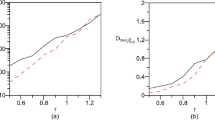
We counted galaxies in the area with 10 Mpc radius around 30 isolated ACO clusters at redshifts z < 0.1. We show that surface densities of galaxies around clusters regularly decrease till 10 Mpc. Separate counts of blue and red galaxies of the cluster environment revealed that at all cluster-centric distances the surface density of red galaxies are higher than that of blue ones. The surface density of red galaxies decrease significantly with increase of distance from the cluster. Meanwhile, the decrease of the surface density of blue galaxies is very smooth and is almost not noticeable at higher cluster-centric distances. It is suggested that the red population of the cluster environment consists of backsplash galaxies that form the cluster halo, which is extended farther than 10 Mpc from the cluster center. The blue population consists mainly of the field galaxies. The velocity dispersion of blue galaxies in the cluster environment is higher than the velocity dispersion of red galaxies, which is evidences of their different entities. The mass of the halo is comparable to the cluster mass.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. R. GottIII and M. J. Rees, Astron. Astrophys., 45, 365, 1975.
W. H. Press and P. Schechter, Astrophys. J., 187, 425, 1974.
S. D. M. White and M. J. Rees, Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc., 183, 341, 1978.
A. V. Kravtsov and S. Borgani, Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys, 50, 353, 2012.
G. O. Abell, H. Jr. Corwin, and R. P. Olowin, Astron. J., 70, 1, 1989.
G. O. Abell, Astropys. J. Suppl. Ser., 3, 211, 1958.
H. Andernach, H. Waldhausen, and R. Wielebinski, Astron. Astrophys. Suppl., 41, 339, 1980.
G. Chincarini and H. J. Rood, Nature, 257, 294, 1975.
M. Seldner and P. J. E. Peebles, Astrophys. J., 215, 703, 1977.
R. S. Bogart and R. V. Wagoner, Astrophys. J., 181, 609, 1973.
M. G. Hauser and P. J. E.Peebles, Astrophys. J., 185, 757, 1973.
C. A. Collins et al., Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc., 274, 1071, 1995.
C. Ahn et al., Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser., 203, 21, 2012.
A. Oemler, Astrophys. J., 194, 1, 1974.
H. Butcher and Jr. A. Oemler, Astrophys. J., 219, 18, 1978.
A.Dressler, Astrophys. J., 236, 351, 1980.
A. Dressler et al., Astrophys. J., 490, 577, 1997.
T. Treu et al., Astrophys. J., 591, 53, 2003.
M. L. Balogh, J. F. Navarro, and S. L. Morris, Astrophys. J., 540, 113, 2000.
B. M. Poggianti et al., Astrophys. J., 642, 188, 2006.
P. Capak et al., Astropys. J. Suppl. Ser., 172, 284, 2007.
E. Hubble and M. L. Humason, Astrophys. J., 74, 43, 1931.
J. Melnick and W. L. W. Sargent, Astrophys. J., 215, 401, 1977.
K.- H.Schmidt, P. Bohm, and H. Elsasser, Astron. Nachr., 318, 81, 1997.
A. Klypin et al., Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc., 454, 1798, 2014.
Y. Zhang, J. Dietrich, T. A. McKay et al., Astrophys. J., 773, 115, 2013.
I. Strateva, Ivezic', G. R. Knapp et al., Astron. J., 122, 1861, 2001.
G. A. Mamon, T. Sanchis, E. Salvador-Solé et al., Astron. Astrophys., 414, 445, 2004.
S. P. D. Gill, A. Knebe, and B. K. Gibson, Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc., 356, 1327, 2005.
K. Rines, M. J. Geller, M. J. Kurtz et al., Astron. J., 130, 1482, 2005.
K. A. Pimbblet, Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc., 411, 2637, 2011.
H. Muriel and V. Coenda, Astron. Astrophys., 564A, 85, 2014.
S. Adhikari, N. Dalal, and R. T. Chamberlain, J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys., 7, 22, 2016.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tovmassian, H.M. On the Size and Mass of Galaxy Clusters. Astrophysics 63, 23–31 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10511-020-09610-x
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10511-020-09610-x