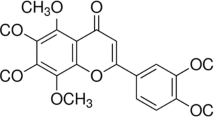
Abstract
Liver injury is the early stage of liver disease, which is caused by multiple factors. Baicalein has shown extensive bioactivity. But whether baicalein has a protective effect on liver injury has not been reported thus far. In this study, we aim to investigate the protective effects of baicalein on liver injury induced by oxidative stress. H2O2 and CCl4 were employed to establish liver injury models in vivo and in vitro, respectively. The protective effect of baicalein on oxidative stress–induced liver injury was evaluated by detecting the mitochondrial dynamics, the level of autophagy and apoptosis, the histopathology of liver, the indicators of liver function, and the level of oxidative stress in vitro and in vivo. March5 is the key regulator during liver injury induced by oxidative stress. March5 can ubiquitinate Drp1 and promote Drp1 degradation, then maintain the homeostasis of mitochondrial dynamics, keep the balance of autophagy, and reduce apoptosis. Baicalein is able to effectively reduce liver injury; it can contribute to the expression of March5 by regulating KLF4 during liver injury. These results indicate that baicalein plays a key role in salvaging liver from injury induced by oxidative stress via regulating the KLF4-March5-Drp1 signal pathway.







Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
18 July 2020
The original version of this article unfortunately contains errors in methods and figures. In methods, animal experiments part: ���2��ml/kg��� and ���after two days��� were described incorrectly which were actually ���4��ml/kg��� and ���after eight days��� respectively.
Abbreviations
- March5:
-
Membrane-associated RING-CH 5
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- Drp1:
-
Dynamin related protein 1
- KLF4:
-
Kruppel-like factor 4
- H2DCFDA:
-
2′,7′-Dichlorofluorescin-diacetate
- 8-OHG:
-
8-Hydroxyguanosine
- PARP:
-
Poly (ADP‑ribose) polymerase
- Bcl:
-
B‑cell lymphoma‑2
- BAX:
-
Bcl-2 associated X protein
- LC3-I:
-
Microtubule associated protein 1 light chain 3 I
- LC3-II:
-
Microtubule associated protein 1 light chain 3 II
- SiRNA:
-
Small interfering RNA
- ALT:
-
Alanine aminotransferase
- AST:
-
Aspartate aminotransferase
- DBIL:
-
Direct bilirubin
- TBIL:
-
Total bilirubin
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- CAT:
-
Catalase; GSH-PX, glutathione peroxidase
References
Wang G, Yeung CK, Wong WY, Zhang N, Wei YF, Zhang JL, Yan Y, Wong CY, Tang JJ, Chuai M, Lee KK, Wang LJ, Yang X (2016) Liver Fibrosis Can Be Induced by High Salt Intake through Excess Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Production. Journal of agricultural and food chemistry 64(7):1610–1617. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.5b05897
Standish RA, Cholongitas E, Dhillon A, Burroughs AK, Dhillon AP (2006) An appraisal of the histopathological assessment of liver fibrosis. Gut 55(4):569–578. https://doi.org/10.1136/gut.2005.084475
Ghafoory S, Varshney R, Robison T, Kouzbari K, Woolington S, Murphy B, Xia L (2018) Platelet TGF-β1 deficiency decreases liver fibrosis in a mouse model of liver injury. Blood Adv 2(5):470–480. https://doi.org/10.1182/bloodadvances.2017010868
Li C, Ming Y, Hong W, Tang Y, Lei X, Li X, Mao Y (2018) Comparison of hepatic transcriptome profiling between acute liver injury and acute liver failure induced by acetaminophen in mice. Toxicol Lett 283:69–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2017.11.020
Thawley V (2017) Acute Liver Injury and Failure. Vet Clin North Am Small Anim Pract 47(3):617–630. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cvsm.2016.11.010
Lee KSSS, Li D, Ramjit A, Serrano K, Ginsberg MD, Ding BS, Rafii S, Madoff DC (2017) Catheter-directed Intraportal Delivery of Endothelial Cell Therapy for Liver Regeneration: A Feasibility Study in a Large-Animal Model of Cirrhosis. Radiology 285(1):114–123
