Abstract
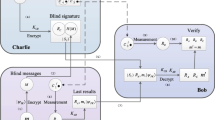
Quantum walks have been widely used in quantum computing and quantum simulation, and can be applied for quantum teleportation. In this paper, a quantum blind signature scheme with quantum walk-based teleportation is proposed. The sender Alice encodes the message into quantum states and divides the encrypted information into two qubit strings. Alice teleports them separately to the signer Charlie and the verifier Bob by quantum walks. Charlie accepts Alice’s request and uses Pauli operation to generate the quantum blind signatures, then sends the signatures to Bob. Bob measures two quantum messages in hands to complete verification of Charlie’s signature. In this protocol, the messages to be signed are ingeniously blinded and prepared in single particle states, the teleportation of particle states is achieved by quantum walks. Security analysis shows that the scheme can not only resist the repudiation of the signer and denial of the verifier, but also detect the forgery of the attacker, which can be widely applied in e-commerce or e-payment system.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Diffie, W., Hellman, M.: New Directions in Cryptography. IEEE Press, New directions in cryptography (1976)
Merkle, R.C.: A Certified Digital Signature. Conference on the Theory and Application of Cryptology. Springer, New York (1989)
Yen, S.M., Laih, C.S.: New digital signature scheme based on discrete logarithm. Electron. Lett. 29(12), 1120–1121 (1993)
Shor, P.W.: Polynomial-time algorithms for prime factorization and discrete logarithms on a quantum computer. SIAM Rev. 41(2), 303–332 (1999)
Shor, P.: Algorithms for quantum computation. Discrete logarithms and factoring. In: Proceedings of 35th Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Scienece (1994)
Gottesman, D., Chuang, I.: Quantum digital signatures. arXiv preprint arXiv:quant-ph/0105032 (2001)
Barnum, H., Crepeau, C,. Gottesman, D., et al.: Authentication of quantum messages. In: Proceedings of the 43rd Annual IEEE Symposium on the Foundations of Computer Science (FOCS ‘02), 10 pages (2002)
Zeng, G., Keitel, C.H.: Arbitrated quantum-signature scheme. Phys. Rev. A. 65(4), 042312 (2002)
Shi, R.H., Ding, W.T., Shi, J.J.: Arbitrated quantum signature with Hamiltonian algorithm based on blind quantum computation. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 57, 1961–1973 (2018)
Yan, L.L., Chang, Y., Zhang, S.B., et al.: A quantum multi-proxy weak blind signature scheme based on entanglement swapping. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 56(2), 634–642 (2017)
Yan, L.L., Sun, Y.H., Chang, Y., et al.: Semi-quantum protocol for deterministic secure quantum communication using Bell states. Quantum Inf. Process. 17(11), 315 (2018)
Chaum, D., Rivest, R., et al.: Blind signatures for untraceable payments. Advances in Cryptology. 199–203 (1983)
Wen, X., Chen, Y., Fang, J.: An inter-bank E-payment protocol based on quantum proxy blind signature. Quantum Inf. Process. 12(1), 549–558 (2013)
Wen, X., Niu, X., Ji, L., et al.: A weak blind signature scheme based on quantum cryptography. Opt. Commun. 282(4), 666–669 (2009)
Wang, T.Y., Wen, Q.Y.: Fair quantum blind signatures. Chinese Physics B. 06, 70–74 (2010)
Shi, J.J., Shi, R.H., Guo, Y., et al.: Batch proxy quantum blind signature scheme. Sci. China (Inf. Sci.). 05, 202–210 (2013)
Liang, J.W., Liu, X.S., Shi, J.J., et al.: Multiparty Quantum Blind Signature Scheme Based on Graph States. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 57(5), 2404–2414 (2018)
Cao, H.J., Yu, Y.F., et al.: A quantum proxy weak blind signature scheme based on controlled quantum teleportation. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 54(4), 1325–1333 (2015)
Lou, X., Chen, Z., Guo, Y.: A weak quantum blind signature with entanglement permutation. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 54(9), 3283–3292 (2015)
