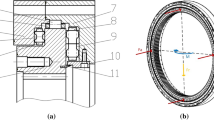
Abstract
The single-row four-point contact ball slewing bearing has a large structure and is subjected to heavy load, which requires extremely high carrying capacity. The structural parameters of the ball diameter and the number of balls are optimized with the fixed size of the inner and outer rings of the slewing bearing. Numerical methods based on static bearing capacity and fatigue life are used to optimize the structural parameters of the slewing bearing. The finite element model and the local finite element model of the slewing bearing are established to analyze the carrying capacity of different structural parameters. The Hertz contact theory and the experiment are used to compare the theoretically calculated load distribution, contact stress, contact area and deformation. Optimization of structural parameters of the slewing bearing is beneficial to improve the carrying capacity and service life, which provides an important reference for designers.





















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- \(\alpha\) (o):
-
Contact angle
- \(a\) (mm):
-
Contact ellipse long half-axis length
- \(a^{*}\) :
-
Function related to \(F\left( \rho \right)\)
- \(b\) (mm):
-
Contact ellipse short half-axis length
- \(b^{*}\) :
-
Function related to \(F\left( \rho \right)\)
- \(C_{\text{a}}\) (N):
-
Axial basic dynamic load rating
- \(D_{\text{L}}\) (mm):
-
Raceway center diameter
- \(D_{\text{i}}\) (mm):
-
Outer ring inner diameter
- \(D_{\text{O}}\) (mm):
-
Outer ring outer diameter
- \(D_{\text{w}}\) (mm):
-
Ball diameter
- \(d_{\text{i}}\) (mm):
-
Inner ring inner diameter
- \(d_{\text{o}}\) (mm):
-
Inner ring outer diameter
- \(E_{1}\) (MPa):
-
Ball elastic modulus
- \(E_{2}\) (MPa):
-
Raceway elastic modulus
- f cm :
-
Variable
- \(f\) :
-
Groove radius coefficient
- \(F_{\text{a}}\) (N):
-
Axial load
- \(F_{\text{r}}\) (N):
-
Radial load
- \(F\left( \rho \right)\) :
-
Principal curvature difference function
- \(H\) (mm):
-
Outer ring height
- \(H_{1}\) (mm):
-
Total height
- \(i\) :
-
Rolling element row
- \(h\) (mm):
-
Inner ring height
- \(K\) :
-
Value related to the cage
- \(K_{\text{c}}\) :
-
Ball stiffness
- \(L\) (106 r/min):
-
Fatigue life
- \(M\) (N mm):
-
Overturning moment
- \(P_{\text{ea}}\) (N):
-
Dynamic equivalent axial load rating
- \(P_{\text{a}}\) (N):
-
Single load of axial force
- \(P_{\text{M}}\) (N):
-
Single load of overturning moment
- \(Q\) (N):
-
Contact load
- \(Q_{\hbox{max} }\) (N):
-
Maximum contact load
- \(r_{{1{\rm I}}}\) (mm):
-
Radius of the plane 1 of the object 1
- \(r_{1\coprod }\) (mm):
-
Radius of the plane 2 of the object 1
- \(r_{{2{\rm I}}}\) (mm):
-
Radius of the plane 1 of the object 2
- \(r_{2\coprod }\) (mm):
-
Radius of the plane 2 of the object 2
- \(Z\) :
-
Ball number
- \(\delta\) (mm):
-
Deformation
- \(\mu_{1}\) :
-
Ball Poisson ratio
- \(\mu_{2}\) :
-
Raceway Poisson ratio
- \(\sigma_{\hbox{max} }\) (MPa):
-
Maximum contact stress
- \(\sum \rho\) :
-
Sum of curvature
- \(\rho_{{1{\rm I}}}\) :
-
Curvature of plane 1 of object 1
- \(\rho_{1\coprod }\) :
-
Curvature of plane 2 of object 1
- \(\rho_{{2{\rm I}}}\) :
-
Curvature of plane 1 of object 2
- \(\rho_{2\coprod }\) :
-
Curvature of the plane 2 of the object 2
References
IMO (2019) DV 313D slewing ring product catalogue. http://www.goimo.com
Jose IA, Xabier S, Jorge D (2003) Load distribution in a four contact-point slewing bearing. Mech Mach Theory 38:479–496
Peter G, Rok P, Srečko G (2013) Computational model for determination of dynamic load capacity of large three-row roller slewing bearing. Eng Fail Anal 32(9):44–53
Peter G, Rok P, Srečko G (2013) Computational model for determination of static load capacity of three-row roller slewing bearings with arbitrary clearance and predefined raceway deformations. Int J Mech Sci 73:82–92
Peiyu H, Rongjing H, Hua W et al (2018) Calculation analysis of the yaw bearing with a hardened raceway. Int J Mech Sci 144:540–552
Tadeusz S, Eugeniusz R (2007) Superelement-based modeling of load distribution in large-size slewing bearings. J Mech Des 129(4):459–463
Tadeusz S, Damian D, Mariusz S (2008) Evaluation of load distribution in the superstructure rotation joint of single-bucket caterpillar excavators. Autom Constr 17(3):218–223
Peter G, Srečko G (2014) Rolling contact fatigue life assessment of induction hardened raceway. Procedia Eng 74:392–397
Branch NA, Arakere NK, Svendsen V et al (2010) Stress field evolution in a ball bearing raceway fatigue spall. J ASTM Int 7(2):1–18
Vikas W, Rajiv T (2014) Optimization of needle roller bearing design using novel hybrid methods. Mech Mach Theory 72(1):71–85
Rajiv T, Kumar KS, Reddy RS (2012) An optimal design methodology of tapered roller bearings using genetic algorithms. Int J Comput Methods Eng Sci Mech 13(13):108–127
Kumar KS, Tiwari R, Reddy RS (2008) Development of an optimum design methodology of cylindrical roller bearings using genetic algorithms. Int J Comput Methods Eng Sci Mech 9(6):321–341
Rao BR, Tiwari R (2007) Optimum design of rolling element bearings using genetic algorithms. Mech Mach Theory 42(2):233–250
Mohamed HA, Ayman MAY, Sayed MM (2001) Ball bearing fatigue and wear life optimization using elastohydrodynamic and genetic algorithm. In: International design engineering technical conferences and computers and information in engineering conference, vol 1, pp 849–856
JB/T 2300-2011 (2011) Slewing bearing. In: People’s Republic of China machinery industry standards, China
Xunlei Z, Fengchang S, Chengxi C (1995) Optimization design of bi-objective function for dynamic load and stiffness of angular contact ball bearings. Bearing 7:2–4
Jiwei L (2003) Ball bearing design calculation. Mechanical Industry Press, Beijing
Harris T, Rumbarger JH, Butterfield CP (2009) National renewable energy laboratory. Technical report with number NREL/TP-500-42362 Wind turbine design guideline DG03: yaw and pitch rolling bearing life
ISO 16281 (2008) Rolling bearings—METHODS for calculating the modified reference rating life for universally loaded bearings
Johnson KL (1985) Contact mechanics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Jiayu G (2012) Research on slewing bearing materials and mechanical properties. Hefei University of Technology, Hefei
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the support provided by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51575245, 51679112, 51805225, and 51875273) and Jiangsu Province Key Research and Development Program (BE2016161).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Technical Editor: João Marciano Laredo dos Reis.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, P., Wang, Y., Liu, H. et al. Optimization design of structural parameters of single-row four-point contact ball slewing bearing. J Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 42, 291 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-020-02391-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-020-02391-6