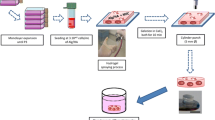
Abstract
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are promising cell candidates for cartilage regeneration. Furthermore, it is important to control the cell-matrix interactions that have a direct influence on cell functions. Providing an appropriate microenvironment for cell differentiation in response to exogenous stimuli is a critical step towards the clinical utilization of MSCs. In this study, hydrogels consisted of different proportions of alginates that were modified using gelatin, collagen type I and arginine-glycine-aspartic acid (RGD) and were evaluated regarding their effects on mesenchymal stem cells. The effect of applying hydrostatic pressure on MSCs encapsulated in collagen-modified alginate with and without chondrogenic medium was evaluated 7, 14 and 21 days after culture, which is a comprehensive evaluation of chondrogenesis in 3D hydrogels with mechanical and chemical stimulants. Alcian blue, safranin O and dimethyl methylene blue (DMMB) staining showed the chondrogenic phenotype of cells seeded in the collagen- and RGD-modified alginate hydrogels with the highest intensity after 21 days of culture. The results of real-time PCR for cartilage-specific extracellular matrix genes indicated the chondrogenic differentiation of MSCs in all hydrogels. Also, the synergic effects of chemical and mechanical stimuli are indicated. The highest expression levels of the studied genes were observed in the cells embedded in collagen-modified alginate by loading after 14 days of exposure to the chondrogenic medium. The effect of using IHP on encapsulated MSCs in modified alginate with collagen type I is equal or even higher than using TGF-beta on encapsulated cells. The results of immunohistochemical assessments also confirmed the real-time PCR data.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amin S, Banijamali SE, Tafazoli-Shadpour M, Shokrgozar MA, Dehghan MM, Haghighipour N, Mahdian R, Bayati V, Abbasnia P (2014) Comparing the effect of equiaxial cyclic mechanical stimulation on GATA4 expression in adipose-derived and bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Biol Int 38:219–227
Angele P (2003) Cyclic hydrostatic pressure enhances the chondrogenic phenotype of human mesenchymal progenitor cells differentiated in vitro. J Orthop Res 21:451–457
Arnsdorf EJ, Tummala P, Kwon RY, Jacobs CR (2009) Mechanically induced osteogenic differentiation--the role of RhoA, ROCKII and cytoskeletal dynamics. J Cell Sci 122:546–553
Awad HA, Wickham MQ, Leddy HA, Gimble JM, Guilak F (2004) Chondrogenic differentiation of adipose-derived adult stem cells in agarose, alginate, and gelatin scaffolds. Biomaterials 25:3211–3222
Barczyk M, Carracedo S, Gullberg D (2010) Integrins. Cell Tissue Res 339:269–280
Bianco P, Riminucci M, Gronthos S, Robey PG (2001) Bone marrow stromal stem cells: nature, biology, and potential applications. Stem Cells 19:180–192
Blaney Davidson EN, van der Kraan PM, van den Berg WB (2007) TGF-beta and osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr Cartil 15:597–604
Bosnakovski D, Mizuno M, Kim G, Takagi S, Okumura M, Fujinaga T (2006) Chondrogenic differentiation of bovine bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) in different hydrogels: influence of collagen type II extracellular matrix on MSC chondrogenesis. Biotechnol Bioeng 93:1152–1163
Bourns B, Franklin S, Cassimeris L, Salmon ED (1988) High hydrostatic pressure effects in vivo: changes in cell morphology, microtubule assembly, and actin organization. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton 10:380–390
Bratt-Leal AM, Carpenedo RL, Ungrin MD, Zandstra PW, McDevitt TC (2011a) Incorporation of biomaterials in multicellular aggregates modulates pluripotent stem cell differentiation. Biomaterials 32:48–56
Bratt-Leal AM, Kepple KL, Carpenedo RL, Cooke MT, McDevitt TC (2011b) Magnetic manipulation and spatial patterning of multi-cellular stem cell aggregates. Integrat Biol 3:1224–1232
Chung C, Burdick JA (2009) Influence of three-dimensional hyaluronic acid microenvironments on mesenchymal stem cell chondrogenesis. Tissue Eng A 15:243–254
