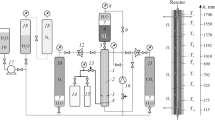
Abstract
The paper presents the results of investigation of the products of oxidation of sludge-lignin (waste from the Baikal pulp and paper mill) in H\(_{2}\)O/O\(_{2}\) mixture in the autoclave and semi-flow modes at uniform heating of the reactor up to 750 K. The time dependencies of the reactor wall temperature and the power of ohmic heaters imply that the oxidation starts at 440 K and the maximum oxidation rate is realized at 583-643 K. Mass spectrometry measurements of the composition of the volatile products yielded the temperature dependency of the degree of removal of carbon occurring in CO and CO\(_{2}\) from sludge-lignin. Using physical and chemical methods of analysis it was shown that Al\(_{2}\)O\(_{3}\) (AlOOH in the autoclave mode), Fe\(_{2}\)O\(_{3}\), SiO\(_{2}\), AlPO\(_{4}\), and CaSO\(_{4}\) were major components of the residue after the sludge-lignin conversion. Formation of HCl and H\(_{2}\)SO\(_{4}\) in the course of oxidation of chlorine- and sulfur-containing organic compounds was found to cause corrosion of stainless steel.







Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
On the Issue of Disposal of Waste of the Baikal Pulp and Paper Mill, Meeting of the Interdepartmental Commission for the Protection of Lake Baikal on 27.05.2009; http://geol.irk.ru/baikal/baikal/baikal_law_fulfilment/mvk/050609/infdocs/quest1.pdf.
Timofeeva, S.S., Cheremis, N.V., Ignat’eva, L.P., and Nikolaeva, L.A., Chlorodioxins in Slime Accumulators of the Baikal Region,Vestnik Irkutsk Gos. Tekhn. Univ., 2008, no. 3, pp. 174–181.
Shatrova, A.S., Bogdanov, A.V., and Kachor, O.L., Investigation of Physical and Chemical Properties of Sludge-Lignin Sediments of the Baikal Pulp and Paper Mill under Freezing, Vestnik Irkutsk Gos. Tekhn. Univ., 2015, no. 8, pp. 99–107.
Svanstrom, M., Froling, M., Modell, M., Peters, W.A., and Tester, J., Environmental Assessment of Supercritical Water Oxidation of Sewage Sludge, Resources, Conservation, Recycling, 2004, vol. 41, pp. 321–338.
Gasafi, E., Reinecre, M., Kruse, A., and Scheber, L., Economic Analysis of Sewage Sludge Gasification in Supercritical Water,Biomass Bioenergy, 2008, vol. 32, pp. 1085–1096.
Marulanda, V., and Bolanos, G., Supercritical Water Oxidation of a Heavy PCB-Contaminated Mineral Transformer Oil: Laboratory-Scale Data and Economic Assessment, J. Supercrit. Fluids, 2010, vol. 54, pp. 258–265.
Yesodharam, S., Supercritical Water Oxidation: An Environmentally Safe Method for the Disposal of Organic Wastes,Current Sci., 2002, vol. 82, pp. 1112–1122.
Bermejo, M.D., and Cocero, M.J., Supercritical Water Oxidation: A Technical Review, AIChe J., 2006, vol. 52, pp. 3933–3951.
Fedyaeva, O.N. and Vostrikov, A.A., Disposal of Hazardous Organic Substances in Supercritical Water, Russ. J. Phys. Chem. B, 2012, vol. 6, pp. 884–860.
Xu, D., Wang, S., Zhang, J., Tang, X., Guo, Y., and Huang, C., Supercritical Water Oxidation of a Pesticide Wastewater, Chem. Eng. Res. Design, 2015, vol. 94, pp. 396–406.
Yang, B., Shen, Z., Cheng, Z., and Ji, W., Total Nitrogen Removal, Products and Molecular Characteristics of 14 N-Containing Compounds in Supercritical Water Oxidation,Chemosphere, 2017, vol. 188, pp. 642–649.
Prasad Mylapilli, S.V., and Reddy, S.N., Sub and Supercritical Water Oxidation of Pharmaceutical Wastewater, J. Environ. Chem. Eng., 2019, vol. 7, p. 103165.
Muthukumaran, P., and Gupta, R.B., Sodium-Carbonate-Assisted Supercritical Water Oxidation of Chlorinated Waste, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2000, vol. 39, pp. 4555–4563.
Stark, K., Plaza, E., and Hultman, B., Phosphorus Release from Ash Dried Sludge and Sludge Residue from Supercritical Water Oxidation by Acid or Base, Chemosphere, 2006, vol. 62, pp. 827–832.
Veriansyah, B., Kim, J.-D., and Lee, J.-C., Destruction of Chemical Agent Simulants in a Supercritical Water Oxidation Bench-Scale Reactor, J. Hazard. Mater., 2007, vol. 147, pp. 8–14.
Guo, Y., Wang, S.Z., Xu, D.H., Gong, Y.M., Ma, H.H., and Tang, X.Y., Review of Catalytic Supercritical Water Gasification for Hydrogen Production from Biomass, Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev., 2010, vol. 14, pp. 334–343.
Correa, C.R., and Kruse, A., Supercritical Water Gasification of Biomass for Hydrogen Production—Review, J. Supercrit. Fluids, 2018, vol. 133, pp. 573–590.
Cocero, M.J., Cabeza, A., Abad, N.A., Adamovic, T., Vaquerizo, L., Martinez, C.M., and Pazo-Cepeda, M.V., Understanding Biomass Fractionation in Supercritical Water, J. Supercrit. Fluids, 2018, vol. 133, pp. 550–565.
Perez, E., Tuck, C.O., and Poliakoff, M., Valorisation of Lignin by Depolymerization and Fractionation Using Supercritical Fluids and Conventional Solvents, J. Supercrit. Fluids, 2018, vol. 133, pp. 690–695.