Tian, J.H.: A quantum multi-proxy blind signature scheme based on genuine four-Qubit entangled state. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 55(2), 809–816 (2016)
Yan, L.L., Chang, Y., Zhang, S.B., et al.: A quantum multi-proxy weak blind signature scheme based on entanglement swapping. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 56(2), 634–642 (2017)
Li, W., Shi, J.J., Shi, R.H., et al.: Blind quantum signature with controlled four-particle cluster states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 56, 1–9 (2017)
Aharonov, Y., Davidovich, L., Zagury, N.: Quantum random walks. Phys. Rev. A. 48(2), 1687–1690 (1993)
Ambainis, A., Bachy, E., Nayakz, A., et al.: One-dimensional quantum walks. In: Proceedings of the Thirty-Third Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing (STOC01), 37–49 (2001)
Aharonov, D., Ambainis, A., Kempe, J., et al.: Quantum walks on graphs. In: Proceedings of the Thirty-Third Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing (STOC01), 50–59 (2001)
Du, J., Li, H., Xu, X., et al.: Experimental implementation of the quantum random-walk algorithm. Phys. Rev. A. 67(4), 042316 (2003)
Di, T., Hillery, M., Zubairy, M.S.: Cavity QED-based quantum walk. Phys. Rev. A. 70(3), 032304 (2004)
Eckert, K., Mompart, J., Birkl, G., et al.: One- and two-dimensional quantum walks in arrays of optical traps. Phys. Rev. A. 72(1), 573–573 (2005)
Zou, X., Dong, Y., Guo, G.: Optical implementation of one-dimensional quantum random walks using orbital angular momentum of a single photon. New J. Phys. 8, (2006)
Perets, H.B., Lahini, Y., Pozzi, F., et al.: Realization of quantum walks with negligible Decoherence in waveguide lattices. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100(17), 38–41 (2008)
Bian, Z.H., Li, J., Zhan, X., et al.: Experimental implementation of a quantum walk on a circle with single photons. Phys. Rev. A. 95(5), 052338 (2017)
Tang, H., Lin, X.F., Feng, Z., et al.: Experimental two-dimensional quantum walk on a photonic chip. Sci. Adv. 4(5), eaat3174 (2018)
Wang, Y., Shang, Y., Xue, P.: Generalized teleportation by quantum walks. Quantum Inf. Process. 16(9), 221 (2017)
Shang, Y., Wang, Y., Li, M., et al.: Quantum communication protocols by quantum walks with two coins. EPL (Europhysics Letters) (2018)
Childs, A.M.: On the relationship between continuous- and discrete-time quantum walk. Commun. Math. Phys. 294(2), 581–603 (2010)
Shikano, Y.: From discrete time quantum walk to continuous time quantum walk in limit distribution. J. Comput. Theor. Nanosci. 10(7), 1558–1570 (2013)
Shi, J.J., Chen, H., Zhou, F., et al.: Quantum blind signature scheme with cluster states based on quantum walk cryptosystem. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 58(4), 1337–1349 (2019)
Feng, Y., Shi, R., Shi, J., et al.: Arbitrated quantum signature scheme with quantum walk-based teleportation. Quantum Inf. Process. 18(5), 154 (2019)
Feng, Y.Y., Shi, R.H., Shi, J.J., et al.: Arbitrated quantum signature scheme based on quantum walks. Acta Phys. Sin. 68(12), 120302 (2019)
Xue, P., Zhang, R., Qin, H., et al.: Experimental quantum-walk revival with a time-dependent coin. Phys. Rev. Lett. 114(14), 140502 (2015)
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.61572086, No.61402058), the Key Research and Development Project of Sichuan Province (No. 20ZDYF2324, No. 2019ZYD027, No. 2018TJPT0012), the Innovation Team of Quantum Security Communication of Sichuan Province (No.17TD0009), the Academic and Technical Leaders Training Funding Support Projects of Sichuan Province (No. 2016120080102643), the Application Foundation Project of Sichuan Province(No.2017JY0168), the Science and Technology Support Project of Sichuan Province (No.2018GZ0204, No.2016FZ0112).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, XY., Chang, Y., Zhang, SB. et al. Quantum Blind Signature Scheme Based on Quantum Walk. Int J Theor Phys 59, 2059–2073 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-020-04478-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-020-04478-1