, Fletcher CS, Westcott DA, Ling SD (2017b) Body size and substrate type modulate movement by the western Pacific crown-of-thorns starfish. Acanthaster solaris. PloS One 12:e0180805
Pratchett MS, Cumming GS (2019) Managing cross-scale dynamics in marine conservation: pest irruptions and lessons from culling of crown-of-thorns starfish (Acanthaster spp.). Biol Conserv 238:108211
R Core Team (2018) R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Found Stat Comput
Reichelt RE, Bradbury RH, Moran PJ (1990) Distribution of Acanthaster planci outbreaks on the Great Barrier Reef between 1966 and 1989. Coral Reefs 9:97–103
Rogers JGD, Pláganyi ÉE, Babcock RC (2017) Aggregation, Allee effects and critical thresholds for the management of the crown-of-thorns starfish Acanthaster planci. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 578:99–114
Uthicke S, Fisher EE, Patel F, Diaz-Guijarro B, Doyle JR, Messmer V, Pratchett MS (2019) Spawning time of Acanthaster cf. solaris on the Great Barrier Reef inferred using qPCR quantification of embryos and larvae: do they know it’s Christmas? Mar Biol 166:133
Vanhatalo J, Hosack GR, Sweatman H (2016) Spatiotemporal modelling of crown-of-thorns starfish outbreaks on the Great Barrier Reef to inform control strategies. J Appl Ecol 54:188–197
Veron JEN (2000) Corals of the world: vol 1. Australian Institute of Marine Science, Townsville, p 463
Yamaguchi M (1973) Early life histories of coral reef asteroids, with special reference to Acanthaster planci (L.). In: Jones OA, Endean R (eds) Biology and geology of coral reefs. Academic Press Inc, New York, pp 369–387
Yamaguchi M (1974) Growth of juvenile Acanthaster planci (L.) in the laboratory. Pacific Sci 28:123–138
Yokochi H, Ogura M (1987) Spawning period and discovery of juvenile Acanthaster planci (L.) (Echinodermata: Asteroidea) at northwestern Iriomote-jima. Ryukyu Islands. Bull Mar Sci 41:611–616
Wilmes J, Matthews S, Schultz D, Messmer V, Hoey A, Pratchett M (2016) Modelling growth of juvenile crown-of-thorns starfish on the northern Great Barrier Reef. Diversity 9:172–182
Wilmes JC, Caballes CF, Cowan ZL, Hoey AS, Lang BJ, Messmer V, Pratchett MS (2018) Contributions of pre- versus post-settlement processes to fluctuating abundance of crown-of-thorns starfishes (Acanthaster spp.). Mar Pollut Bull 135:332–345
Wilmes J, Hoey A, Messmer V, Pratchett M (2019) Incidence and severity of injuries among juvenile crown-of-thorns starfish on Australia’s Great Barrier Reef. Coral Reefs 38:1187–1195
Wilmes JC, Hoey AS, Pratchett MS (In review) Contrasting size and fate of juvenile crown-of-thorns starfish linked to ontogenetic diet shifts. Proc Royal Soc B
Wilson SK, Graham NAJ, Polunin NVC (2007) Appraisal of visual assessments of habitat complexity and benthic composition on coral reefs. Mar Biol 151:1069–1076
Zann L, Brodie J, Berryman C, Naqasima M (1987) Recruitment, ecology, growth and behavior of juvenile Acanthaster planci (L.) (Echinodermata: Asteroidea). Bull Mar Sci 41:561–575
Zann L, Brodie J, Vuki V (1990) History and dynamics of the crown-of-thorns starfish Acanthaster planci (L.) in the Suva area. Fiji. Coral Reefs 9:135–144
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the Ian Potter Foundation through the Lizard Island Reef Research Foundation, the ARC Centre of Excellence for Coral Reef Studies at James Cook University, as well as the Tropical Water Quality Hub of the Australian Government’s National Environmental Science Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Topic Editor Simon Davy
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wilmes, J.C., Schultz, D.J., Hoey, A.S. et al. Habitat associations of settlement-stage crown-of-thorns starfish on Australia’s Great Barrier Reef. Coral Reefs 39, 1163–1174 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00338-020-01950-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00338-020-01950-6