Watanabe, M., Inomata, H., Osada, M., Sato, T., Adschiri, T., and Arai, K., Catalytic Effects of NaOH and ZrO\(_{2}\) for Partial Oxidative Gasification of N-Hexadecane and Lignin in Supercritical Water, Fuel, 2003, vol. 82, pp. 545–552.
Drews, M.J., Barr, M., and Williams, M., A Kinetic Study of the SCWO of a Sulfonated Lignin Waste Stream, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2000, vol. 39, pp. 4784–4793.
Fedyaeva, O.N., Vostrikov, A.A., Shishkin, A.V., and Sokol, M.Y., Transformation of Lignin under Uniform Heating. II. Combustion in a Flow of Water-Oxygen Mixture, J. Supercrit. Fluids, 2019, vol. 148, pp. 24–32.
Lemmon, E.W., McLinden, M.O., and Freid, D.G., Thermophysical Properties of Fluid Systems, in NIST Chemistry WebBook, NIST Standard Reference Database, No. 69, Linstrom, P.J. and Mallard, W.G., Eds., Gaithersburg MD: National Institute of Standards and Technology, 2018, 20899; http://webbook.nist.gov/chemistry/fluid/.
Perry’s Chemical Engineers’ Handbook, 7th ed., Perry, P.H., Green, D.W., and Maloney, J.O., Eds., New York: McGraw-Hill, 1997.
Powder Diffraction File, PDF-4+. Release, 2012.
Fedyaeva, O.N., Vostrikov, A.A., Shishkin, A.V., Sokol, M.Y., Borisova, L.S., and Kashirtsev, V.A., Conversion of Brown Coal in Sub- and Supercritical Water at Cyclic Pressurization and Depressurization,Russ. J. Phys. Chem. B, 2012, vol. 6, no. 7, pp. 793–803.
Fedyaeva, O.N., Vostrikov, A.A., Shishkin, A.V., and Sokol, M.Y., Transformation of Lignin under Uniform Heating. I. Gasification in a Flow of Water Vapor and Supercritical Water, J. Supercrit. Fluids, 2019, vol. 148, pp. 84–92.
Vostrikov, A.A., Fedyaeva, O.N., Shishkin, A.V., Sokol, M.Y., Oxidation of Hydrogen Sulfide and Corrosion of Stainless Steel in a Gas Mixture Containing H\(_{2}\)S, O\(_{2}\), H\(_{2}\)O, and CO\(_{2}\),J. Eng. Thermophys., 2017, vol. 26, no. 3, pp. 314–324.
Wiśniewska, M., Chibowski, S., and Urban, T., Modification of the Alumina Surface Properties by Adsorbed Anionic Polyacrylamide—Impact of Polymer Hydrolysis, J. Ind. Eng. Chem., 2015, vol. 21, pp. 925–931.
Kitahara, Y., Okuyama, K., Ozawa, K., Suga, T., Takahashi, S., and Fujii, T., Thermal Decomposition of Acrylamide from Polyacrylamide. Time-Resolved Pyrolysis with Ion-Attachment Mass Spectrometry, J. Therm. An. Calorim., 2012, vol. 110, pp. 423–429.
Ma, Q., Shuler, P.J., Aften, C.W., and Tang, Y., Theoretical Studies of Hydrolysis and Stability of Polyacrylamide Polymers,Polym. Degrad. Stab., 2015, vol. 121, pp. 69–77.
Crain, N., Tebbal, S., Li, L., and Gloyna, E.F., Kinetics and Reaction Pathways of Pyridine Oxidation in Supercritical Water,Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 1993, vol. 32, pp. 2259–2268.
Chen, H., Wang, G., Xu, Y., Chen, Z., and Yin, F., Green Process for Supercritical Water Oxidation of Sewage Sludge with Red Mud as CO\(_{2}\) Adsorbent, J. Envir. Chem. Eng., 2016, vol. 4, pp. 3065–3074.
Ivankin, Y.D., Danchevskaya, M.N., Torbin, S.N., Kreisberg, V.A., and Martynova, L.F., Role of Water Fluid in the Formation of Solid Phase Oxides, Proc. 7th Meeting Supercritical Fluids Particles Design, Materials Natural Products Processing, vol. 1, Antibes, France, 2000, pp. 525–536.
Ivankin, Y.D., Danchevskaya, M.N., Ovchinnikova, O.G., Muraeva, G.P., and Kreisberg, V.A., Kinetics and Mechanism of Doped Corundum Structure Formation in Water Fluid, Supercrit. Fluids: Theory Pract., 2008, vol. 3, no. 4, pp. 11–34.
Fang, Z., Xu, S.-K., and Kozinski, J.A., Flameless Oxidation of Chlorinated Wastes in Supercritical Water using Sodium Carbonate as the Oxidation Stimulant, Proc. Combust. Inst., 2002, vol. 29, pp. 2485–2492.
Sun, Z., Takahashi, F., Odaka, Y., Fukushi, K., Oshima, Y., and Yamamoto, K., Effect of Potassium Alkalis and Sodium Alkalis on the Dechlorination of o-Chlorophenol in Supercritical Water,Chemosphere, 2007, vol. 66, pp. 151–157.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors are grateful to D.A. Yatsenko and E.A. Maksimovskii for X-ray diffraction and electron-microscopy analysis of samples.
Funding
This work was supported by the Russian Science Foundation (grant no. 18-19-00165).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fedyaeva, O.N., Vostrikov, A.A., Artamonov, D.O. et al. Combustion of Sludge-Lignin in Water-Oxygen Mixture. J. Engin. Thermophys. 29, 26–41 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1810232820010038
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1810232820010038