Abstract
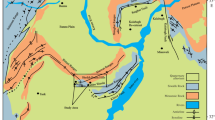
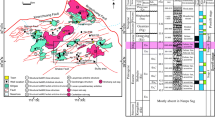
The Es1 sandstone is a fruitful hydrocarbon zone of Eocene Shahejie Formation. Therefore, the present study comprises the subsurface facies analysis established on the description of seven wells. Methods include core observation, thin section petrography, scanning electron microscope (SEM), cathodoluminescence (CL), and X-ray diffraction to evaluate the microfacies, lithofacies, and rock characteristics. Two microfacies of lithofacies have been established as sandstone microfacies and mudstone microfacies on the basis of grain size. Among them, sandstone is further divided into four sub-microfacies on the basis of microscopic studies, rock fragments and mineral composition, which are arkose sandstone, lithic arkose, feldspathic litharenite, and litharenite. These microfacies consisting quartz, feldspar as abundant detrital grains followed by rock fragments and micas, whereas calcite, ferro-calcite, quartz overgrowth, and clay are the main cement. The Es1 sandstone consists of good primary porosity and permeability as well as good secondary porosity caused by fracturing and dissolution of unstable minerals that enhance the reservoir quality. Whereas cementation and compaction reduce the reservoir characteristics. Studied formation divided into five lithofacies including conglomerate sandstone lithofacies, medium to coarse-grain sandstone lithofacies, fine sandstone lithofacies, siltstone lithofacies, and mudstone lithofacies. Core observation, sedimentary structures, facies sequences of the well log, and sedimentary composition reveal that Es1 deposited into the lacustrine delta fan depositional environment. Rock grain size indicates that Es1 contains mixtures of grains including pebbles, sand-size as well as minor silt and clay size. Grain size varies from conglomerate to clay size. The Es1 sandstone was deposited in braided river (conglomerates sandstone), channel bar, lacustrine, fluvial channel (massive bedding, cross-bedding, and graded bedding sandstone), deltaic, and flood-plain (siltstone and mudstone) sedimentary environment. It is concluded that higher transport energies in channels deposited coarse-grain sediments in shallowest part of the lake setting. However, the energy decreases towards greater depth which deposited mudstone in central part of the lake.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armitage P, Worden R, Faulkner D, Aplin A, Butcher A, Iliffe J (2010) Diagenetic and sedimentary controls on porosity in Lower Carboniferous fine-grained lithologies, Krechba field, Algeria: a petrological study of a caprock to a carbon capture site. Mar Pet Geol 27(7):1395–1410
Arribas J, González-Acebrón L, Omodeo-Salè S, Mas R (2014) The influence of the provenance of arenite on its diagenesis in the Cameros Rift Basin (Spain). Geol Soc Lond Spec Publ 386(1):63–73
Bjørlykke K (2011) Open-system chemical behavior of Wilcox Group mudstones. How is large scale mass transfer at great burial depth in sedimentary basins possible? A discussion. Mar Petrol Geol 28(7):1381–1382
Bjørlykke K, Egeberg P (1993) Quartz cementation in sedimentary basins. Am Assoc Petrol Geosci Bull 77:1538–1548
Barclay SA, Worden RH (2000) Effects of reservoir wettability on quartz cementation in oil fields. Quartz Cement Sandstones 29:103–117
Bjørlykke K (2014) Relationships between depositional environments, burial history and rock properties. Some principal aspects of the diagenetic process in sedimentary basins. Sed Geol 301:1–14
