Abstract
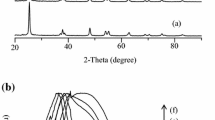
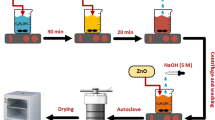
Here, we developed a sustainable solution to address the water pollution especially due to organic dye industries. Visible light-activated catalytic degradation of aqueous solution of methylene blue (MB) dye was studied by using trivalent metal ion-doped ZnO nanoparticles as a photocatalyst. The nano-photocatalysts were synthesized by microwave-irradiated solution combustion method using d-glucose as a fuel. Various experimental parameters were optimized using Taguchi design of experiment, analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Grey relational analysis in order to obtain potential ZnO photocatalyst. Using ANOVA and Grey relation analysis, the optimum conditions were estimated that 5.5 mol% Cr3+-doped ZnO with 4 min MW heating and calcined at 450 °C, which shows very impressing photo-catalytic property. The ANOVA confirms that the calcination temperature and dopants significantly influence crystallite size with contribution factor of 42.28% and 40.02%, respectively. The band gap energy of the photocatalyst was largely influenced by a type of dopant with contribution 85.77%. Grey relational grading indicates that the 5.5% Al3+ doping, 4 min MW heat treatment, 450 °C calcination temperature to get lesser band gap (3.05 eV) and smaller crystallite size (46.96 nm). As compared with other L9 orthogonal array, the degradation efficiency is found to be higher (89.31%) on the Grey theory predication result for MB dye. Herewith, we strongly confirm that the Taguchi design was an promising tool in engineering the ZnO photocatalyst with a very less experimental trials and cost saving approach.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adeleke JT, Theivasanthi T, Thiruppathi M, Swaminathan M, Akomolafe T, Alabi AB (2018) Photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue by ZnO/NiFe2O4 nanoparticles. Appl Surf Sci 455:195–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.05.184
Ba-Abbad MM, Kadhum AAH, Mohamad AB, Takriff MS, Sopian K (2013) Optimization of process parameters using d-optimal design for synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles via sol–gel technique. J Ind Eng Chem 19:99–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2012.07.010
Bousslama W, Elhouichet H, Férid M (2017) Enhanced photocatalytic activity of Fe doped ZnO nanocrystals under sunlight irradiation. Optik 134:88–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2017.01.025
Chang C-J, Yang T-L, Weng Y-C (2014) Synthesis and characterization of Cr-doped ZnO nanorod-array photocatalysts with improved activity. J Solid State Chem 214:101–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssc.2013.09.039
Chen KJ, Fang TH, Hung FY, Ji LW, Chang SJ, Young SJ, Hsiao YJ (2008) The crystallization and physical properties of Al-doped ZnO nanoparticles. Appl Surf Sci 254:5791–5795. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2008.03.080
Goktas A, Mutlu IH, Yamada Y (2013) Influence of Fe-doping on the structural, optical, and magnetic properties of ZnO thin films prepared by sol–gel method. Superlattices Microstruct 57:139–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spmi.2013.02.010
Hoque A, Boruah R, Das SK (2014) Tunable optical properties of ZnO via doping monovalent (Li+), divalent (Mn2+) and trivalent (Fe3+) cations. Mater Chem Phys 147:213–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2014.04.031
Inamdar DY, Pathak AK, Dubenko I, Ali N, Mahamuni S (2011) Room temperature ferromagnetism and photoluminescence of Fe doped ZnO nanocrystals. J Phys Chem C 115:23671–23676. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp205854p
Jayanthi K, Chawla S, Joshi AG, Khan ZH, Kotnala RK (2010) Fabrication of luminescent, magnetic hollow core nanospheres and nanotubes of Cr-doped ZnO by inclusive coprecipitation method. J Phys Chem C 114:18429–18434. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp107086h
Jena M, Manjunatha C, Shivaraj BW, Nagaraju G, Ashoka S, Sham Aan MP (2019) Optimization of parameters for maximizing photocatalytic behaviour of Zn1−xFexO nanoparticles for methyl orange degradation using Taguchi and Grey relational analysis approach. Mater Today Chem 12:187–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtchem.2019.01.004
Kim KD, Choi DW, Choa Y-H, Kim HT (2007) Optimization of parameters for the synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles by Taguchi robust design method. Colloids Surf, A 311:170–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2007.06.017
Kim SM, Park KS, Kim KD, Park SD, Kim HT (2009) Optimization of parameters for the synthesis of bimodal Ag nanoparticles by Taguchi method. J Ind Eng Chem 15:894–897. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2009.09.019
Kumar SG, Rao KSRK (2015) Zinc oxide based photocatalysis: tailoring surface-bulk structure and related interfacial charge carrier dynamics for better environmental applications. RSC Adv 5:3306–3351. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4RA13299H
Kumar S, Tiwari N, Jha SN, Chatterjee S, Bhattacharyya D, Ghosh AK (2016) Structural and optical properties of sol–gel derived Cr-doped ZnO diluted magnetic semiconductor nanocrystals: an EXAFS study to relate the local structure. RSC Adv 6:107816–107828. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra15685a
Li QH, Zhu D, Liu W, Liu Y, Ma XC (2008) Optical properties of Al-doped ZnO thin films by ellipsometry. Appl Surf Sci 254:2922–2926. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2007.09.104
Li H, Zhang Z, Huang J, Liu R, Wang Q (2013) Optical and structural analysis of rare earth and Li co-doped ZnO nanoparticles. J Alloy Compd 550:526–530. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2012.10.080
