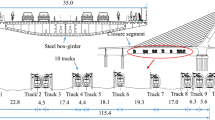
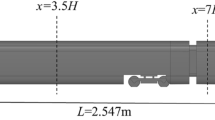
Abstract
Serviceability and running safety of the high-speed train on/through a bridge are of major concern in China. Due to the uncertainty chain of the train dynamic analysis in crosswinds originating mainly from the aerodynamic assessment, this paper primarily reviews five meaningful progresses on the aerodynamics of the train-bridge system done by Wind Tunnel Laboratory of Central South University in the past several years. Firstly, the flow around the train and the uncertainty origin of the aerodynamic assessment are described from the fluid mechanism point of view. After a brief introduction of the current aerodynamic assessment methods with their strengths and weaknesses, a new-developed TRAIN-INFRASTRUCTURE rig with the maximum launch speed of 35 m/s is introduced. Then, several benchmark studies are presented, including the statistic results of the characterized geometry parameters of the currently utilized bridge-decks, the aerodynamics of the train, and the aerodynamics of the flat box/truss bridge-decks. Upon compared with the foregoing mentioned benchmarks, this paper highlights the aerodynamic interference of the train-bridge system associated with its physical natures. Finally, a porosity- and orientation-adjustable novel wind barrier with its effects on the aerodynamics of the train-bridge system is discussed.
摘要
本文主要综述了中南大学工程研究中心在桥梁-列车系统横风气动特性研究领域的重要成果。 首先,从流体力学的角度分析了列车周围的流场特性,从而揭示了目前高速列车横风气动力评估方法 的主要误差来源。然后,介绍了现场实测,数值模拟,动、静模型风洞实验等四种列车气动力评估方 法及其优缺点。同时介绍了中南大学风工程研究中心最新开发的列车-线路系统动模型实验装置。为 深化研究桥梁和列车之间的气动干扰规律。本文首先详细论述了与桥梁-列车系统横风气动特性相关 的基础研究成果,主要包括既有高速铁路桥梁特征几何参数的统计结果,简化列车的气动特性,以及 大跨度扁平箱梁和桁架主梁的气动特性。在上述研究的基础上,重点讨论了扁平箱梁和桁架主梁与列 车之间的气动干扰规律。最后,对中南大学风工程研究中心开发的可调风向和透风率的新型风屏障及 其相关研究结果进行了详细介绍。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
LI Huan, HE Xu-hui, WANG Han-feng, KAREEM A. Aerodynamics of a scale model of a high-speed train on a streamlined deck in cross winds [J]. Journal of Fluids and Structures, 2019, 91: 102717. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfluidstructs.2019.102717.
HU Nan, DAI Gong-lian, YAN Bin, LIU Ke. Recent development of design and construction of medium and long span high-speed railway bridges in China [J]. Engineering Structures, 2014, 74: 233–241. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engstruct.2014.05.052.
HE Xu-hui, WU Teng, ZOU Yun-feng, CHEN Frank Y., GUO Hui, YU Zhi-wu. Recent developments of high-speed railway bridges in China [J]. Structure and Infrastructure Engineering, 2017a, 13(12): 1584–1595. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/15732479.2017.1304429.
LI Yong-le, HU Peng, XU Xin-yu, QIU Jun-jie. Wind characteristics at bridge site in a deep-cutting gorge by wind tunnel test [J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2017, 160: 30–46. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jweia.2016.11.002.
CHELI F, CORRADI R, ROCCHI D, MAESTRINI E. Wind tunnel tests on train scale models to investigate the effect of infrastructure scenario [J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2010a, 98(6, 7): 353–362. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/jjweia.2010.01.001.
TSI, EC. Technical specification for interoperability of the trans-european high speed rail system. european law [S]. Official Journal of the European Communities, 2008.
BAKER C. The flow around high speed trains [J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2010a, 98(6, 7): 277–298. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/jjweia.2009.11.002.