Bloch S, Lander R, Bonnell L (2002) Anomalously high porosity and permeability in deeply buried sandstone reservoirs: origin and predictability. AAPG Bull 86(2):301–328
Cao Y, Yuan G, Li X, Wang Y, Xi K, Wang X, Yang T (2014) Characteristics and origin of abnormally high porosity zones in buried Paleogene clastic reservoirs in the Shengtuo area, Dongying Sag, East China. Petrol Sci 11(3):346–362
Chamley H (1989a) Clay formation through weathering. Clay sedimentology. Springer, Berlin, pp 21–50
Chamley H (1989b) Clay sedimentology. Springer, Berlin, p 623
Chen X, Li S, Dong Y, Pang X, Wang Z, Ren M, Zhang H (2016) Characteristics and genetic mechanisms of offshore natural gas in the Nanpu Sag, Bohai Bay Basin, eastern China. Org Geochem 94:68–82
Curtis C (1978) Possible links between sandstone diagenesis and depth-related geochemical reactions occurring in enclosing mudstones. J Geol Soc 135(1):107–117
Caracciolo L, Gramigna P, Critelli S, Calzona AB, Russo F (2013) Petrostratigraphic analysis of a Late Miocene mixed siliciclastic-carbonate depositional system (Calabria, Southern Italy): implications for Mediterranean palaeogeography. Sed Geol 284:117–132
Dong Y, Xiao L, Zhou H, Wang C, Zheng J (2010a) The Tertiary evolution of the prolific Nanpu Sag of Bohai Bay Basin, China: constraints from volcanic records and tectono–stratigraphic sequences. GSA Bull 122:609–626
Do Campo M, del Papa C, Nieto F, Hongn F, Petrinovic I (2010) Integrated analysis for constraining palaeoclimatic and volcanic influences on clay–mineral assemblages in orogenic basins (Palaeogene Andean foreland, Northwestern Argentina). Sed Geol 228(3–4):98–112
Dutton S (2008) Calcite cement in Permian deep-water sandstones, Delaware Basin, west Texas: Origin, distribution, and effect on reservoir properties. AAPG Bull 92(6):765–787. https://doi.org/10.1306/01280807107
Dott RH (1964) Wacke, graywacke and matrix; what approach to immature sandstone classification? J Sediment Res 34(3):625–632
Dong Y, Xiao L, Zhou H, Wang C, Zheng J (2010b) The tertiary evolution of the prolific Nanpu sag, Bohai Bay Basin, China: constraints from volcanic record and tecton0- stratigraphic sequences. Geol Soc Am Bull 122:609–626
Folk R, Andrews P, Lewis D (1970) Detrital sedimentary rock classification and nomenclature for use in New Zealand. NZ J Geol Geophys 13(4):937–968
Feng Y, Jiang S, Hu S, Li S, Lin C, Xie X (2016) Sequence stratigraphy and importance of syn-depositional structural slope-break for the architecture of Paleogene syn-rift lacustrine strata, Bohai Bay Basin E China. Mar Petrol Geol 69:183–204
Gong ZS (1997) Giant offshore oil and gas fields in China. Petroleum Industry Press, Beijing (article in Chinese with an abstract in English)
Gluyas J, Cade CA (1997) Prediction of porosity in compacted sands. AAPG Memoir 69:19–28
Guo Y, Pang X, Dong Y, Jiang Z, Chen D, Jiang F (2013) Hydrocarbon generation and migration in the Nanpu Sag, Bohai Bay Basin, eastern China: insight from basin and petroleum system modelling. J Asian Earth Sci 77:140–150
Gao Y, Zhang J, Li H, Yu X (2016) Diagenesis and porosity evaluation of deep Es32+3 formation in Gaoshangpu oilfield Nanpu Sag. Fault-Block Oil Gas Field 23(6):703–708
Guo J, Xu J, Guo F, Li J, Pang X, Dong Y, Hu T (2016) Functional-element constraint hydrocarbon distribution model and its application in the 3rd member of Dongying Formation, Nanpu Sag, Bohai Bay Basin, eastern China. J Petrol Sci Eng 139:71–84
