Abstract
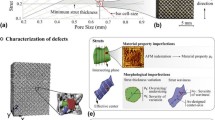
The manufacturing of additives with projection micro litho stereo exposure (PµLSE) has provided an opportunity for the fabrication of metastructures with complex microstructures at micro-nano resolutions. However, the performance evaluation of as-fabricated metastructures is challenging. The benefit of synchrotron radiation-based 3D imaging techniques and advanced image processing methods makes it is feasible to study fabrication defects and damage processes of micro-nanoscale body-centered cubic (BCC) lattices manufactured with PµLSE. First, synchrotron radiation technology is used to capture the structural features inside the micro-lattice samples. Subsequently, several types of statistical defects-based image finite element models are adopted to analyze the failure process of the structure under compression loading. Finally, comparisons between in situ experiments and numerical simulation results are performed for verification. The method of the combined non-destructive testing of synchrotron radiation and image finite element technology provides a robust technique for evaluating the performances of additive-manufactured micro-lattice with complex microstructures.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. M. Latture, R. X. Rodriguez, L. R. Holmes Jr., and F. W. Zok, Acta Mater. 149, 78 (2018).
Q. Wu, A. Vaziri, M. E. Asl, R. Ghosh, Y. Gao, X. Wei, L. Ma, J. Xiong, and L. Wu, J. Mech. Phys. Solids 125, 112 (2019).
M. T. Hsieh, B. Endo, Y. Zhang, J. Bauer, and L. Valdevit, J. Mech. Phys. Solids 125, 401 (2019), arXiv: 1904.06733.
R. M. Gorguluarslan, S. K. Choi, and C. J. Saldana, J. Mech. Behav. BioMed. Mater. 71, 428 (2017).
L. R. Meza, G. P. Phlipot, C. M. Portela, A. Maggi, L. C. Montemayor, A. Comella, D. M. Kochmann, and J. R. Greer, Acta Mater. 140, 424 (2017).
T. Tancogne-Dejean, and D. Mohr, Int. J. Mech. Sci. 141, 101 (2018).
F. Wang, J. Mech. Phys. Solids 114, 303 (2018).
Y. Qin, Q. Qi, P. J. Scott, and X. Jiang, Comput.-Aided Des. 111, 44 (2019).
F. Forsberg, R. Mooser, M. Arnold, E. Hack, and P. Wyss, J. Struct. Biol. 164, 3 (2008).
J. J. Williams, K. E. Yazzie, E. Padilla, N. Chawla, X. Xiao, and F. De Carlo, Int. J. Fatigue 57, 79 (2013).
S. C. Garcea, I. Sinclair, S. M. Spearing, and P. J. Withers, Compos. Sci. Tech. 149, 81 (2017).
A. Haboub, H. A. Bale, J. R. Nasiatka, B. N. Cox, D. B. Marshall, R. O. Ritchie, and A. A. MacDowell, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 85, 8 (2014).
C. Petit, E. Maire, S. Meille, and J. Adrien, Mater. Des. 120, 117 (2017).
F. Rosa, S. Manzoni, and R. Casati, Mater. Des. 160, 1010 (2018).
Y. Amani, S. Dancette, P. Delroisse, A. Simar, and E. Maire, Acta Mater. 159, 395 (2018).
B. Yu, R. Blanc, C. Soutis, and P. J. Withers, Compos. Part A-Appl. Sci. Manufact. 82, 279 (2016).
M. Blacklock, H. Bale, M. Begley, and B. Cox, J. Mech. Phys. Solids 60, 3 (2012).
R. G. Rinaldi, M. Blacklock, H. Bale, M. R. Begley, and B. N. Cox, J. Mech. Phys. Solids 60, 8 (2012).
A. Drach, B. Drach, and I. Tsukrov, Adv. Eng. Software 72, 18 (2014).
A. J. Thompson, B. El Said, D. Ivanov, J. P. H. Belnoue, and S. R. Hallett, Int. J. Solids Struct. 154, 104 (2018).
N. Naouar, E. Vidal-Salle, J. Schneider, E. Maire, and P. Boisse, Composite Struct. 132, 1094 (2015).
N. Naouar, E. Vidal-Sallé, J. Schneider, E. Maire, and P. Boisse, Composite Struct. 116, 165 (2014).
I. Straumit, S. V. Lomov, and M. Wevers, Compos. Part A-Appl. Sci. Manufact. 69, 150 (2015).
G. Fang, C. Chen, S. Yuan, S. Meng, and J. Liang, Appl. Compos. Mater. 25, 3 (2018).
X. Zhu, S. Ai, X. Lu, K. Cheng, X. Ling, L. Zhu, and B. Liu, Comput. Mater. Sci. 85, 38 (2014).
M. A. Kader, M. A. Islam, P. J. Hazell, J. P. Escobedo, M. Saadatfar, A. D. Brown, and G. J. Appleby-Thomas, Int. J. Impact Eng. 96, 78 (2016).
L. Liu, P. Kamm, F. Garcia-Moreno, J. Banhart, and D. Pasini, J. Mech. Phys. Solids 107, 160 (2017).
J. Song, L. Gao, K. Cao, H. Zhang, S. Xu, C. Jiang, J. U. Surjadi, Y. Xu, and Y. Lu, Composite Struct. 203, 750 (2018).
Y. Xu, H. Zhang, B. Šavija, S. Chaves Figueiredo, and E. Schlangen, Mater. Des. 162, 143 (2019).
M. Kunt, Signal Process. 2, 3 (1980).
M. Smith, Z. Guan, and W. J. Cantwell, Int. J. Mech. Sci. 67, 28 (2013).
C. Li, H. Lei, Y. Liu, X. Zhang, J. Xiong, H. Zhou, and D. Fang, Int. J. Mech. Sci. 145, 389 (2018).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 11702023, and 11972081). The authors would like to thank the BMF Precision Technology Co., Ltd. for supporting the micro/nanoscale 3D printing work.
Supporting Information
The supporting information is available online at phys.scichina.com and link.springer.com. The supporting materials are published as submitted, without typesetting or editing. The responsibility for scientific accuracy and content remains entirely with the authors.
Electronic Supplementary Material
11433_2019_1522_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Damage evolution of PµLSE additive-manufactured micro-lattice metastructures: Synchrotron radiation 3D tomography image-based analysis
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zeng, Q., Wu, W., Hu, W. et al. Damage evolution of PµLSE additive-manufactured micro-lattice metastructures: Synchrotron radiation 3D tomography image-based analysis. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 63, 104611 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-019-1522-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-019-1522-4