BAKER C. The simulation of unsteady aerodynamic cross wind forces on trains [J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2010b, 98(2): 88–99. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jweia.2009.09.006.
CEN. Railway applications-aerodynamics-part 6: Requirements and test procedures for cross wind assessment [S]. 2018.
CHELI F, RIPAMONTI F, ROCCHI D, TOMASINI G. Aerodynamic behaviour investigation of the new EMUV250 train to cross wind [J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2010b, 98(4, 5): 189–201. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/jjweia.2009.10.015.
NOGUCHI Y, SUZUKI M, BAKER C, NAKADE K. Numerical and experimental study on the aerodynamic force coefficients of railway vehicles on an embankment in crosswind [J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2019, 184: 90–105. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jweia.2018.11.019.
TOMASINI G, GIAPPINO S, CORRADI R. Experimental investigation of the effects of embankment scenario on railway vehicle aerodynamic coefficients [J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2014, 131: 59–71. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jweia.2014.05.004.
TIAN Hong-qi. Review of research on high-speed railway aerodynamics in China [J]. Transportation Safety and Environment, 2019, 1: 1–21. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/tse/tdz014.
LU Chun-fang. A discussion on technologies for improving the operational speed of high-speed railway networks [J]. Transportation Safety and Environment, 2019, 1: 22–36. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/tse/tdz003.
TAO Yu, YANG Ming-zhi, QIAN B, WU Fan, WANG Tian-tian. Numerical and experimental study on ventilation panel models in a subway passenger compartment [J]. Engineering, 2019, 5(2): 329–336. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eng.2018.12.007.
WANG Tian-tian, WU Fan, YANG Ming-zhi, JI Peng, QIAN B. Reduction of pressure transients of high-speed train passing through a tunnel by cross-section increase [J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2018, 183: 235–242. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/jjweia.2018.11.001.
CHEN Zheng-wei, LIU Tang-hong, YAN Chun-guang, YU Miao, GUO Zi-jian, WANG Tian-tian. Numerical simulation and comparison of the slipstreams of trains with different nose lengths under crosswind [J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2019, 190: 256–272. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/zj.jweia.2019.05.005.
BAKER C. Ground vehicles in high cross winds, part I: steady aerodynamic forces [J]. Journal of Fluids and Structures, 1991a, 5(1): 69–90. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0889-9746(91)80012-3.
BAKER C. Ground vehicles in high cross winds part II: unsteady aerodynamic forces [J]. Journal of Fluids and Structures, 1991b, 5(1): 91–111. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0889-9746(91)80013-4.
BAKER C. Ground vehicles in high cross winds part III: The interaction of aerodynamic forces and the vehicle system [J]. Journal of Fluids and Structures, 1991c, 5(2): 221–241. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0889-9746(91)90478-8.
LI Yong-le, QIANG Shi-zhong, LIAO Hai-li, XU You-lin. Dynamics of wind-rail vehicle-bridge systems [J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2005, 93(6): 483–507. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/jjweia.2005.04.001.
XU You-lin, DING Quan-shun. Interaction of railway vehicles with track in cross-winds [J]. Journal of Fluids and Structures, 2006, 22(3): 295–314. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfluidstructs.2005.11.003
BAKER C. A framework for the consideration of the effects of crosswinds on trains [J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2013, 123: 130–142. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jweia.2013.09.015.
BAKER C, CHELI F, ORELLANO A, PARADOT N, PROPPE C, ROCCHI D. Cross-wind effects on road and rail vehicles [J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2009, 47(8): 983–1022. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/00423110903078794.
BAKER C. A review of train aerodynamics Part 1-Fundamentals [J]. The Aeronautical Journal, 2014a, 118(1201): 201–228. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1017/S000192400000909X.
BAKER C. A review of train aerodynamics, Part 2-Applications [J]. The Aeronautical Journal, 2014b, 118(1202): 345–382. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1017/S0001924000009179.