Correia C, Pereira AL, Duarte AR, Frias AM, Pedro AJ, Oliveira JT, Sousa RA, Reis RL (2012) Dynamic culturing of cartilage tissue: the significance of hydrostatic pressure. Tissue Eng A 18:1979–1991
Dickhut A, Gottwald E, Steck E, Heisel C, Richter W (2008) Chondrogenesis of mesenchymal stem cells in gel-like biomaterials in vitro and in vivo. Front Biosci 13:4517–4528
Elder SH, Sanders SW, McCulley WR, Marr ML, Shim JW, Hasty KA (2006) Chondrocyte response to cyclic hydrostatic pressure in alginate versus pellet culture. J Orthop Res 24:740–747
Fan L, Cao M, Gao S, Wang T, Wu H, Peng M, Zhou X, Nie M (2013) Preparation and characterization of sodium alginate modified with collagen peptides. Carbohydr Polym 93(2):380–385
Finger AR, Sargent CY, Dulaney KO, Bernacki SH, Loboa EG (2007) Differential effects on messenger ribonucleic acid expression by bone marrow-derived human mesenchymal stem cells seeded in agarose constructs due to ramped and steady applications of cyclic hydrostatic pressure. Tissue Eng 13:1151–1158
Ghahramanpoor MK, Hassani Najafabadi SA, Abdouss M, Bagheri F, Baghaban Eslaminejad M (2011) A hydrophobically-modified alginate gel system: utility in the repair of articular cartilage defects. J Mater Sci Mater Med 22:2365–2375
Giancotti FG, Ruoslahti E (1999) Integrin signaling. Science (New York, NY) 285:1028–1032
Hall BK, Miyake T (1995) Divide, accumulate, differentiate: cell condensation in skeletal development revisited. Int J Dev Biol 39:881–893
Hasanzadeh E, Amoabediny G, Haghighipour N, Gholami N, Mohammadnejad J, Shojaei S, Salehi-Nik N (2017) The stability evaluation of mesenchymal stem cells differentiation toward endothelial cells by chemical and mechanical stimulation. In vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 53:818–826
Hosseini M, Tafazzoli-Shadpour M, Haghighipour N, Aghdami N, Goodarzi A (2015) The synergistic effects of shear stress and cyclic hydrostatic pressure modulate chonderogenic induction of human mesenchymal stem cells. Int J Artif Organs 38(10):557–564
Huang AH, Farrell MJ, Kim M, Mauck RL (2010) Long-term dynamic loading improves the mechanical properties of chondrogenic mesenchymal stem cell-laden hydrogel. Eur Cells Mater 19:72–85
Hunziker EB (1999) Articular cartilage repair: are the intrinsic biological constraints undermining this process insuperable? Osteoarthr Cartil 7:15–28
Hunziker EB (2002) Articular cartilage repair: basic science and clinical progress. A review of the current status and prospects. Osteoarthr Cartil 10:432–463
Jeong JY, Park SH, Shin JW, Kang YG, Han KH, Shin JW (2012) Effects of intermittent hydrostatic pressure magnitude on the chondrogenesis of MSCs without biochemical agents under 3D co-culture. J Mater Sci Mater Med 23:2773–2781
Karkhaneh A, Naghizadeh Z, Shokrgozar MA, Bonakdar S, Solouk A, Haghighipour N (2014) Effects of hydrostatic pressure on biosynthetic activity during chondrogenic differentiation of MSCs in hybrid scaffolds. Int J Artif Organs 37:142–148
Kavalkovich KW, Boynton RE, Murphy JM (2002) Chondrogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells within an alginate layer culture system. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 38:457–466
Khani MM, Tafazzoli-Shadpour M, Goli-Malekabadi Z, Haghighipour N (2015) Mechanical characterization of human mesenchymal stem cells subjected to cyclic uniaxial strain and TGF-beta1. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 43:18–25
Lee KY, Mooney DJ (2012) Alginate: properties and biomedical applications. Prog Polym Sci 37:106–126
Liu J, Lin H, Li X, Fan Y, Zhang X (2015) Chondrocytes behaviors within type I collagen microspheres and bulk hydrogels: an in vitro study. RSC Adv 5:54446–54453
Loeser RF (2014) Integrins and chondrocyte-matrix interactions in articular cartilage. Matrix Biol 39:11–16
Mauck RL, Nicoll SB, Seyhan SL, Ateshian GA, Hung CT (2003) Synergistic action of growth factors and dynamic loading for articular cartilage tissue engineering. Tissue Eng 9:597–611
Mauck RL, Yuan X, Tuan RS (2006) Chondrogenic differentiation and functional maturation of bovine mesenchymal stem cells in long-term agarose culture. Osteoarthr Cartil 14:179–189
