Abstract
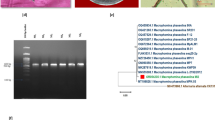
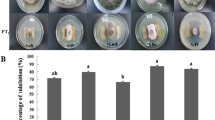
Role of rhizobacteria and zinc (Zn) was investigated in the management of charcoal rot disease in mungbean [Vigna radiata (L.) Wilczek] caused by Macrophomina phaseolina (Tassi) Goid. In vitro, screening tests with eight rhizobacteria [Bacillus subtilis (FCBP-0324), B. subtilis (FCBP-0189), Rhizobacter daucus (FCBP-0450), Azospirillum brasilense (FCBP-0025), Azospirillum lipoferum (FCBP-0022), Pseudomonas malophilia (FCBP-0099), Pseudomonas florescense (FCBP-0083) and Ochrobactrum ciceri (FCBP-0727)] were conducted against M. phaseolina and FCBP-0727 were found as the most effective biocontrol agent. Molecular analyses of 16S rDNA combined with cultural and biochemical analyses confirmed FCBP-0727 identification (GeneBank Accession No. LC415039). Cell-free culture filtrate (CFCF) and cell culture of O. ciceri were separated and antifungal trials of both substrates indicated inhibition in mycelial growth and suppression in sclerotia formation, although the CFCF appeared to be more destructive against the pathogen. Ethyl-acetate and chloroform extracts of bacterial secondary metabolites completely halted the growth of M. phaseolina. The GC–MS analysis of CFCF of chloroform extract proved to be rich sources of bioactive fungicide like phthalates, adipic acid, propanoic acid, and linoleic acid. Likewise, CFCF of ethyl acetate also exhibited important organic compounds like phthalates, diisopropylglycol and octasiloxan. Pot experiment revealed that soil inoculation with O. ciceri in combination with Zn (2.5 mg/kg) protected mungbean plants against M. phaseolina through improving photosynthetic pigment, total protein content and activities of antioxidant enzymes (catalase, peroxidase and polyphenol oxidase). The present study will open new vistas for biological management of charcoal rot disease of mungbean using a combination of rhizobacteria and Zn.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelmoteleb A, Troncoso-Rojas R, Gonzalez-Soto T, González-Mendoza D (2017) Antifungical activity of autochthonous Bacillus subtilis isolated from Prosopis juliflora against phytopathogenic fungi. Mycobiology 45:385–391
Atiq M, Asad S, Rafique M, Khan NA, Rehman AU, Younis M, Shafiq M, Ahmad K, Bashir N, Khan WA (2014) Identification of source of resistance in mungbean germplasm against charcoal rot disease. Pak J Phytopathol 26:133–136
Awan ZA, Shoaib A (2019) Combating early blight infection by employing Bacillus subtilis in combination with plant fertilizers. Curr Plant Biol 20:100125
Awan ZA, Shoaib A, Khan KA (2018) Variations in total phenolics and antioxidant enzymes cause phenotypic variability and differential resistant response in tomato genotypes against early blight disease. Sci Hortic 239:216–223
Awan ZA, Shoaib A, Khan KA (2019) Crosstalk of Zn in combination with other fertilizers underpins interactive effects and induces resistance in tomato plants against early blight disease. J Plant Pathol 35:330–340
Azarmi F, Mozafari V, Dahaji PA, Hamidpour M (2016) Biochemical, physiological and antioxidant enzymatic activity responses of pistachio seedlings treated with plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria and Zn to salinity stress. Acta Physiol Plant 38:21
Aziz-ur-Rehman KME, Kaukab S, Saeed S, Aqeel M, Riasat G, Rafiq CM (2019) Prospects of Mungbean as an additional crop in rice wheat system of Punjab Pakistan. Univ J Agric Res 7:136–141
Balouiri M, Sadiki M, Ibnsouda SK (2016) Methods for in vitro evaluating antimicrobial activity: a review. J Pharm Anal 6:71–79
Diamante C, Fiume MZ, Bergfeld WF, Belsito DV, Hill RA, Klaassen CD, Liebler DC, Marks JG, Shank RC, Slaga TJ, Snyder PW, Alan Andersen F (2010) Final safety assessment of thiodipropionic acid and its dialkyl esters as used in cosmetics. Int J Toxicol 29:137–150
Expósito RG, Bruijn ID, Postma J, Raaijmakers JM (2017) Current insights into the role of rhizosphere bacteria in disease suppressive soils. Front Microbiol 8:1–12
Fu LH, Hu KD, Hu LY, Li YH, Hu LB, Yan H, Liu YS, Zhang H (2014) An antifungal role of hydrogen sulfide on the postharvest pathogens Aspergillus niger and Penicillium italicum. PLoS ONE 9:e104206
Ganesan K, Xu B (2018) A critical review on phytochemical profile and health-promoting effects of mungbean (Vigna radiata). Food Sci Hum Wellness 7:11–33
Hafeez B, Khanif YM, Saleem M (2013) Role of zinc in plant nutrition—a review. Am J Exp Agric 3:374–391
Hassan MN, Afghan S, Hassan Z, Hafeez FY (2014) Biopesticide activity of sugarcane associated rhizobacteria: Ochrobactrum intermedium strain NH-5 and Stenotrophomonas maltophilia strain NH-300 against red rot under field conditions. Phytopathol Mediterr 5:27–37
