Abstract
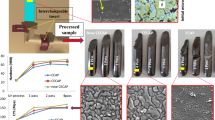
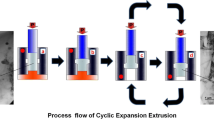
Hydrostatic cyclic expansion extrusion (HCEE) process at elevated temperatures is proposed as a method for processing less deformable materials such as magnesium and for producing long ultrafine-grained rods. In the HCEE process at elevated temperatures, high-pressure molten linear low-density polyethylene (LLDPE) was used as a fluid to eliminate frictional forces. To study the capability of the process, AM60 magnesium rods were processed and the properties were investigated. The mechanical properties were found to improve significantly after the HCEE process. The yield and ultimate strengths increased from initial values of 138 and 221 MPa to 212 and 317 MPa, respectively. Moreover, the elongation was enhanced due to the refined grains and the existence of high hydrostatic pressure. Furthermore, the microhardness was increased from HV 55.0 to HV 72.5. The microstructural analysis revealed that ultrafine-grained structure could be produced by the HCEE process. Moreover, the size of the particles decreased, and these particles thoroughly scattered between the grains. Finite element analysis showed that the HCEE was independent of the length of the sample, which makes the process suitable for industrial applications.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
F. Akbaripanah, F. Fereshteh-Saniee, R. Mahmudi, and H.K. Kim, Microstructural homogeneity, texture, tensile and shear behavior of AM60 magnesium alloy produced by extrusion and equal channel angular pressing, Mater. Des., 43(2013), p. 31.
S. Amani, G. Faraji, H.K. Mehrabadi, K. Abrinia, and H. Ghanbari, A combined method for producing high strength and ductility magnesium microtubes for biodegradable vascular stents application, J. Alloys Compd., 723(2017), p. 467.
W.J. Xia, Z.H. Chen, D. Chen, and S.Q. Zhu, Microstructure and mechanical properties of AZ31 magnesium alloy sheets produced by differential speed rolling, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 209(2009), No. 1, p. 26.
D. Rahmatabadi, M. Tayyebi, R. Hashemi, and G. Faraji, Microstructure and mechanical properties of Al/Cu/Mg laminated composite sheets produced by the ARB process, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater., 25(2018), No. 5, p. 564.
R. Valiev, Nanostructuring of metals by severe plastic deformation for advanced properties, Nat. Mater., 3(2004), No. 8, p. 511.
R.K. Islamgaliev, O.B. Kulyasova, B. Mingler, M. Zehetbauer, and A. Minkow, Structure and fatigue properties of the Mg alloy AM60 processed by ECAP, Mater. Sci. Forum, 584–586(2008), p. 803.
W. Pachla, M. Kulczyk, M. Sus-Ryszkowska, A. Mazur, and K.J. Kurzydlowski, Nanocrystalline titanium produced by hydrostatic extrusion, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 205(2008), No. 1–3, p. 173.
P. Bridgman, Effects of high shearing stress combined with high hydrostatic pressure, Phys. Rev., 48(1935), No. 10, p. 825.
M. Janeček, M. Popov, M.G. Krieger, R.J. Hellmig, and Y. Estrin, Mechanical properties and microstructure of a Mg alloy AZ31 prepared by equal-channel angular pressing, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 462(2007), No. 1–2, p. 116.
G.J. Raab, R.Z. Valiev, T.C. Lowe, and Y.T. Zhu, Continuous processing of ultrafine grained Al by ECAP-Conform, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 382(2004), No. 1–2, p. 30.
H. Utsunomiya, K. Hatsuda, T. Sakai, and Y. Saito, Continuous grain refinement of aluminum strip by conshearing, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 372(2004), No. 1–2, p. 199.
M. Eskandarzadeh, A. Masoumi, G. Faraji, M. Mohammadpour, and X.S. Yan, A new designed incremental high-pressure torsion process for producing long nanostructured rod samples, J. Alloys Compd., 695(2017), p. 1539.
