Abstract
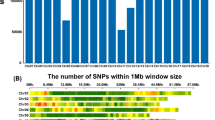
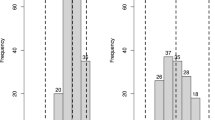
Coffee Berry Disease (CBD) caused by the fungal pathogen Colletotrichum kahawae destroys about 80% of the crop on susceptible Coffea arabica cultivars if no control is applied. Resistance to CBD is governed by three genes: T, R that are dominant, and the recessive k in varieties Hibrido de Timor, Rume Sudan (RS), and K7 respectively. The marker for the T-gene had earlier been identified. The study aimed to identify the DNA marker for the R-gene from RS. The mapping population comprised of 106 F2 genotypes from varieties RS (resistant) and SL28 (susceptible). The genotypes were assessed for their reaction to CBD using hypocotyl inoculation test on a scale of 1–12. The Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP) markers were obtained through Genotyping by Sequencing. The population structure was assessed by both principal component analysis and marker-based kinship while pairwise linkage disequilibrium was estimated using squared allele frequency correlations (r2). Genome-Wide Association Study was carried out using a compressed mixed linear model in Genomic Association and Prediction Integrated Tool. Two SNP markers were significantly associated with CBD resistance in coffee Chromosomes (Chr) 1 and 2 accounting for 12.5% and 11% respectively of the total phenotypic variation explained by the model. The sequence search for the markers was associated with proteins for disease resistance within the NCBI database. The two SNP markers 100025973|F|0-59:T > C-59:T > C and 100034991|F|0-44:C > T-44:C > T are identified as DNA markers for the genetic loci conferring resistance to CBD in RS, christened as Ck-2 and Ck-3 and are recommended for marker assisted selection.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abed A, Belzile F (2019) Comparing single-SNP, multi-SNP, and haplotype-based approaches in association studies for major traits in barley. Plant Genome 12:190036. https://doi.org/10.3835/plantgenome2019.05.0036
Agwanda CO, Lashermes P, Trouslot P, Combes MC, Charrier A (1997) Identification of RAPD markers for resistance to coffee berry disease, Colletotrichum kahawae, in Arabica coffee. Euphytica 97:241–248
Anthony F, Combes MC, Astorga C, Bertrand B, Graziosi G, Lashermes P (2002) The origin of cultivated Coffea arabica L. varieties revealed by AFLP and SSR markers. Theor Appl Genet 104:894–900
Baison J (2014) Mapping and identification of disease resistance candidate genes in three Malus populations using SSRs, DArT and Infinium SNP markers and Illumina sequencing technology. PhD thesis, University of the Western Cape, South Africa
Barilli E, Cobos MJ, Carrillo E, Kilian A, Carling J, Rubiales D (2018) A high-density integrated DArTseq SNP-based genetic map of Pisum fulvum and identification of QTLs controlling rust resistance. Front Plant Sci 9:167. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.00167
Baruah A, Naik V, Hendre PS, Rajkumar P, Aggarwal RK (2003) Isolation and characterization of nine microsatellite markers from Coffea arabica L. showing wide cross-species amplifications. Mol Ecol Notes 3:647–650. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1471-8286.2003.00544.x
Bo K, Wei S, Wang W, Miao H, Dong S, Zhang S et al (2019) QTL mapping and genome-wide association study reveal two novel loci associated with green flesh color in cucumber. BMC Plant Biol 19:243. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-019-1835-6
Bradbury PJ, Zhang Z, Kroon DE, Casstevens TM, Ramdoss Y, Buckler ES (2007) TASSEL: software for association mapping of complex traits in diverse samples. Bioinformatics 23(19):2633–2635. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btm308
Brito GG, Caixeta ET, Gallina AP, Zambolim EM, Zambolim L, Diola V et al (2010) Inheritance of coffee leaf rust resistance and identification of AFLP markers linked to the resistance gene. Euphytica 173:255–264
Brito AC, Oliveira SAS, Oliveira EJ (2017) Genome-wide association study for resistance to cassava root rot. J Agric Sci 155:1424–1441. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0021859617000612
