Abstract
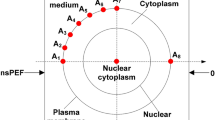
Membrane proteins are the major component of plasma membranes, and they play crucial roles in all organisms. To understand the influence of the presence of KcsA channel on cell membrane electroporation induced by picosecond pulse trains (psPT), in this paper, the electroporation of KcsA membrane protein system and bare lipid bilayer system (POPC) with the applied psPT are simulated using molecular dynamics (MD) method. First, we find that the average pore formation time of the KcsA system is longer than the bare system with the applied psPT. In the KcsA system, water protrusions appear more slowly. Then, the system size effects of psPT in the MD simulations are investigated. When the system size decreases, the average pore formation time of small KcsA membrane protein system is shorter than the bare system with the applied psPT. It is found that the psPT makes the protein fluctuation of small system increase greatly; meanwhile the instability of protein disturbs the water and then affects the water protrusion appearance time. Furthermore, it shows that the protein fluctuation of constant electric field is smaller than that of psPT and no field, and protein fluctuation increases with the psPT repetition frequency increasing.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
PT Vernier ZA Levine MC Ho S Xiao I Semenov AG Pakhomov 2015 Picosecond and terahertz perturbation of interfacial water and electropermeabilization of biological membranes J Membr Biol 248 837 847
SA Kirsch RA Böckmann 2016 Membrane pore formation in atomistic and coarse-grained simulations Biochim Biophys Acta 1858 2266 2277
M Casciola MA Kasimova L Rems S Zullino F Apollonio M Tarek 2016 Properties of lipid electropores I: molecular dynamics simulations of stabilized pores by constant charge imbalance Bioelectrochemistry 109 108 116
L Delemotte M Tarek 2012 Molecular dynamics simulations of lipid membrane electroporation J Membr Biol 245 531 543
M Casciola M Tarek 2016 A molecular insight into the electro-transfer of small molecules through electropores driven by electric fields Biochim Biophys Acta 1858 2278 2289
PT Vernier MJ Ziegler Y Sun MA Gundersen DP Tieleman 2006 Nanopore-facilitated, voltage-driven phosphatidylserine translocation in lipid bilayers—in cells and in silico Phys Biol 3 233
MP Stewart R Langer KF Jensen 2018 Intracellular delivery by membrane disruption: mechanisms, strategies, and concepts Chem Rev 118 7409 7531
I Uitert van S Gac Le A Berg van den 2010 The influence of different membrane components on the electrical stability of bilayer lipid membranes Biochim Biophys Acta 1798 21 31
GC Troiano KJ Stebe RM Raphael L Tung 1999 The effects of gramicidin on electroporation of lipid bilayers Biophys J 76 3150 3157
M Tarek 2005 Membrane electroporation: a molecular dynamics simulation Biophys J 88 4045 4053
SW Siu RA Böckmann 2007 Electric field effects on membranes: gramicidin A as a test ground J Struct Biol 157 545 556
Z Cournia TW Allen I Andricioaei B Antonny D Baum G Brannigan R Friedman 2015 Membrane protein structure, function, and dynamics: a perspective from experiments and theory J Membr Biol 248 611 640
SJ Beebe PM Fox LJ Rec ELK Willis KH Schoenbach 2003 Nanosecond, high-intensity pulsed electric fields induce apoptosis in human cells FASEB J 17 11 1493 1495
T Kotnik D Miklavčič 2006 Theoretical evaluation of voltage inducement on internal membranes of biological cells exposed to electric fields Biophys J 90 2 480 491
S Xiao S Guo V Nesin R Heller KH Schoenbach 2011 Subnanosecond electric pulses cause membrane permeabilization and cell death IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 58 1239 1245