N. Pardis, B. Talebanpour, R. Ebrahimi, and S. Zomorodian, Cyclic expansion-extrusion (CEE): A modified counterpart of cyclic extrusion-compression (CEC), Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 528(2011), No. 25–26, p. 7537.
G. Faraji, F. Samadpour, and P. Babaei, Hydrostatic Cyclic Expansion Extrusion Process For Producing Ultrafine-Grained Rods, U.S. Patent, Appl. 15/725232, 2018.
F. Samadpour, G. Faraji, P. Babaie, S.R. Bewsher, and M. Mohammadpour, Hydrostatic cyclic expansion extrusion (HCEE) as a novel severe plastic deformation process for producing long nanostructured metals, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 718(2018), p. 412.
M. Lewandowska and K.J. Kurzydlowski, Recent development in grain refinement by hydrostatic extrusion, J. Mater. Sci., 43(2008), No. 23–24, p. 7299.
K.Y. Rhee, W.Y. Han, H.J. Park, and S.S. Kim, Fabrication of aluminum/copper clad composite using hot hydrostatic extrusion process and its material characteristics, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 384(2004), No. 1–2, p. 70.
N. Stanford and M.R. Barnett, Solute strengthening of prismatic slip, basal slip and \(\left\{{10\overline 1 2} \right\}\) twinning in Mg and Mg-Zn binary alloys, Int. J. Plast., 47(2013), p. 165.
G. Faraji, M.M. Mashhadi, K. Abrinia and H.S. Kim, Deformation behavior in the tubular channel angular pressing (TCAP) as a noble SPD method for cylindrical tubes, Appl. Phys. A, 107(2012), No. 4, p. 819.
G. Faraji, M.M. Mashhadi, S.H. Joo, and H.S. Kim, The role of friction in tubular channel angular pressing, Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci, 31(2012), No. 1, p. 12.
Q. Chen, Z.D. Zhao, G. Chen, and B. Wang, Effect of accumulative plastic deformation on generation of spheroidal structure, thixoformability and mechanical properties of large-size AM60 magnesium alloy, J. Alloys Compd., 632(2015), p. 190.
G. Faraji, M.M. Mashhadi, and H.S. Kim, Microstructure inhomogeneity in ultra-fine-grained bulk AZ91 produced by accumulative back extrusion (ABE), Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 528(2011), No. 13–14, p. 4312.
S. Amani, G. Faraji, and K. Abrinia, Microstructure and hardness inhomogeneity of fine-grained AM60 magnesium alloy subjected to cyclic expansion extrusion (CEE), J. Manuf. Processes, 28(2017), p. 197.
E.D. Hall, The deformation and ageing of mild steel: III discussion of results, Proc. Phys. Soc. B, 64(1951), No. 9, p. 747.
A. Yamashita, Z. Horita, and T.G. Langdon, Improving the mechanical properties of magnesium and a magnesium alloy through severe plastic deformation, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 300(2001), No. 1–2, p. 142.
O. Kulyasova, R. Islamgaliev, B. Mingler, and M. Zehetbauer, Microstructure and fatigue properties of the ultrafine-grained AM60 magnesium alloy processed by equal-channel angular pressing, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 503(2009), No. 1–2, p. 176.
S.M. Masoudpanah and R. Mahmudi, The microstructure, tensile, and shear deformation behavior of an AZ31 magnesium alloy after extrusion and equal channel angular pressing, Mater. Des., 31(2010), No. 7, p. 3512.
Acknowledgement
This work was financially supported by the Iran National Science Foundation (No. 96000854).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Samadpour, F., Faraji, G. & Siahsarani, A. Processing of AM60 magnesium alloy by hydrostatic cyclic expansion extrusion at elevated temperature as a new severe plastic deformation method. Int J Miner Metall Mater 27, 669–677 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-019-1921-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-019-1921-7