Abstract
Purpose
To determine the impact of accelerated telomere shortening on the fertility parameters and treatment outcomes of a woman with dyskeratosis congenita (DKC).
Methods
A case study of the clinical data, blood, discarded oocytes, and arrested embryos of a woman with DKC and donated cryopreserved embryos from unaffected patients. Mean telomere length in blood cells was analyzed by flow cytometry–fluorescence in situ hybridization (flow-FISH) and qPCR. The load of short telomeres in blood cells was measured by universal single telomere length analysis (Universal STELA). The mean telomere length in embryos was analyzed by single-cell amplification of telomere repeats (SCATR) PCR.
Results
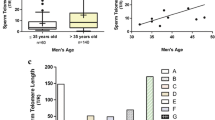
Comparison of clinical parameters revealed that the DKC patient had reduced anti-Mullerian hormone (0.3 vs 4.1 ± 5.7 ng/ML), reduced oocytes retrieved (7 vs 18.5 ± 9.5), reduced fertilization rate, and reduced euploidy rate relative to unaffected patients. Additionally, mean telomere length in DKC embryos were shorter than unaffected embryos. However, hormone treatment led to increased leukocyte telomere length, while the load of short telomeres was also shown to decrease during the course of treatment.
Conclusions
We demonstrate for the first time the direct detrimental impacts of short telomeres on female fertility. We further demonstrate positive effects of hormone treatments for people with telomere disorders.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
de Lange T. Shelterin: the protein complex that shapes and safeguards human telomeres. Genes Dev. 2005;19(18):2100–10.
Feng J, Funk WD, Wang SS, Weinrich SL, Avilion AA, Chiu CP, et al. The RNA Component of Human Telomerase. Science. 1995;269(5228):1236–41.
Blackburn EH. Telomeres and telomerase: their mechanisms of action and the effects of altering their functions. FEBS Lett. 2005;579(4):859–62.
Britt-Compton B, Capper R, Rowson J, Baird DM. Short telomeres are preferentially elongated by telomerase in human cells. FEBS Lett. 2009;583(18):3076–80.
Baker TG. Primordial germ cells. In: Austin CR, Short RV, editors. Reproduction in Mammals, vol. 1:: Germ Cells and Fertilization. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 1970. p. 1–13.
Wright DL, Jones EL, Mayer JF, Oehninger S, Gibbons WE, Lanzendorf SE. Characterization of telomerase activity in the human oocyte and preimplantation embryo. Mol Hum Reprod. 2001;7(10):947–55.
Navot D, Bergh PA, Williams MA, Garrisi GJ, Guzman I, Sandler B, et al. Poor oocyte quality rather than implantation failure as a cause of age-related decline in female fertility. Lancet. 1991;337(8754):1375–7.
Hassold T, Chiu D. Maternal age-specific rates of numerical chromosome abnormalities with special reference to trisomy. Hum Genet. 1985;70(1):11–7.
Plachot M, Veiga A, Montagut J, de Grouchy J, Calderon G, Lepretre S, et al. Are clinical and biological IVF parameters correlated with chromosomal disorders in early life: a multicentric study. Hum Reprod. 1988;3(5):627–35.
Kalmbach KH, Fontes Antunes DM, Dracxler RC, Knier TW, Seth-Smith ML, Wang F, et al. Telomeres and human reproduction. Fertil Steril. 2013;99(1):23–9.
Keefe DL, Liu L, Marquard K. Telomeres and aging-related meiotic dysfunction in women. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2007;64:139–43.
Treff NR, Su J, Taylor D, Scott RT Jr. Telomere DNA deficiency is associated with development of human embryonic aneuploidy. PLoS Genet. 2011;7(6):e1002161.
Liu L, Keefe DL. Nuclear origin of aging-associated meiotic defects in senescence-accelerated mice. Biol Reprod. 2004;71(5):1724–9.
Keefe DL, et al. Telomere length predicts embryo fragmentation after in vitro fertilization in women—toward a telomere theory of reproductive aging in women. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2005;192(4):1256–60.
Butlera MG, Tilburt J, DeVriesa A, Muralidhara B, Auea G, Hedgesa L, Atkinson J, Schwartz H. Comparison of chromosome telomere integrity in multiple tissues from subjects at different ages. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1998;105(2):138–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0165-4608(98)00029-6.
Liu L, Franco S, Spyropoulos B, Moens PB, Blasco MA, Keefe DL. Irregular telomeres impair meiotic synapsis and recombination in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101(17):6496–501.
Keefe DL, Liu L, Marquard K. Telomeres and aging-related meiotic dysfunc-tion in women. Cell Mol Life Sci 2007;64:139–43.
Agarwal S, Loh YH, McLoughlin E, Huang J, Park IH, Miller JD, et al. Telomere elongation in induced pluripotent stem cells from dyskeratosis congenita patients. Nature. 2010;464(7286):292–6.
Batista LF, Pech MF, Zhong FL, Nguyen HN, Xie KT, Zaug AJ, et al. Telomere shortening and loss of self-renewal in dyskeratosis congenita induced pluripotent stem cells. Nature. 2011;474(7351):399–402.
Shay J, Wright W. Telomeres in dyskeratosis congenita. Nat Genet. 2004;36:437–438. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0504-437
Sklavos MM, Stratton P, Giri N, Alter BP, Savage SA, Pinto LA. Reduced serum levels of anti-Mullerian hormone in females with inherited bone marrow failure syndromes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015;100(2):E197–203.
Wang F, Pan X, Kalmbach K, Seth-Smith ML, Ye X, Antumes DM, Yin Y, Liu L, Keefe DL, Weissman SM. Robust measurement of telomere length in single cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110(21):E1906–E1912. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1306639110.
Cawthon RM. Telomere Measurement By Quantiative PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002;30(10):e47. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/30.10.e47.
Bendix L, Horn PB, Jensen UB, Rubelj I, Kolvraa S. The load of short telomeres, estimated by a new method, universal STELA, correlates with number of senescent cells. Aging Cell. 2010;9(3):383–97.
Liu L, Bailey SM, Okuka M, Muñoz P, Li C, Zhou L, et al. Telomere lengthening early in development. Nat Cell Biol. 2007;9(12):1436–41.
Townsley DM, Dumitriu B, Liu D, Biancotto A, Weinstein B, Chen C, et al. Danazol treatment for Telomere diseases. N Engl J Med. 2016;374(20):1922–31.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Robinson, L.G., Pimentel, R., Wang, F. et al. Impaired reproductive function and fertility preservation in a woman with a dyskeratosis congenita. J Assist Reprod Genet 37, 1221–1225 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-020-01758-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-020-01758-x