DING Y, STERLINGS M, BAKER C. An alternative approach to modelling train stability in high cross winds [J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part F: Journal of Rail and Rapid Transit, 2008, 222(1): 85–97. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1243/09544097JRRT138.
GIAPPINO S, ROCCHI D, SCHITO P, TOMASINI G. Cross wind and rollover risk on lightweight railway vehicles [J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2016, 153: 106–112. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jweia.2016.03.013.
OLMOS J, ASTIZ M. Improvement of the lateral dynamic response of a high pier viaduct under turbulent wind during the high-speed train travel [J]. Engineering Structures, 2018, 165: 368–385. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engstruct.2018.03.054.
YU Meng-ge, ZHANG Ji-ye, ZHANG Ke-yue, ZHANG Wei-hua. Crosswind stability analysis of a high-speed train based on fuzzy random reliability [J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part F: Journal of Rail and Rapid Transit, 2015, 229(8): 875–887. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/0954409714524548.
XU You-lin, XIA He, YAN Quan-sheng. Dynamic response of suspension bridge to high wind and running train [J]. Journal of Bridge Engineering, 2003, 8: 46–55. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)1084-0702(2003)8:1(46).
XU You-lin, ZHANG Nan, XIA He. Vibration of coupled train and cable-stayed bridge system in cross wind [J]. Journal of Engineering Structure, 2004, 26: 1389–1406. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engstruct.2004.05.005.
XU You-lin, GUO Wei-wei, CHEN Jun, SHUM K, XIA He. Dynamic response of suspension bridge to typhoon and trains. I: Field measurement results [J]. Journal of Structural Engineering, 2007, 133(1): 3–11. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9445(2007)133:1(3).
GUO Wei-wei, XU You-lin, XIA He, ZHANG Wen-shou, SHUM K. Dynamic response of suspension bridge to typhoon and trains. II: Numerical results [J]. Journal of Structural Engineering, 2007, 133(1): 12–21. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9445(2007)133:1(12).
XIA He, GUO Wei-wei, ZHANG Nan, SUN Guo-jun. Dynamic analysis of a train-bridge system under wind action [J]. Computer and Structures, 2008, 86: 1845–1855. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruc.2008.04.007.
LI Xiao-zhen, WANG Ming, XIAO Jun, ZOU Qi-yang, LIU De-jun. Experimental study on aerodynamic characteristics of high-speed train on a truss bridge: A moving model test [J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2018, 179: 26–38. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/jjweia.2018.05.012.
BOCCIOLONE M, CHELI F, CORRADI R, MUGGIASCA S, TOMASINI G. Crosswind action on rail vehicles: Wind tunnel experimental analyses [J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2008, 96(5): 584–610. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/jjweia.2008.02.030.
CATANZARO C, CHELI F, ROCCHI D, SCHITO P, TOMASINI G. High-speed train crosswind analysis: CFD study and validation with wind-tunnel tests [C]//International Conference on Engineering Conferences International. Springer, 2010: 99–112. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-20122-1_6.
DORIGATTI F, STERLING M, BAKER C, QUINN A. Crosswind effects on the stability of a model passenger train—A comparison of static and moving experiments [J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2015, 138: 36–51. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/jjweia.2014.11.009.
KIKUCHI K, SUZUKI M. Study of aerodynamic coefficients used to estimate critical wind speed for vehicle overturning [J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2015, 147: 1–17. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jweia.2015.09.003.
PREMOLI A, ROCCHI D, SCHITO P, TOMASINI G. Comparison between steady and moving railway vehicles subjected to crosswind by CFD analysis [J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2016, 156: 29–40. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/jjweia.2016.07.006.
COPLEY J. The three-dimensional flow around railway trains [J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 1987, 26(1): 21–52. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-6105(87)90034-1.