Gawthorpe RL, Leeder MR, Kranis H, Skourtsos E, Andrews JE, Henstra GA, Stamatakis M (2018) Tectono-sedimentary evolution of the Plio-Pleistocene Corinth rift Greece. Basin Res 30(3):448–479
Hammer E, Mørk MBE, Næss A (2010) Facies controls on the distribution of diagenesis and compaction in fluvial-deltaic deposits. Mar Pet Geol 27(8):1737–1751
Hyodo A, Kozdon K, Pollington DA, Valley W (2014) Evolution of quartz cementation and burial history of Eau Clair Formation based on in situ oxygen isotope analysis of quartz overgrowth. Chem Geol 384:168–180
Jiang H, Wang H, Lin ZL, Fang XX, Zhao S, Ren GY (2009) Periodic rifting activity and its controlling on sedimentary filling of Paleogene period in Nanpu Sag. Acta Sedimentol Sin 27:976–982
Jiang ZX, Liang C, Wu J, Zhang JG, Zhang WZ, Wang YS, Chen X (2013) Several issues in sedimentological studies on hydrocarbon-bearing fine-grained sedimentary rocks. Acta Petrolei Sin 34(6):1031–1039
Lei Y, Luo X, Song G, Zhang L, Hao X, Yang W, Yang B (2014) Quantitative characterization of connectivity and conductivity of sandstone carriers during secondary petroleum migration, applied to the Third Member of Eocene Shahejie Formation, Dongying Depression, Eastern China. Mar Pet Geol 51:268–285
Li H (1995) Interpretation of stratigraphic inclination logging data in sedimentary studies. J Sed 1:82–87
Li S, Zhao G, Dai L, Zhou L, Liu X, Suo Y, Santosh M (2012) Cenozoic faulting of the Bohai Bay Basin and its bearing on the destruction of the eastern North China Craton. J Asian Earth Sci 47:80–93
Li J, Zhang J, Sun S, Zhang K, Du D, Sun Z, Wang G (2018) Sedimentology and mechanism of a lacustrine syn-rift fan delta system: a case study of the Paleogene Gaobei Slope Belt, Bohai Bay Basin, China. Mar Pet Geol 98:477–490
Liu H, Meng J, Banerjee S (2017) Estimation of palaeo-slope and sediment volume of a lacustrine rift basin: a semi-quantitative study on the southern steep slope of the Shijiutuo Uplift, Bohai Offshore Basin, China. J Asian Earth Sci 147:148–163
Lu C, Liu Z, Jia H, Dai Q, Li M, Ren M, Wang S (2018) The controls of geomorphology and sediment supply on sequence stratigraphic architecture and sediment partitioning of the lacustrine rift basin in the Es3 of Liuzan area, Nanpu Sag, Bohai Bay Basin China. Aust J Earth Sci 65(2):275–301
Loucks R, Dodge M, Galloway W (1984) Regional controls on diagenesis and reservoir quality in lower Tertiary sandstones along the Texas Gulf Coast: Part 1. Concepts and principles.
Moore D, Reynolds RC (1997) X-ray diffraction and the identification and analysis of clay minerals, 2nd edn. Oxford University Press Inc, Oxford, p 371
Makeen YM, Abdullah WH, Ayinla HA, Hakimi MH, Sia SG (2016) Sedimentology, diagenesis and reservoir quality of the upper Abu Gabra Formation sandstones in the Fula Sub-basin, Muglad Basin, Sudan. Mar Pet Geol 77:1227–1242
Miall AD (1990) Principal of sedimentary basin analysis, 2nd edn. Springer-Verlg, New York, p 668
Miall AD (1978) Tectonic setting and syndepositional deformation of molasse and other nonmarine-paralic sedimentary basins. Can J Earth Sci 15(10):1613–1632
Morad S, Al-Ramadan K, Ketzer JM, De Ros LF (2010) The impact of diagenesis on the heterogeneity of sandstone reservoirs: a review of the role of depositional facies and sequence stratigraphy. AAPG Bull 94(8):1267–1309
Pettijohn F, Potter P, Siever R (2012) Sand and sandstone. Springer Science & Business Media, Berlin
Siever R (2007) Arkose. McGraw Hill encyclopedia of science and technology, 10th edn. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 190–191