Imran A, Hafeez FY, Fruhling A, Schumann P, Malik KA, Stackebrandt E (2010) Ochrobactrumciceri sp. nov. Isolated from nodules of Cicer arietinum. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:1548–1553
Imran A, Mirza MS, Shah TM, Malik KA, Hafeez FY (2015) Differential response of kabuli and desi chickpea genotypes toward inoculation with PGPR in different soils. Front Microbiol 6:859
Iqbal U, Mukhtar T (2014) Morphological and pathogenic variability among Macrophomina phaseolina isolates associated with mungbean (Vigna radiata L.) Wilczek from Pakistan. Sci World J. Article ID 950175
Jasmine JM, Latha K, Vanaja R (2013) Determination of bioactive components of decholestrate, a polyherbal formulation by GC–MS analysis. TIC 1(e8):12–39
Khan KA, Shoaib A, Arshad Awan Z, Basit A, Hussain M (2018) Macrophomina phaseolina alters the biochemical pathway in Vigna radiata chastened by Zn2+ and FYM to improve plant growth. J Plant Interact 13:131–140
Korejo F, Noreen R, Ali SA, Humayun F, Rahman A, Sultana V, Ehteshamul-haque S (2017) Evaluation of antibacterial and antifungal potential of endophytic fluorescent pseudomonas associated with Salvadora persica L. and Salvadorao oleoides Decne. Pak J Bot 49:1995–2004
Machado PP, Steiner F, Zuffo AM, Machado RA (2018) Could the supply of boron and zinc improve the resistance of potato to early blight? Potato Res 61:169–182
Mazzola M, Cook RJ, Thomashow LS, Weller D, Pierson LS (1992) Contribution of phenazine antibiotic biosynthesis to the ecological competence of Pseudomonads fluorescent in soil habitats. App Environ Microb 58:2616–2624
Nikolov A, Ganchev D (2010) Effect of zinc undecylenates on plant pathogenic fungi. Bulg J Agric Sci 16:220–226
Parthipan B, Suky MGT, Mohan VR (2015) GC–MS analysis of phytocomponents in Pleiospermium alatum (Wall. ex Wight & Arn.) Swingle, (Rutaceae). J Pharma Phytochem 4:216–222
Patel TS, Minocheherhomji FP (2018) Review: plant growth promoting rhizobacteria: blessing to agriculture. Int J Pure Appl Biosci 6:481–492
Priyanka R, Sevugapperuma N (2018) Ochrobactrum ciceri mediated induction of defence genes and antifungal metabolites enhance the biocontrol efficacy for the management of Botrytis leaf blight of Lilium under protected conditions. J Plant Pathol 101:323–337
Raorane CJ, Gavimath CC, Kukreja GP, Kalsekar DP, Kulkarni SM, Ravishankar BE, Hooli RS (2012) Isolation, identification and phylogenetic analysis of phthalic acid degrading bacteria. Int J Biotechnol Res 3:804–809
Reetha AK, Pavani SL, Mohan S (2014) Hydrogen cyanide production ability by bacterial antagonist and their antibiotics inhibition potential on Macrophomina phaseolina (Tassi.) Goid. Int J Curr Microbiol Appl Sci 3:172–178
Sharma RM, Singh RR (2000) Harvesting, postharvest handling and physiology of fruits and vegetables. Postharvest Technol Fruits Veg 1:94–147
Shoaib A, Awan ZA, Khan KA (2019) Intervention of antagonistic bacteria as potential inducer of disease resistance in tomato to mitigate early blight. Sci Hortic 252:20–28
Siddiqui IA, Shaukat SS, Hamid M (2002) Role of zinc in rhizobacteria-mediated suppression of root-infecting fungi and root-knot nematode. J Phytopathol 150:569–575
Syed-Ab-Rahman SF, Carvalhais LC, Chua E, Xiao Y, Wass TJ, Schenk PM (2018) Identification of soil bacterial isolates suppressing different Phytophthora spp. and promoting plant growth. Front Plant Sci 9:1–18
Thakore Y (2006) The biopesticide market for global agricultural use. Ind Biotechnol 2:194–198
Venkatesh VR, Kalaivani K (2014) Gas chromatography and mass spectrometry analysis of Solanum villosum (Mill) (solanaceae) R. Int J Pharm Sci Res 5:5283–5287
Wang Y, Ren W, Li Y, Xu Y, Teng Y, Christie P, Luo Y (2018) Non-targeted metabolomics analysis to unravel the impact of di (2-ethylhexyl) phthalate stress on root exudates of alfalfa (Medicago sativa). Sci Total Environ 646:212–219
Zarmehri SG, Moosavi SG, Zabihi HR, Seghateslami MJ (2013) The effect of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) and zinc fertilizer on forage yield of maize under water deficit stress conditions. Technol J Eng Appl Sci 3:3281–3290
Zhang D, Gao T, Li H, Lei B, Zhu B (2017) Identification of antifungal substances secreted by Bacillus subtilis Z-14 that suppress Gaeumannomyces graminis var. tritici. Biocontrol Sci Technol 27:237–251
Acknowledgements
Authors are thankful to the University of Punjab to provide funding to accomplish this research work. Authors have no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shoaib, A., Ali, H., Javaid, A. et al. Contending charcoal rot disease of mungbean by employing biocontrol Ochrobactrum ciceri and zinc. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 26, 1385–1397 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-020-00817-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-020-00817-y