CHIU T, SQUIRE L. An experimental study of the flow over a train in a crosswind at large yaw angles up to 90° [J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 1992, 45(1): 47–74. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-6105(92)90005-U.
HEMIDA H, KRAJNOVIĆ S. Exploring flow structures around a simplified ICE2 train subjected to a 30 side wind using LES [J]. Engineering Applications of Computational Fluid Mechanics, 2009, 3(1): 28–41. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/19942060.2009.11015252.
BELL J, BURTON D, THOMPSON M, HERBST A, SHERIDAN J. Wind tunnel analysis of the slipstream and wake of a high-speed train [J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2014, 134: 122–138. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/jjweia.2014.09.004.
SCHETZ J. Aerodynamics of high-speed trains [J]. Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics, 2001, 33(1): 371–414. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.fluid.33.1.371.
NIU Ji-qiang, ZHOU Dan, LIANG Xi-feng. Numerical investigation of the aerodynamic characteristics of highspeed trains of different lengths under crosswind with or without windbreaks [J]. Engineering Applications of Computational Fluid Mechanics, 2018, 12(1): 195–215. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/19942060.2017.1390786.
XIA Chao, WANG Han-feng, BAO Di, YANG Zhi-yang. Unsteady flow structures in the wake of a high-speed train [J]. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 2018, 98: 381–396. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expthermflusci.2018.06.010.
GAWTHORPE R. Aerodynamics of trains in the open air [J]. Railway Engineer International, 1978, 3(3): 7–12. DOI: http://pascal-francis.inist.fr/vibad/index.php?action=getRecordDetail&idt=PASCAL7980168430.
BAKER C. The determination of topographical exposure factors for railway embankments [J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 1985, 21(1): 89–99. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-6105(85)90035-2.
COOPER R. The effect of cross-winds on trains [J]. Journal of Fluids Engineering, 1981, 103(1): 170–178. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1115/1.3240768.
MATSCHKE G, HEINE C. Full scale tests on side wind effects on trains. Evaluation of aerodynamic coefficients and efficiency of wind breaking devices [C]// TRANSAERO-A European Initiative on Transient Aerodynamics for Railway System Optimisation. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 2002: 27–38. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-45854-83.
GALLAGHER M, MORDEN J, BAKER C, SOPER D, QUINN A, HEMIDA H, STERLING M. Trains in crosswinds-Comparison of full-scale on-train measurements, physical model tests and CFD calculations [J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2018, 175: 428–444. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/jjweia.2018.03.002.
KO Y, CHEN C, HOE T, WANG S. Field measurements of aerodynamic pressures in tunnels induced by high speed trains [J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2012, 100(1): 19–29. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jweia.2011.10.008.
SUZUKI M, IDO A, SAKUMA Y, KAJIYAMA H. Full-scale measurement and numerical simulation of flow around high-speed train in tunnel [J]. Journal of Mechanical Systems for Transportation and Logistics, 2008, 1(3): 281–292. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1299/jmtl.1.281.
LIU Tang-hong, TIAN Hong-qi, LIANG Xi-feng. Aerodynamic effects caused by trains entering tunnels [J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering, 2010, 136(9): 846–853. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)TE.1943-5436.0000146.
BAKER C, DALLEY S, JOHNSON T, QUINN A, WRIGHT N. The slipstream and wake of a high-speed train [J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part F: Journal of Rail and Rapid Transit, 2001, 215(2): 83–99. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1243/0954409011531422.
HEMIDA H, KRAJNOVIĆ S. LES study of the influence of a train-nose shape on the flow structures under cross-wind conditions [J]. Journal of Fluids Engineering, 2008, 130(9). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1115/1.2953228.
MORDEN J, HEMIDA H, BAKER C. Comparison of RANS and detached eddy simulation results to wind-tunnel data for the surface pressures upon a class 43 high-speed train [J]. Journal of Fluids Engineering, 2015, 137(4): 041108. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4029261.