JT Camp Y Jing J Zhuang JF Kolb SJ Beebe J Song KH Schoenbach 2012 Cell death induced by subnanosecond pulsed electric fields at elevated temperatures IEEE Trans Plasma Sci 40 10 2334 2347
YY Hua XS Wang YU Zhang CG Yao XM Zhang ZA Xiong 2012 Intense picosecond pulsed electric fields induce apoptosis through a mitochondrial-mediated pathway in HeLa cells Mol Med Rep 5 4 981 987
H Fröhlich 1980 The biological effects of microwaves and related questions Advances in electronics and electron physics Academic Press New York 85 152
PH Siegel 2004 Terahertz technology in biology and medicine IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech 52 10 2438 2447
GJ Wilmink JE Grundt 2011 Invited review article: current state of research onbiological effects of terahertz radiation J Infrared Millimeter Terahertz Waves 32 10 1074 1122
M Borovkova M Serebriakova V Fedorov E Sedykh V Vaks A Lichutin M Khodzitsky 2017 Investigation of terahertz radiation influence on rat glial cells Biomed Opt Exp 8 1 273 280
RL Andrew 2001 Molecular modeling principles and applications 2 Pearson Education Limited Essex
LF Pineda De Castro M Dopson R Friedman 2016 Biological membranes in extreme conditions: simulations of anionic archaeal tetraether lipid membranes PLoS ONE 11 5 e0155287
S Moradi A Nowroozi M Shahlaei 2019 Shedding light on the structural properties of lipid bilayers using molecular dynamics simulation: a review study RSC Adv 9 8 4644 4658
RA Böckmann BL Groot De S Kakorin E Neumann H Grubmüller 2008 Kinetics, statistics, and energetics of lipid membrane electroporation studied by molecular dynamics simulations Biophys J 95 1837 1850
Y Zhou JH Morais-Cabral A Kaufman R MacKinnon 2001 Chemistry of ion coordination and hydration revealed by a K+ channel–Fab complex at 2.0 Å resolution Nature 414 43
L Kalé R Skeel M Bhandarkar R Brunner A Gursoy N Krawetz K Schulten 1999 NAMD2: greater scalability for parallel molecular dynamics J Comput Phys 151 283 312
MP Allen DJ Tildesley 2017 Computer simulation of liquids Oxford University Press Oxford
T Darden D York L Pedersen 1993 Particle mesh Ewald: an N⋅log (N) method for Ewald sums in large systems J Chem Phys 98 10089 10092
U Essmann L Perera ML Berkowitz T Darden H Lee LG Pedersen 1995 A smooth particle mesh Ewald method J Chem Phys 103 8577 8593
GJ Martyna DJ Tobias ML Klein 1994 Constant pressure molecular dynamics algorithms J Chem Phys 101 4177 4189
SE Feller Y Zhang RW Pastor BR Brooks 1995 Constant pressure molecular dynamics simulation: the Langevin piston method J Chem Phys 103 4613 4621
SY Noskov S Berneche B Roux 2004 Control of ion selectivity in potassium channels by electrostatic and dynamic properties of carbonyl ligands Nature 431 830
J Tang H Yin J Ma W Bo Y Yang J Xu Y Gong 2018 Terahertz electric field-induced membrane electroporation by molecular dynamics simulations J Membr Biol 251 681 693
M Tokman JH Lee ZA Levine MC Ho ME Colvin PT Vernier 2013 Electric feld-driven water dipoles: nanoscale architecture of electroporation PLoS ONE 8 e61111
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 61921002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Large bare system electroporation time of all runs. Electronic supplementary material 1 (XLSX 11 kb)
Large KcsA system electroporation time of all runs. Electronic supplementary material 2 (XLSX 12 kb)
Small bare system electroporation time of all runs. Electronic supplementary material 4 (XLSX 17 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, J., Ma, J., Guo, L. et al. The Effect of KcsA Channel on Lipid Bilayer Electroporation Induced by Picosecond Pulse Trains. J Membrane Biol 253, 271–286 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-020-00123-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-020-00123-4