Bush WS, Moore JH (2012) Chapter 11: genome-wide association studies. PLoS Comput Biol 8(12):e1002822. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002822
Camacho LFS, Coan MMD, Scapim CA, Pinto RJB, Tessmann DJ, Contreras-Soto RI (2019) A genome-wide association study for partial resistance to southern corn rust in tropical maize. Wiley- Plant Breed. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbr.12718
Davis AP, Govaerts R, Bridson DM (2006) An annotated taxonomic conspectus of the genus Coffea (Rubiaceae). Bot J Linn Soc 152:465–512
Diniz I, Figueiredo A, Loureiro A, Batista D, Azinheira H, VaÂrzea V et al (2017) A first insight into the involvement of phytohormones pathways in coffee resistance and susceptibility to Colletotrichum kahawae. PLoS ONE 12(5):e0178159. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0178159
Diniz I, Azinheira H, Figueiredo A, Gichuru E, Oliveira H, Guerra-Guimaraes L et al (2019) Fungal penetration associated with recognition, signaling and defence-related genes and peroxidase activity during the resistance response of coffee to Colletotrichum kahawae. Physiol Mol Plant Phathol 105:119–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmpp.2017.12.005
Diola V, Brito GG, Caixeta ET, Zambolim EM, Sakiyama NS, Loureiro ME (2011) High-density genetic mapping for coffee leaf rust resistance. Tree Genet Genomes 7(6):1199–1208. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-011-0406-2
Diola V, Brito GG, Caixeta ET, Pereira LFP, Loureiro ME (2013) A new set of differentially expressed signaling genes is early expressed in coffee leaf rust race II incompatible interaction. Funct Integr Genomics 13(3):379–389
Doyle JJ, Doyle JL (1987) A rapid DNA isolation procedure for small quantities of fresh leaf tissue. Phytochem Bull 19:11–15
Elshire RJ, Glaubitz JC, Sun Q, Poland JA, Kawamoto K, Buckler E et al (2011) A robust, simple genotyping-by-sequencing (GBS) approach for high diversity species. PLoS ONE 6(5):e19379. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0019379
Gao L, Turner MK, Chao S, Kolmer J, Anderson JA (2016) Genome wide association study of seedling and adult plant leaf rust resistance in elite spring wheat breeding lines. PLoS ONE 11(2):e0148671. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0148671
Garavito A, Montagnon C, Guyot R, Bertrand B (2016) Identification by the DArTseq method of the genetic origin of the Coffea canephora cultivated in Vietnam and Mexico. BMC Plant Biol 16:242. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-016-0933-y
Gichuru EK (2007) Characterization of genetic resistance of coffee berry disease (Colletotrichum kahawae, Waller and Bridge) in Arabica coffee (Coffea arabica L.) that is introgressed from Coffea canephora. PhD thesis, University of Nairobi, Kenya
Gichuru EK, Agwanda CO, Combes MC, Mutitu EW, Ngugi ECK, Bertrand B et al (2008) Identification of molecular markers linked to a gene conferring resistance to coffee berry disease (Colletotrichum kahawae) in Coffea arabica. Plant Pathol 57:1117–1124. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3059.2008.01846.x
Gimase JM, Thagana WM, Omondi CO, Ithiru JM (2019) Evaluation of coffee berry disease resistance (Colletotrichum kahawae) in F2 populations derived from Arabica coffee varieties Rume Sudan and SL 28. J Plant Breed Crop Sci 11(9):225–233. https://doi.org/10.5897/JPBCS2019.0829
Gordiard L, Sauviac L, Torii KU, Grenon O, Mangin B, Grimsley NH et al (2003) ERECTA, an LRR receptor-like kinase protein controlling development pleiotropically affects resistance to bacterial wilt. Plant J 36:353–365. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313X.2003.01877.x
Goudet J, Kay T, Weir BS (2018) How to estimate kinship. Mol Ecol 00:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1111/mec.14833
Hall D, Zhao W, Wennström U, Gull BA, Wang XR (2020) Parentage and relatedness reconstruction in Pinus sylvestris using genotyping-by-sequencing. Heredity. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41437-020-0302-3