Kerr PF (1977) Optical mineralogy. Mc Graw-Hill Book Company, New York
Qi J, Yang Q (2010) Cenozoic structural deformation and dynamic processes of the Bohai Bay basin province China. Marine Petrol Geol 27(4):757–771
Ramm M (2000) Reservoir quality and its relationship to facies and provenance in Middle to Upper Jurassic sequences, northeastern North Sea. Clay Miner 35(1):77–77
Rossi C, Kälin O, Arribas J, Tortosa A (2002) Diagenesis, provenance and reservoir quality of Triassic TAGI sandstones from Ourhoud field, Berkine (Ghadames) Basin Algeria. Mar Petrol Geol 19(2):117–142
Saiag J, Brigaud B, Portier E, Desaubliaux G (2016) Sedimentological control on the diagenesis and reservoir quality of the tidal sandstone of the Upper Cap Hay Formation (Permian, Bonaparte Basin, Australia). Mar Pet Geol 77:597–624
Scholz CA, Rosendahl BR, Scott DL (1990) Development of coarse-grained facies in lacustrine rift basins: examples from East Africa. Geology 18(2):140–144
Wang H, Wang F, Zhou H, Dong Y, Wang J, Ceng G, Chen L (2002) Evolutionary dynamics and formation-deposition dynamics of Nanpu sag. China University of Geosciences Press, Wuhan, p 182
Worden RH, Morad S (2003) Clay mineral cements in sandstones. Blackwell Pub, New York
Walker R, Cant DG (1984) Sandy fluvial system. In: Walker RG (Eds) Facies models, 2nd edition, Geoscience Canada reprint series 1:71–89
Yuan G, Gluyas J, Cao Y, Oxtoby N, Jia Z, Wang Y, Li X (2015a) Diagenesis and reservoir quality evolution of the Eocene sandstones in the northern Dongying Sag, Bohai Bay Basin, East China. Mar Pet Geol 62:77–89
Yuan G, Cao Y, Gluyas J, Li X, Xi K, Wang Y, Oxtoby NH (2015b) Feldspar dissolution, authigenic clays, and quartz cements in open and closed sandstone geochemical systems during diagenesis: typical examples from two sags in Bohai Bay Basin East China. AAPG Bull 99(11):2121–2154
Yuan G, Cao Y, Zhang Y, Gluyas J (2017) Diagenesis and reservoir quality of sandstones with ancient “deep” incursion of meteoric freshwater-An example in the Nanpu Sag, Bohai Bay Basin, East China. Mar Pet Geol 82:444–464
Zhu GY, Zhang SC, Wang YJ, Wang ZJ, Zheng HJ, Xiong Y, Zhang B (2011) Forming condition and enrichment mechanism of the Nanpu Oilfield in Bohai Bay Basin China. Acta Geol Sin 85(1):97–113
Zhang WC, He L, Li HJ, Meng YL, Yang FB (2008) Genesis and distribution of secondary porosity in the deep horizon of Gaoliu area Nanpu Sag. Petrol Explor Dev 35(3):308–312
Zhang J, Jiang Z, Gierlowski-Kordesch E, Xian B, Li Z, Wang S, Wang X (2017) A double-cycle lake basin formed in extensional to transtentional setting: the Paleogene Nanpu Sag, Bohai Bay Basin, China. Sed Geol 349:15–32
Acknowledgements
Muhammad Kashif would like to thank, China scholarship council (CSC) China for granting me a full scholarship (2015–2018) to carry out the research. This study was funded by the Natural Science Foundation of China Project (No. 41602138), National Science and Technology Special Grant (No. 2016ZX05006-007), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation-funded project (2015M580617; 2017T100524). The anonymous reviewers are sincerely acknowledged for their helpful comments and suggestions on an earlier version of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kashif, M., Cao, Y., Yuan, G. et al. Sedimentology of Shahejie Formation, Bohai Bay Basin: a case study of Es1 member in Nanpu Sag. Carbonates Evaporites 35, 52 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13146-020-00579-4
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13146-020-00579-4