Meyer EG, Buckley CT, Steward AJ, Kelly DJ (2011) The effect of cyclic hydrostatic pressure on the functional development of cartilaginous tissues engineered using bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 4:1257–1265
Mirahmadi F, Tafazzoli-Shadpour M, Shokrgozar MA, Bonakdar S (2013) Enhanced mechanical properties of thermosensitive chitosan hydrogel by silk fibers for cartilage tissue engineering. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl 33:4786–4794
Miyanishi K, Trindade MC, Lindsey DP, Beaupre GS, Carter DR, Goodman SB, Schurman DJ, Smith RL (2006a) Dose- and time-dependent effects of cyclic hydrostatic pressure on transforming growth factor-beta3-induced chondrogenesis by adult human mesenchymal stem cells in vitro. Tissue Eng 12:2253–2262
Miyanishi K, Trindade MC, Lindsey DP, Beaupre GS, Carter DR, Goodman SB, Schurman DJ, Smith RL (2006b) Effects of hydrostatic pressure and transforming growth factor-beta 3 on adult human mesenchymal stem cell chondrogenesis in vitro. Tissue Eng 12:1419–1428
Murphy CM, Matsiko A, Haugh MG, Gleeson JP, O’Brien FJ (2012) Mesenchymal stem cell fate is regulated by the composition and mechanical properties of collagen-glycosaminoglycan scaffolds. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 11:53–62
Ng KK, Thatte HS, Spector M (2011) Chondrogenic differentiation of adult mesenchymal stem cells and embryonic cells in collagen scaffolds. J Biomed Mater Res A 99:275–282
Nuernberger S, Cyran N, Albrecht C, Redl H, Vecsei V, Marlovits S (2011) The influence of scaffold architecture on chondrocyte distribution and behavior in matrix-associated chondrocyte transplantation grafts. Biomaterials 32:1032–1040
Urban P. G. J. (1994) The chondrocyte: A cell under pressure
Pawelec KM, Best SM, Cameron RE (2016) Collagen: a network for regenerative medicine. J Mater Chem B 4:6484–6496
Puetzer J, Williams J, Gillies A, Bernacki S, Loboa EG (2013) The effects of cyclic hydrostatic pressure on chondrogenesis and viability of human adipose- and bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in three-dimensional agarose constructs. Tissue Eng A 19:299–306
Rashidi N, Tafazzoli-Shadpour M, Haghighipour N, Khani MM (2018) Morphology and contractile gene expression of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells in response to short-term cyclic uniaxial strain and TGF-beta1. Biomed Tech (Berl) 63:317–326
Rokstad AM, Brekke OL, Steinkjer B, Ryan L, Kollarikova G, Strand BL, Skjak-Braek G, Lacik I, Espevik T, Mollnes TE (2011) Alginate microbeads are complement compatible, in contrast to polycation containing microcapsules, as revealed in a human whole blood model. Acta Biomater 7:2566–2578
Ruoslahti E (1996) RGD and other recognition sequences for integrins. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 12:697–715
Safshekan F, Tafazzoli-Shadpour M, Shokrgozar M, Haghighipour N, Alavi H (2014) Effects of short-term cyclic hydrostatic pressure on initiating and enhancing the expression of chondrogenic genes in human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells. J Mech Med Biol 14(04):1450054
Safshekan F, Tafazzoli-Shadpour M, Shokrgozar MA, Haghighipour N, Mahdian R, Hemmati A (2012) Intermittent hydrostatic pressure enhances growth factor-induced chondroinduction of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Artif Organs 36:1065–1071
Salinas CN, Anseth KS (2008) The enhancement of chondrogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells by enzymatically regulated RGD functionalities. Biomaterials 29:2370–2377
Schwartz MA, Schaller MD, Ginsberg MH (1995) Integrins: emerging paradigms of signal transduction. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 11:549–599
Shen J, Li S, Chen D (2014) TGF-beta signaling and the development of osteoarthritis. Bone Res 2. https://doi.org/10.1038/boneres.2014.2
Shokrgozar MA, Bonakdar S, Dehghan MM, Emami SH, Montazeri L, Azari S, Rabbani M (2013) Biological evaluation of polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel crosslinked by polyurethane chain for cartilage tissue engineering in rabbit model. J Mater Sci Mater Med 24:2449–2460