Fukui H, Saito H, Ueno Y, Uto H, Obara K, Sakaida I, Shibuya A, Seike M, Nagoshi S, Segawa M, Tsubouchi H, Moriwaki H, Kato A, Hashimoto E, Michitaka K, Murawaki T, Sugano K, Watanabe M, Shimosegawa T (2016) Evidence-based clinical practice guidelines for liver cirrhosis 2015. J Gastroenterol 51(7):629–650. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-016-1216-y
Nagai T, Yamada H (1989) Inhibition of mouse liver sialidase by the root of Scutellaria baicalensis. Planta Med 55(1):27–29. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2006-961769
Li X, Luo W, Ng TW, Leung PC, Zhang C, Leung KC, Jin L (2017) Nanoparticle-encapsulated baicalein markedly modulates pro-inflammatory response in gingival epithelial cells. Nanoscale 9(35):12897–12907. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7nr02546g
Ma Z, Otsuyama K, Liu S, Abroun S, Ishikawa H, Tsuyama N, Obata M, Li FJ, Zheng X, Maki Y, Miyamoto K, Kawano MM (2005) Baicalein, a component of Scutellaria radix from Huang-Lian-Jie-Du-Tang (HLJDT), leads to suppression of proliferation and induction of apoptosis in human myeloma cells. Blood 105(8):3312–3318. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2004-10-3915
Sithisarn P, Rojsanga P, Sithisarn P (2019) Inhibitory Effects on Clinical Isolated Bacteria and Simultaneous HPLC Quantitative Analysis of Flavone Contents in Extracts from Oroxylum indicum. Molecules 24(10):1937. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24101937
Karbowski M, Neutzner A, Youle RJ (2007) The mitochondrial E3 ubiquitin ligase MARCH5 is required for Drp1 dependent mitochondrial division. The Journal of cell biology 178(1):71–84. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200611064
Yonashiro R, Ishido S, Kyo S, Fukuda T, Goto E, Matsuki Y, Ohmura-Hoshino M, Sada K, Hotta H, Yamamura H, Inatome R (2006) A novel mitochondrial ubiquitin ligase plays a critical role in mitochondrial dynamics. EMBO J 25(15):3618–3626. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.emboj.7601249
Zhang C, Shi Z, Zhang L, Zhou Z, Zheng X, Liu G, Bu G, Fraser PE, Xu H, YW Z (2016) Appoptosin interacts with mitochondrial outer-membrane fusion proteins and regulates mitochondrial morphology. J Cell Sci 29(5):994–1002. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.176792
Yonashiro R, Sugiura A, Miyachi M, Fukuda T, Matsushita N, Inatome R, Ogata Y, Suzuki T, Dohmae N (2009) Mitochondrial ubiquitin ligase MITOL ubiquitinates mutant SOD1 and attenuates mutant SOD1-induced reactive oxygen species generation. Mol Biol Cell 20(21):4524–4530. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E09-02-0112
Wang S, Chi Q, Hu X, Cong Y, Li S (2019) Hydrogen sulfide-induced oxidative stress leads to excessive mitochondrial fission to activate apoptosis in broiler myocardia. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 183:109578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.109578
Li PF, Li J, Müller EC, Otto A, Dietz R, vH R (2002) Phosphorylation by protein kinase CK2: a signaling switch for the caspase-inhibiting protein ARC. Mol Cell 10(2):247–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1097-2765(02)00600-7
Wang K, Long B, Jiao JQ, Wang JX, Liu JP, Li Q, Li PF (2012) miR-484 regulates mitochondrial network through targeting Fis1. Nature communications 3:781. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms1770
Wang JX, Jiao JQ, Li Q, Long B, Wang K, Liu JP, Li YR, Li PF (2011) miR-499 regulates mitochondrial dynamics by targeting calcineurin and dynamin-related protein-1. Nat Med 17(1):71–78. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.2282
Li S, Tan HY, Wang N, Zhang ZJ, Lao L, Wong CW, Feng Y (2015) The Role of Oxidative Stress and Antioxidants in Liver Diseases. Int J Mol Sci 16(11):26087–26124. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161125942