Liu Y et al (2009) Effects of Cr-doping on the optical and magnetic properties in ZnO nanoparticles prepared by sol–gel method. J Alloys Compd 486:835–838. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2009.07.076
Liu H, Zhong L, Govindaraju S, Yun K (2019) ZnO rod decorated with Ag nanoparticles for enhanced photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue. J Phys Chem Solids 129:46–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2018.12.040
Manjunatha C et al (2012) Structural characterization, EPR and thermoluminescence properties of Cd1−xNixSiO3 nanocrystalline phosphors. Mater Res Bull 47:2306–2314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2012.05.039
Manjunatha C, Nagabhushana BM, Sunitha DV, Nagabhushana H, Sharma SC, Chakradhar RPS (2013) Influence of halide flux on the crystallinity, microstructure and thermoluminescence properties of CdSiO3:Co2+ nanophosphor. Mater Res Bull 48:158–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2012.09.068
Mascolo G, Comparelli R, Curri ML, Lovecchio G, Lopez A, Agostiano A (2007) Photocatalytic degradation of methyl red by TiO2: comparison of the efficiency of immobilized nanoparticles versus conventional suspended catalyst. J Hazard Mater 142:130–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.07.068
Meng A, Xing J, Li Z, Li Q (2015) Cr-doped ZnO nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization, adsorption property, and recyclability. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:27449–27457. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b09366
Priyanka, Srivastava VC (2013) Photocatalytic oxidation of dye bearing wastewater by iron doped zinc oxide. Ind Eng Chem Res 52:17790–17799. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie401973r
Rastogi K, Sahu JN, Meikap BC, Biswas MN (2008) Removal of methylene blue from wastewater using fly ash as an adsorbent by hydrocyclone. J Hazard Mater 158:531–540. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.01.105
Roguai S, Djelloul A, Nouveau C, Souier T, Dakhel AA, Bououdina M (2014) Structure, microstructure and determination of optical constants from transmittance data of co-doped Zn0.90Co0.05M0.05O (MAl, Cu, Cd, Na) films. J Alloys Compd 599:150–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2014.02.080
Schmidt-Mende L, MacManus-Driscoll JL (2007) ZnO-nanostructures, defects, and devices. Mater Today 10:40–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1369-7021(07)70078-0
Shan FK, Yu YS (2004) Band gap energy of pure and Al-doped ZnO thin films. J Eur Ceram Soc 24:1869–1872. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0955-2219(03)00490-4
Shemin Z, Yuesong S, Weifeng L, Yayun L (2006) Effects of doping CeO2, Er2O3 on properties of TiO2–SiO2 ceramics for catalyst supporter of deNOx. J Rare Earths 24:234–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0721(07)60369-X
Shivaraj BW, Murthy HNN, Krishna M, Nagabhushana BM, Shandilya SD, Satyanarayana BS (2015) Influence of deposition parameters on structural, morphological and optical properties of ZnO films using robust design approach. Int J Mater Eng Innov 6:154–169. https://doi.org/10.1504/ijmatei.2015.072205
Srinivasulu T, Saritha K, Reddy KTR (2017) Synthesis and characterization of Fe-doped ZnO thin films deposited by chemical spray pyrolysis. Mod Electron Mater 3:76–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.moem.2017.07.001
Vidya C, Manjunatha C, Chandraprabha MN, Rajshekar M, Raj MALA (2017) Hazard free green synthesis of ZnO nano-photo-catalyst using Artocarpus Heterophyllus leaf extract for the degradation of Congo red dye in water treatment applications. J Environ Chem Eng 5:3172–3180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2017.05.058
Viswanatha R, Sapra S, Sen Gupta S, Satpati B, Satyam PV, Dev BN, Sarma DD (2004) Synthesis and characterization of Mn-doped ZnO nanocrystals. J Phys Chem B 108:6303–6310. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp049960o
Vivek A, Chavan A, Wali SB, Murthy HNN, Krishna M, Sathyanarayana BS (2017) Optimisation of spin coating parameters for the preparation of ZnO thin films by Grey–Taguchi method. Int J Nanomanuf 13:197–209. https://doi.org/10.1504/ijnm.2017.085107
Wang C, Chen Z, He Y, Li L, Zhang D (2009) Structure, morphology and properties of Fe-doped ZnO films prepared by facing-target magnetron sputtering system. Appl Surf Sci 255:6881–6887. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2009.03.008
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the Management of Rashtreeya Sikshana Samithi Trust (RSST) and the Principal and HODs of mechanical engineering, chemistry and Physics, R. V. College of Engineering, Bengaluru, India, for constant support and encouragement. Authors are also thankful to Principal and HOD of Chemistry, Siddaganga institute of technology, Tumakuru, Karnataka, India, for providing laboratory facilities to carry out part of this research work. The portion of this research work (FESEM studies) was performed using facilities at Centre for Nano Science and Engineering (CeNSE), funded by Department of Information Technology, Government of India, located at Indian Institute of Science (IISc), Bangalore, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Manjunatha, C., Abhishek, B., Shivaraj, B.W. et al. Engineering the MxZn1−xO (M = Al3+, Fe3+, Cr3+) nanoparticles for visible light-assisted catalytic mineralization of methylene blue dye using Taguchi design. Chem. Pap. 74, 2719–2731 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-020-01113-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-020-01113-5