Solouk A, Mirzadeh H, Shokrgozar MA, Solati-Hashjin M, Najarian S, Seifalian AM (2011) The study of collagen immobilization on a novel nanocomposite to enhance cell adhesion and growth. Iran Biomed J 15:6–14
Sridharan B, Lin SM, Hwu AT, Laflin AD, Detamore MS (2015) Stem cells in aggregate form to enhance chondrogenesis in hydrogels. PLoS One 10:e0141479
Stenvik J, Sletta H, Grimstad O, Pukstad B, Ryan L, Aune R, Strand W, Tondervik A, Torp SH, Skjak-Braek G, Espevik T (2012) Alginates induce differentiation and expression of CXCR7 and CXCL12/SDF-1 in human keratinocytes--the role of calcium. J Biomed Mater Res A 100:2803–2812
Steward AJ, Kelly DJ (2015) Mechanical regulation of mesenchymal stem cell differentiation. J Anat 227:717–731
Steward AJ, Liu Y, Wagner DR (2011) Engineering cell attachments to scaffolds in cartilage tissue engineering. JOM 63:74–82
Steward AJ, Thorpe SD, Vinardell T, Buckley CT, Wagner DR, Kelly DJ (2012) Cell-matrix interactions regulate mesenchymal stem cell response to hydrostatic pressure. Acta Biomater 8:2153–2159
Steward AJ, Wagner DR, Kelly DJ (2013) The pericellular environment regulates cytoskeletal development and the differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells and determines their response to hydrostatic pressure. Eur Cells Mater 25:167–178
Tabatabaei FS, Jazayeri M, Ghahari P, Haghighipour N (2014) Effects of equiaxial strain on the differentiation of dental pulp stem cells without using biochemical reagents. Mol Cell Biomech 11:209–220
Talia Gross-Aviv BBD, French MM, Athanasiou KA, Vago R (2008) A study of crystalline biomaterials for articular cartilage bioengineering. Mater Sci Eng C 28:1388–1400
Tibbitt MW, Anseth KS (2009) Hydrogels as extracellular matrix mimics for 3D cell culture. Biotechnol Bioeng 103:655–663
Vinardell T, Rolfe RA, Buckley CT, Meyer EG, Ahearne M, Murphy P, Kelly DJ, Kelly DJ (2012) Hydrostatic pressure acts to stabilise a chondrogenic phenotype in porcine joint tissue derived stem cells. Eur Cell Mater 23:121–134
Vinatier C, Mrugala D, Jorgensen C, Guicheux J, Noel D (2009) Cartilage engineering: a crucial combination of cells, biomaterials and biofactors. Trends Biotechnol 27:307–314
Wagner DR, Lindsey DP, Li KW, Tummala P, Chandran SE, Smith RL, Longaker MT, Carter DR, Beaupre GS (2008) Hydrostatic pressure enhances chondrogenic differentiation of human bone marrow stromal cells in osteochondrogenic medium. Ann Biomed Eng 36:813–820
Wang N, Butler JP, Ingber DE (1993) Mechanotransduction across the cell surface and through the cytoskeleton. Science (New York, NY) 260:1124–1127
Williamson AK, Chen AC, Sah RL (2001) Compressive properties and function-composition relationships of developing bovine articular cartilage. J Orthop Res 19:1113–1121
Xie L, Zhang N, Marsano A, Vunjak-Novakovic G, Zhang Y, Lopez MJ (2013) In vitro mesenchymal trilineage differentiation and extracellular matrix production by adipose and bone marrow derived adult equine multipotent stromal cells on a collagen scaffold. Stem Cell Rev 9:858–872
Xu J, Wang W, Ludeman M, Cheng K, Hayami T, Lotz JC, Kapila S (2008) Chondrogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells in three-dimensional alginate gels. Tissue Eng A 14:667–680
You M, Peng G, Li J, Ma P, Wang Z, Shu W, Peng S, Chen GQ (2011) Chondrogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) scaffolds coated with PHA granule binding protein PhaP fused with RGD peptide. Biomaterials 32:2305–2313
Funding
This work has been financially supported by NCBI, Pasteur Institute of Iran (Grant No. 665).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human and animal participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 1516 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jahanbakhsh, A., Nourbakhsh, M.S., Bonakdar, S. et al. Evaluation of alginate modification effect on cell-matrix interaction, mechanotransduction and chondrogenesis of encapsulated MSCs. Cell Tissue Res 381, 255–272 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-020-03216-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-020-03216-7