Hackenhaar FS, Fumagalli F, Li Volti G, Sorrenti V, Russo I, Staszewsky L, Masson S, Latini R (2014) Relationship between post-cardiac arrest myocardial oxidative stress and myocardial dysfunction in the rat. J Biomed Sci. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12929-014-0070-6
Medina V, Edmonds B, Young GP, James R, Appleton S (1997) Induction of caspase-3 protease activity and apoptosis by butyrate and trichostatin A (inhibitors of histone deacetylase): dependence on protein synthesis and synergy with a mitochondrial/cytochrome c-dependent pathway. Cancer Res 57(17):3697–3707
Wang H, Ge W, Jiang W, Li D, Ju X (2018) SRPK1siRNA suppresses K562 cell growth and induces apoptosis via the PARPcaspase3 pathway. Molecular medicine reports 17(1):2070–2076. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2017.8032
Salazar G, Cullen A, Huang J, Zhao Y, Serino A, Hilenski L, Patrushev N, Forouzandeh F, Hwang HS (2019) SQSTM1/p62 and PPARGC1A/PGC-1alpha at the interface of autophagy and vascular senescence. Autophagy. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2019.1659612
Yang B, Xue Q, Guo J, Wang X, Zhang Y, Guo K, Li W, Chen S, Xue T, Qi X, Wang J (2019) Autophagy induction by the pathogen receptor NECTIN4 and sustained autophagy contribute to peste des petits ruminants virus infectivity. Autophagy. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2019.1643184
Cao P, Sun J, Sullivan MA, Huang X, Wang H, Zhang Y, Wang N, Wang K (2018) Angelica sinensis polysaccharide protects against acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury and cell death by suppressing oxidative stress and hepatic apoptosis in vivo and in vitro. Int J Biol Macromol 111:1133–1139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.01.139
Gu H, Li Q, Huang S, Lu W, Cheng F, Gao P, Wang C, Miao L, Mei Y, Wu M (2015) Mitochondrial E3 ligase March5 maintains stemness of mouse ES cells via suppression of ERK signalling. Nature communications 6:7112. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms8112
Fonseca TB, Sanchez-Guerrero A, Milosevic I, Raimundo N (2019) Mitochondrial fission requires DRP1 but not dynamins. Nature 570(7761):E34–E42. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-1296-y
Sanchez-Lopez E, Zhong Z, Stubelius A, Sweeney SR, Booshehri LM, Antonucci L, Liu-Bryan R, Lodi A, Terkeltaub R, Lacal JC, Murphy AN, Hoffman HM, Tiziani S, Guma M, Karin M (2019) Choline Uptake and Metabolism Modulate Macrophage IL-1beta and IL-18 Production. Cell Metab 29(6):1350–1362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2019.03.011
Takeda K, Nagashima S, Shiiba I, Uda A, Tokuyama T, Ito N, Fukuda T, Matsushita N, Ishido S, Iwawaki T, Uehara T, Inatome R, Yanagi S (2019) MITOL prevents ER stress-induced apoptosis by IRE1alpha ubiquitylation at ER-mitochondria contact sites. The EMBO journal. https://doi.org/10.15252/embj.2018100999
Yang C-H, Ting W-J, Shen C-Y, Hsu H-H, Lin Y-M, Chang S-H, Tsai F-J, Padma VV, Huang C-Y, Tsai Y (2015) SHSST-cyclodextrin complex inhibits TGF-β/Smad3/CTGF to a greater extent than silymarin in a rat model of carbon tetrachloride-induced liver injury. Molecular medicine reports 12(4):6053–6059. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2015.4190
Zeybel M, Hardy T, Wong YK, Mathers JC, Fox CR, Gackowska A, Oakley F, Burt AD, Wilson CL, Anstee QM, Barter MJ, Masson S, Elsharkawy AM, Mann DA, Mann J (2012) Multigenerational epigenetic adaptation of the hepatic wound-healing response. Nat Med 18(9):1369–1377. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.2893
Zira A, Kostidis S, Theocharis S, Sigala F, Engelsen SB, Andreadou I, Mikros E (2013) 1H NMR-based metabonomics approach in a rat model of acute liver injury and regeneration induced by CCl4 administration. Toxicology 303:115–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2012.10.015