CHEN Zheng-wei, LIU Tang-hong, JIANG Zhen-hua, GUO Zi-jian, ZHANG Jie. Comparative analysis of the effect of different nose lengths on train aerodynamic performance under crosswind [J]. Journal of Fluids and Structures, 2018, 78: 69–85. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfluidstructs.2017.12.016.
NIU Ji-qiang, ZHOU Dan, LIU Tang-hong, LIANG Xi-feng. Numerical simulation of aerodynamic performance of a couple multiple units high-speed train [J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2017, 55(5): 681–703. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/00423114.2016.1277769.
ZHANG Jie, LI Jing-juan, TIAN Hong-qi, GAO Guan-jun, SHERIDAN J. Impact of ground and wheel boundary conditions on numerical simulation of the high-speed train aerodynamic performance [J]. Journal of Fluids and Structures, 2016, 61: 249–261. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfluidstructs.2015.10.006.
GUO Zi-jian, LIU Tang-hong, YU Miao, CHEN Zheng-wei, LI Wen-hui, HUO Xiao-shuai, LIU Hong-kang. Numerical study for the aerodynamic performance of double unit train under crosswind [J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2019, 191: 203–214. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jweia.2019.06.014.
KHIER W, BREUER M, DURST F. Flow structure around trains under side wind conditions: A numerical study [J]. Computers & Fluids, 2000, 29(2): 179–195. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-7930(99)00008-0.
MA Cun-ming, DUAN Qing-song, LI Qiu-sheng, CHEN Ke-jian, LIAO Hai-li. Buffeting forces on static trains on a truss girder in turbulent crosswinds [J]. Journal of Bridge Engineering, 2018, 23(11): 04018086. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)BE.1943-5592.0001305.
HE Xu-hui, ZOU Yun-feng, WANG Han-feng, HAN Yan, SHI Kang. Aerodynamic characteristics of a trailing rail vehicles on viaduct based on still wind tunnel experiments [J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2014, 135: 22–33. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jweia.2014.10.004.
KWON H, PARK Y, LEE D, KIM M. Wind tunnel experiments on Korean high-speed trains using various ground simulation techniques [J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2001, 89(13): 1179–1195. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-6105(01)00107-6.
SUZUKI M, TANEMOTO K, MAEDA T. Aerodynamic characteristics of train/vehicles under cross winds [J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2003, 91(1, 2): 209–218. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-6105(02)00346-X.
SCHOBER M, WEISE M, ORELLANO A, DEEG P, WETZEL W. Wind tunnel investigation of an ICE 3 endcar on three standard ground scenarios [J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2010, 98(6, 7): 345–352. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jweia.2009.12.004.
BARCALA M, MESEGUER J. An experimental study of the influence of parapets on the aerodynamic loads under cross wind on a two-dimensional model of a railway vehicle on a bridge [J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part F: Journal of Rail and Rapid Transit, 2007, 221(4): 487–494. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1243/09544097JRRT53.
BARCALA M, MESEGUER J. Visualization study of the influence of parapets on the flow around a train vehicle under cross winds [J]. WIT Transactions on The Built Environment, 2008, 103: 797–806. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2495/CR080771.
XIANG Huo-yue, LI Yong-le, LIAO Hai-li, LI Cui-juan. An adaptive surrogate model based on support vector regression and its application to the optimization of railway wind barriers [J]. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization, 2017, 55(2): 701–713. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-016-1528-9.
XIANG Huo-yue, LI Yong-le, WANG Bin. Aerodynamic interaction between static vehicles and wind barriers on railway bridges exposed to crosswinds [J]. Wind and Structures, 2015, 20(2): 237–247. DOI: https://doi.org/10.12989/was.2015.20.2.237.
OGUETA M, FRANCHINI S, ALONSO G. Effects of bird protection barriers on the aerodynamic and aeroelastic behaviour of high speed train bridges [J]. Engineering Structures, 2014, 81: 22–34. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engstruct.2014.09.035.
