Abstract
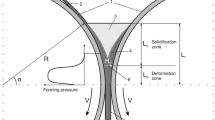
A new twin-roll casting (TRC) process to produce Cu/Invar/Cu clad strips, which have greater application potential, is proposed. The symmetrical cast-rolling zone is divided into two asymmetrical parts by introducing the substrate strip in the middle. The thermal-flow coupled simulation was conducted, and it realized the coupling analysis of casting roll, molten pool, and substrate strip. The results indicate that the kissing point (KP) shape in each part is asymmetric and vortexes are more likely to occur near the KP. Besides, univariate analyses show that the influence of the cast-rolling velocity, substrate preheat temperature and casting temperature on the KP length and average outlet temperature is linear, and the influence of the substrate thickness is nonlinear. Process window prediction models were obtained, which laid the foundation of setting process parameter combinations for providing the required KP length. Furthermore, numerical simulation results indicate that the fluidity of the liquid metal ensures the continuity of production. The macro-structures evolution in the cast-rolling zone indicates that deformation below the KP ensures the quality of the product. Finally, the Cu/Invar/Cu clad strips with metallurgical bonding were fabricated. The ultimate tensile strength and maximum peeling strength are 250 MPa and 126.5 N/mm, respectively. Hence, the TRC process for trimetallic clad strips is developed successfully and stability is basically achieved through equipment design, process window prediction, experimental validation, and bonding strength characterization. These methods can be conducive to the development of other new TRC processes for multiply clad strips.
Graphic Abstract





















Similar content being viewed by others
References
[1] Y. Zhao, W.N. Zhang, X. Liu, Z.Y. Liu, and G.D. Wang: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2016, vol. 47A, pp. 6292–6303.
[2] M. Xu, and M. Zhu: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2016, vol. 47B, pp. 740–48.
[3] C. Ji, H.G. Huang, J.N. Sun, and P. Chen: J. Manuf. Process, 2018, vol. 34, pp. 593–602.
[4] J.J. Park: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2018, vol. 49A, pp. 4748–58.
[5] J. Park, H. Song, J.S. Kim, S.S. Sohn, and S. Lee: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2017, vol. 48A, pp. 57–62.
[6] C. Ji, H.G. Huang, and J.N. Sun: Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 2018, vol. 120, pp. 1305–14.
[7] O. Grydin, G. Gerstein, F. Nurnberger, M. Schaper, and V. Danchenko: J. Manuf. Process, 2013, vol. 15, pp. 501–07.
[8] M. Vidoni, R. Ackermann, S. Richter, and G. Hirt: Adv. Eng. Mater., 2015, vol. 17, pp. 1588–97.
[9] H.G. Huang, Y.K. Dong, M. Yan, and F.S. Du: Trans. Nonferr. Metal Soc., 2017, vol. 27, pp. 1019–25.
[10] T. Haga, K. Okamura, S. Nishida, H. Watari, and K. Matsuzaki: Mater. Sci. Forum, 2017, vol. 879, pp. 671–76.
[11] H.G. Huang, P. Chen, and C. Ji: Mater. Des., 2017, vol. 118, pp. 233–44.
[12] D. Münster, B. Zhang, and G. Hirt: Steel Res. Int., 2016, vol. 88, pp. 1–7.
[13] R. Nakamura, T. Yamabayashi, T. Haga, S. Kumai, and H. Watari: Archives of Materials Science and Engineering, 2010, vol. 41(2), pp. 112–20.
[14] J.J. Park: Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 2016, vol. 93, pp. 491–99.
[15] B.X. Liu, J.Y. Wei, M.X. Yang, F.X. Yin, and K.C. Xu: Vacuum, 2018, vol. 154, pp. 250–58.
[16] D. Münster, and G. Hirt: Metals, 2019, vol. 9, pp. 1156-61.
[17] M. Vidoni, M. Daamen, and G. Hirt: Key Eng. Mater. Trans Tech Publications, 2015, vol. 651, pp. 689–94.
[18] P. Chen, H.G. Huang, C. Ji, X. Zhang, and Z.H. Sun: Trans.Nonferrous Met. Soc. China, 2018, vol. 28, pp. 2460-69.
[19] V.R. Voller, and C. Prakash: Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 1987, vol. 30, pp. 1709–19.
[20] P.K. Penumakala, A.K. Nallathambi, E. Specht, U. Urlau, D. Hamilton, and C. Hamilton: Appl. Therm. Eng., 2018, vol. 134, pp. 275–86.
[21] J.J. Park: Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 2016, vol. 100, pp. 590–98.
[22] H. Zhang, C. Zhou, and C. Wei: ISIJ International, 2017, vol. 57, pp. 1811–20.
[23] M. Stolbchenko, O. Grydin, A. Samsonenko, V. Khvist, and M. Schaper: Forsch Ingenieurwes, 2014, vol. 3, pp. 121–30.
[24] C. Ji, H.G. Huang, J.P. Zhang, and R.D. Zhao: Appl. Therm. Eng., 2019, vol. 158, pp. 113818.
Acknowledgments
This project is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51974278, 51474189), the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province Distinguished Young Fund Project (E2018203446), the Graduate Student Innovation Project of Hebei Province (CXZS201803, CXZZBS2019047), and the China Scholarship Council.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Manuscript submitted October 16, 2019.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ji, C., Huang, H., Zhang, X. et al. Numerical and Experimental Research on Fluid Flow, Solidification, and Bonding Strength During the Twin-Roll Casting of Cu/Invar/Cu Clad Strips. Metall Mater Trans B 51, 1617–1631 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-020-01854-4
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-020-01854-4