Hamon P, Hamon S, Razafinarivo NJ, Guyot R, Siljak-Yakovlev S, Couturon E, De Kochko A (2015) Coffea genome organization and evolution. In: Coffee in health and disease prevention. Elsevier Inc, pp 29–37. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-409517-5.00004-8
He Y, Wu D, Wei D, Ying FY, Cui Y, Dong H et al (2017) GWAS, QTL mapping and gene expression analyses in Brassica napus reveal genetic control of branching morphogenesis. Sci Rep 7:15971. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-15976-4
Hindorf H, Omondi CO (2011) A review of three major fungal diseases of Coffea arabica L. in the rainforests of Ethiopia and progress in breeding for resistance in Kenya. J Adv Res 2(2):109–120
Jordá L, Sopeña-Torres S, Escudero V, Nuñez-Corcuera B, Delgado-Cerezo M, Torii KU, Molina A (2016) ERECTA and BAK1 receptor like kinases interact to regulate immune responses in Arabidopsis. Front Plant Sci 7:897. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.00897
Kankanala P, Nandety RS, Mysore KS (2019) Genomics of plant disease resistance in legumes. Front Plant Sci 10:1345. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.01345
Kathurima CW (2013) Characterization of coffee genotypes in Kenya by genetic, biochemical and beverage quality profiles. PhD thesis, Jomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and Technology, Kenya
Kim SM, Reinke RF (2019) A novel resistance gene for bacterial blight in rice, Xa43(t) identified by GWAS, confirmed by QTL mapping using a bi-parental population. PLoS ONE 14(2):e0211775. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0211775
Kjeldsen SR, Raadsma HW, Leigh KA, Tobey JR, Phalen D, Krockenberger A et al (2018) Genomic comparisons reveal biogeographic and anthropogenic impacts in the koala (Phascolarctos cinereus): a dietary-specialist species distributed across heterogeneous environments. Heredity 122:525–544. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41437-018-0144-4
Lashermes P, Combes MC (2018) Diversity and genome evolution in coffee. In: Lashermes P (ed) Achieving sustainable cultivation of coffee. BDS Publ., Cambridge, pp 3–20
Lashermes P, Combes MC, Ansaldi C, Gichuru E, Noir S (2011) Analysis of alien introgression in coffee tree (Coffea arabica L.). Mol Breed 27:223–232. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-010-9424-2
Li Q, Guo J, Chao K, Yang J, Yue W, Ma D et al (2018) High-density mapping of an adult-plant stripe rust resistance gene YrBai in wheat landrace baidatou using the whole genome DArTseq and SNP analysis. Front Plant Sci 9:1120. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.01120
Lipka AE, Tian F, Wang Q, Peiffer J, Li M, Bradbury PJ et al (2012) GAPIT: genome association and prediction integrated tool. Genet Popul Anal 28(18):2397–2399. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bts444
Llorente F, Alonso-Blanco C, Sanchez-Rodriguez C, Jorda L, Molina A (2005) ERECTA receptor-like kinase and heterotrimeric G protein from Arabidopsis are required for resistance to the necrotrophic fungus Plectosphaerella cucumerina. Plant J 43:165–180. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2005.02440.x
Lo S, Munoz-Amatriain M, Hokin SA, Cisse N, Roberts PA, Farmer AD, Xu S, Close TJ (2019) A genome-wide association and meta-analysis reveal regions associated with seed size in cowpea [Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp]. Theor Appl Genet 132:3079–3087. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-019-03407-z
Loureiro A, Nicole MR, Várzea V, Moncada P, Bertrand B, Silva MC (2012) Coffee resistance to Colletotrichum kahawae is associated with lignification, accumulation of phenols and cell death at infection sites. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 77:23–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmpp.2011.11.002
Manickavelu A, Joukhadar R, Jighly A, Lan C, Huerta-Espino J, Stanikzai AS et al (2016) Genome wide association mapping of stripe rust resistance in Afghan wheat landraces. Plant Sci 252:222–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2016.07.018