HE Xu-hui, SHI Kang, WU Teng, ZOU Yun-feng, WANG Han-feng, QIN Hong-xi. Aerodynamic performance of a novel wind barrier for train-bridge system [J]. Wind and Structures, 2016, 23(3): 171–189. DOI: https://doi.org/10.12989/was.2016.23.3.171.
SAYYAADI H, SHOKOUHI N. A new model in rail-vehicles dynamics considering nonlinear suspension components behavior [J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2009, 51(3): 222–232. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2009.01.003.
LI Yong-le, HU Peng, XU You-lin, ZHANG, Ming-jin, LIAO Hai-li. Wind loads on a moving vehicle-bridge deck system by wind-tunnel model test [J]. Wind and Structures, 2014, 19(2): 145–167. DOI: https://doi.org/10.12989/was.2014.19.2.145.
CHOI H, LEE J, PARK H. Aerodynamics of heavy vehicles [J]. Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics, 2014, 46: 441–468. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-fluid-011212-140616.
POLHAMUSL E. C. Effect of flow incidence and Reynolds number on low-speed aerodynamic characteristics of several noncircular cylinders with applications to directional stability and spinning [R]. Technical Report Archive & Image Library, 1985. DOI: https://ntrs.nasa.gov/search.jsp?R=19930085064.
CARASSALE L, FREDA A, MARRÈ-BRUNENGHI M. Experimental investigation on the aerodynamic behavior of square cylinders with rounded corners [J]. Journal of Fluids & Structures, 2014, 44(7): 195–204. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfluidstructs.2013.10.010
HINSBERG N P, SCHEWE G, JACOBS M. Experiments on the aerodynamic behaviour of square cylinders with rounded corners at Reynolds numbers up to 12 million [J]. Journal of Fluids and Structures, 2017, 74: 214–233. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfluidstructs.2017.08.002
SCHEWE G. On the force fluctuations acting on a circular cylinder in crossflow from subcritical up to transcritical Reynolds numbers [J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1983, 133: 265–285. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022112083001913
HE Xu-hui, LI Huan, WANG Han-feng, FANG Dong-xu, LIU Meng-ting. Effects of geometrical parameters on the aerodynamic characteristics of a streamlined flat box bridge-deck [J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2017, 170: 56–67. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jweia.2017.08.009.
ERICKSON G. High angle-of-attack aerodynamics [J]. Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics, 1995, 27(1): 45–88. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.fl.27.010195.000401.
ERICSSON L, REDING J. Fluid mechanics of dynamic stall part I. Unsteady flow concepts [J]. Journal of Fluids and Structures, 1988, 2(1): 1–33. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0889-9746(88)90116-8.
NAUDASCHER E, WANG Yi-nan. Flow-induced vibrations of prismatic bodies and grids of prisms [J]. Journal of Fluids & Structures, 1993, 7(4): 341–373. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1006/jfls.1993.1021.
DENIZ S, STAUBLI T. Oscillating rectangular and octagonal profiles: Interaction of leading-and trailing-edge vortex formation [J]. Journal of Fluids and Structures, 1997, 11(1): 3–31. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1006/jfls.1996.0065.
MANNINI C, MARRA A, PIGOLOTTI L, BARTOLI G. The effects of free-stream turbulence and angle of attack on the aerodynamics of a cylinder with rectangular 5: 1 cross section [J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2017, 161: 42–58. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jweia.2016.12.001.
MANNINI C, ŠODA A, SCHEWE G. Numerical investigation on the three-dimensional unsteady flow past a 5: 1 rectangular cylinder [J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2011, 99(4): 469–482. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jweia.2010.12.016.
PAÏDOUSSIS M, PRICE S, de LANGRE E. Fluid-structure interactions: Cross-flow-induced instabilities [M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2010.