Nissen NN, M P (2002) Hepatocellular carcinoma: the high-risk patient. J Clin Gastroenterol 35:79–85. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004836-200211002-00003
Sjouke B, Langslet G, Ceska R, Nicholls SJ, Nissen SE, Öhlander M, Ladenson PW, Olsson AG, Hovingh GK, Kastelein JJP (2014) Eprotirome in patients with familial hypercholesterolaemia (the AKKA trial): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 study. The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology 2(6):455–463. https://doi.org/10.1016/s2213-8587(14)70006-3
Cao WR, Ge JQ, Xie X, Fan ML, Fan XD, Wang H, Dong ZY, Liao ZH, Lan XZ, Chen M (2017) Protective effects of petroleum ether extracts of Herpetospermum caudigerum against alpha-naphthylisothiocyanate-induced acute cholestasis of rats. J Ethnopharmacol 198:139–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2017.01.003
Zhu X, Yao P, Liu J, Guo X, Jiang C, Tang Y (2010) Baicalein attenuates impairment of hepatic lysosomal acidification induced by high fat diet via maintaining V-ATPase assembly. Food Chem Toxicol 136:110990. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2019.110990
Pellicoro A, Ramachandran P, Iredale JP, Fallowfield JA (2014) Liver fibrosis and repair: immune regulation of wound healing in a solid organ. Nat Rev Immunol 14(3):181–194. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri3623
Yang CH, Ting WJ, Day CH, Ju DT, Yeh YL, Chung LC, Tsai FJ, Tsai CH, Tsai Y, Huang CY (2014) SHSST cyclodextrin complex prevents the fibrosis effect on CCl4- induced cirrhotic cardiomyopathy in rats through TGF-β pathway inhibition effects. Int J Mol Sci. 15(5):8037–8048. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms15058037
Guo M, Wang Y, Zhao H, Mu M, Yang X, Fei D, Liu Y, Zong H, Xing M (2020) Oxidative damage under As and/or Cu stress leads to apoptosis and autophagy and may be cross-talking with mitochondrial disorders in bursa of Fabricius. J Inorg Biochem 205:110989. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2019.110989
Schwabe RF, Luedde T (2018) Apoptosis and necroptosis in the liver: a matter of life and death. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 15(12):738–752. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41575-018-0065-y
dO MR, SF N, SH I, EO MD, SM N (2015) The effects of baicalein and baicalin on mitochondrial function and dynamics: a review. Pharmacol Res 100:296–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2015.08.021
Gao L, Zhou F, Wang KX, Zhou YZ, Du GH, Qin XM (2020) Baicalein protects PC12 cells from Aβ-induced cytotoxicity via inhibition of apoptosis and metabolic disorders. Life Sci 248:117471. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117471
Song M, Mihara K, Chen Y, Scorrano L (2015) Mitochondrial fission and fusion factors reciprocally orchestrate mitophagic culling in mouse hearts and cultured fibroblasts. Cell Metab 21(2):273–286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2014.12.011
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Science Foundation of China (grant numbers 81741173; 31430041; 31671447; 91849209).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZY, YW and PL generated the idea, edited the manuscript; ZY and QL performed the experiments and analyzed the data; ZY, QL prepared the manuscript; PL provided the funding.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Research involving human participants and animals
This article contained studies with mice. All experiments were performed according to the protocols approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, Z., Li, Q., Wang, Y. et al. A potent protective effect of baicalein on liver injury by regulating mitochondria-related apoptosis. Apoptosis 25, 412–425 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-020-01608-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-020-01608-2