Masaba DM, Van Der Vossen HAM (1982) Evidence of cork barrier formation as a resistance mechanism to berry disease (Colletotrichum coffeanum) in Arabica coffee. Neth J Plant Pathol 88:19–32
Merot-L’anthoene V, Tournebize R, Darracq O, Rattina V, Lepelley M, Bellanger L et al (2019) Development and evaluation of a genome-wide Coffee 8.5 K SNP array and its application for high density genetic mapping and for investigating the origin of Coffea arabica L. Plant Biotechnol J. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.13066
Mogga M, Sibiya J, Shimelis H, Lamo J, Yao N (2018) Diversity analysis and genome-wide association studies of grain shape and eating quality traits in rice (Oryza sativa L.) using DArT markers. PLoS ONE 13(6):e0198012. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0198012
Moncada MP, Tovar E, Montoya JC, González A, Spindel J, McCouch S (2016) A genetic linkage map of coffee (Coffea arabica L.) and QTL for yield, plant height, and bean size. Tree Genet Genomes 12:5. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-015-0927-1
Nemli S, Asciogul TK, Ates D, Esiyok D, Tanyola MB (2017) Diversity and genetic analysis through DArTseq in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) germplasm from Turkey. Turk J Agric For 41:389–404. https://doi.org/10.3906/tar-1707-89
Nyine M, Uwimana B, Akech V, Brown A, Ortiz R, Doležel J et al (2019) Association genetics of bunch weight and its component traits in East African highland banana (Musa spp AAA group). Theor Appl Genet. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-019-03425-x
Omondi CO (1994) Resistance to coffee berry disease in Arabica coffee variety, Ruiru 11. Plant Breed 112:256–259
Pestana KN, Capucho AS, Caixeta ET, de Almeida DP, Zambolim EM, Cruz CD et al (2015) Inheritance study and linkage mapping of resistance loci to Hemileia vastatrix in Híbrido de Timor UFV 443-03. Tree Genet Genomes 11:72. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-015-0903-9
Poland J, Endelman J, Dawson J, Rutkoski J, Wu S, Manes Y et al (2012) Genomic selection in wheat breeding using genotyping-by-sequencing. Plant Genome 5(3):103–113. https://doi.org/10.3835/plantgenome2012.06.0006
Prakash NS, Combes MC, Somanna N, Lashermes P (2002) AFLP analysis of introgression in coffee cultivars (Coffea arabica L) derived from a natural interspecific hybrid. Euphytica 124:265–271
Sanchez-Rodriguez C, Estevez JM, Llorente F, Hernandez-Blanco C, Jorda L, Pagan I et al (2009) The ERECTA receptor-like kinase regulates cell wall-mediated resistance to pathogens in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 22:953–963. https://doi.org/10.1094/MPMI-22-8-0953
Sant’Ana GC, Pereira LFP, Pot D, Ivamoto ST, Domingues DS, Ferreira RV et al (2018) Genome-wide association study reveals candidate genes influencing lipids and diterpenes contents in Coffea arabica L. Sci Rep 8:465. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-18800-1
Santos RM (2019) Preliminary studies on genetic profiling of coffee and caffeine consumption. Beverages 5:41. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages5030041
Schwarz G (1978) Estimating the dimension of a model. Ann Stat 6(2):461–464. https://doi.org/10.1214/aos/1176344136
Shchennikova AV, Kochieva EZ, Beletsky AV, Filyushin MA, Shulga OA, Ravin NV, Skryabin KG (2017) Identification and expression analysis of receptor-like kinase gene ERECTA in mycoheterotrophic plant Monotropa hypopitys. Mol Biol 51(5):681–686
Shin JH, Blay S, McNeney B (2006) LDheatmap: an R function for graphical display of pairwise linkage disequilibria between single nucleotide polymorphisms. J Stat Softw 16 Code Snippet 3. http://www.jstatsoft.org/. Accessed 21 Nov 2019
Sousa TV, Caixeta ET, Alkimim ER, Oliveira ACB, Pereira TV, Sakiyama NS et al (2017) Population structure and genetic diversity of coffee progenies derived from Catuaí and Híbrido de Timor revealed by genome-wide SNP marker. Tree Genet Genome 13:124. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-017-1208-y