TAYLOR Z, PALOMBI E, GURKA R, KOPP G. Features of the turbulent flow around symmetric elongated bluff bodies [J]. Journal of Fluids and Structures, 2011, 27(2): 250–265. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfluidstructs.2010.10.004.
ITO Y, SHIRATO H, MATSUMOTO M. Coherence characteristics of fluctuating lift forces for rectangular shape with various fairing decks [J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2014, 135: 34–45. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jweia.2014.10.003.
WANG Ming, LI Xiao-zhen, XIAO Jun, ZOU Qi-yang, SHA Hai-qing. An experimental analysis of the aerodynamic characteristics of a high-speed train on a bridge under crosswinds [J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2018, 177: 92–100. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jweia.2018.03.021.
ZOU Yun-feng, HE Xu-hui, ZOU Si-min, HUANG Yong-ming, ZUO Tai-hui. A U-shape launching ramp and method for aerodynamic characteristic testing of running train-bridge system [J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2018, 15: 1747–1753. DOI: https://doi.org/10.19713/j.cnki.43-1423/u.2018.07.016.
HE Xu-hui, ZOU Si-min. Wind tunnel test on aerodynamic characteristics of high-speed train running on bridge under crosswind [C]// Word Transport Convention. Beijing, 2019: 13–16.
FUJII T, MAEDA T, ISHIDA H, IMAI T, TANEMOTO K, SUZUKI M. Wind-induced accidents of train/vehicles and their measures in Japan [J]. Quarterly Report of RTRI, 1999, 40(1): 50–55. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2219/rtriqr.40.50.
HOPPMANN U, KOENIG S, TIELKES T, MATSCHKE G. A short-term strong wind prediction model for railway application: design and verification [J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2002, 90(10): 1127–1134. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-6105(02)00226-X.
IMAI T, FUJII T, TANEMOTO K, SHIMAMURA T, MAEDA T, ISHIDA H, HIBINO Y. New train regulation method based on wind direction and velocity of natural wind against strong winds [J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2002, 90(12–15): 1601–1610. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-6105(02)00273-8.
ZHANG Tian, XIA He, GUO Wei-wei. Analysis on running safety of train on bridge with wind barriers subjected to cross wind [J]. Wind Structures, 2013, 17(3): 203–225. DOI: https://doi.org/10.12989/was.2013.17.2.203.
GUO Wei-wei, XIA He, KAROUMI R, ZHANG Tian, LI Xiao-zhen. Aerodynamic effect of wind barriers and running safety of trains on high-speed railway bridges under cross winds [J]. Wind Structures, 2015, 20(2): 213–236. DOI: https://doi.org/10.12989/was.2015.20.2.213.
AVILA-SANCHEZ S, LOPEZ-GARCIA O, CUERVA A, MESEGUER J. Characterisation of cross-flow above a railway bridge equipped with solid windbreaks [J]. Engineering Structures, 2016, 126: 133–146. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engstruct.2016.07.035.
HE Xu-hui, ZHOU Lei, CHEN Zheng-wei, JING Hai-quan, ZOU Yun-feng, WU Teng. Effect of wind barriers on the flow field and aerodynamic forces of a train-bridge system [J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part F: Journal of Rail and Rapid Transit, 2019, 233(3): 283–297. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/0954409718793220.
HASHMI S, HEMIDA H, SOPER D. Wind tunnel testing on a train model subjected to crosswinds with different windbreak walls [J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2019, 195: 104013. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jweia.2019.104013.
MOHEBBI M, REZVANI M. Analysis of the effects of lateral wind on a high speed train on a double routed railway track with porous shelters [J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2019, 184: 116–127. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jweia.2018.11.011.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Project(2017YFB1201204) supported by National Key R & D Program of China; Projects(51925808, U1934209) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, Xh., Li, H. Review of aerodynamics of high-speed train-bridge system in crosswinds. J. Cent. South Univ. 27, 1054–1073 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-020-4351-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-020-4351-9