Sousa TV, Caixeta ET, Alkimim ER, Oliveira ACB, Pereira AA, Sakiyama NS et al (2019) Early Selection enabled by the implementation of genomic selection in Coffea arabica breeding. Front Plant Sci 9:19–34. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.01934
Tran HTM, Ramaraj T, Furtado A, Lee LS, Henry RJ (2018a) Use of a draft genome of coffee (Coffea arabica) to identify SNPs associated with caffeine content. Plant Biotechnol J 16:1756–1766. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.12912
Tran HTM, Furtado A, Vargas CAC, Smyth HL, Lee HLS, Henry R (2018b) SNP in the Coffea arabica genome associated with coffee quality. Tree Genet Genomes 14:72. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-018-1282-9
Tran DT, Steketee CJ, Boehm JD, Noe J, Li Z (2019) Genome-wide association analysis pinpoints additional major genomic regions conferring resistance to Soybean cyst nematode (Heterodera glycines Ichinohe). Front. Plant Sci. 10:401. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.00401
Van der Vossen HAM, Walyaro DJ (1980) Breeding for resistance to coffee berry disease in Coffea arabica L. II. Inheritance of the resistance. Euphytica 29:777–791
Van der Vossen HAM, Walyaro DJ (1981) Coffee Breeding programme in Kenya. A review of progress made since 1971 and a plan of action for the coming years. Kenya Coffee 46:113–130
Van der Vossen HAM, Cook RTA, Murakaru GNW (1976) Breeding for resistance to coffee berry disease caused by Colletotrichum coffeanum Noack sensu Hindorf in Coffea arabica L. I. Methods of pre-selection for resistance. Euphytica 25:733–756
Van der Vossen H, Bertrand B, Charrier A (2015) Next generation variety development for sustainable production of Arabica coffee (Coffea arabica L.): a review. Euphytica 204:243. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-015-1398-z
VanLiere JN, Rosenberg NA (2008) Mathematical properties of the r2 measure of linkage disequilibrium. Theor Popul Biol 74(1):130–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tpb.2008.05.006
VanRaden PM (2008) Efficient methods to compute genomic predictions. J Dairy Sci 91:4414–4423. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2007-0980
Vieira A, Diniz I, Loureiro A, Pereira AP, Silva MC, Varzea V et al (2019) Aggressiveness profiling of the coffee pathogen Colletotrichum kahawae. Plant Pathol 68:358–368. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppa.12950
Walyaro DJA (1983) Considerations in breeding for improved yield and quality in Arabica coffee (Coffea arabica L.), Doctoral thesis, Wageningen, The Netherlands
Zaidi PH, Seetharam K, Krishna G, Krishnamurthy L, Gajanan S, Babu R et al (2016) Genomic regions associated with root traits under drought stress in tropical maize (Zea mays L.). PLoS ONE 11(10):e0164340. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0164340
Zhou L, Vega FE, Tan H, Lluch RAE, Meinhardt LW, Fang W et al (2016) Developing single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) markers for the identification of coffee germplasm. Trop Plant Biol 9:82–95. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12042-016-9167-2
Acknowledgements
This work was co-financed by KALRO-Coffee Research Institute (CRI) and International Livestock Research Institute (ILRI) through a collaborative project ‘Integrated Genotyping Service and Support’ with subsidy Funding from Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation. Thanks are due to Director General – KALRO (through the Institute Director – CRI) and Director General ILRI.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared that there was no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gimase, J.M., Thagana, W.M., Omondi, C.O. et al. Genome-Wide Association Study identify the genetic loci conferring resistance to Coffee Berry Disease (Colletotrichum kahawae) in Coffea arabica var. Rume Sudan. Euphytica 216, 86 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-020-02621-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-020-02621-x