Abstract
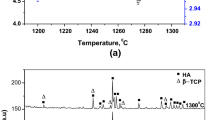
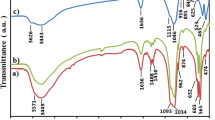
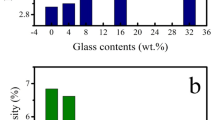
A series of hydroxyapatite/barium titanate (HA/BT) and tricalcium phosphate/barium titanate (TCP/BT) composites were prepared in various mixing ratios and sintered at temperatures between 500 and 1300 °C using the powder metallurgy method. Sintering was performed under different atmospheres to evaluate the effect of the atmosphere on the phase stability of the composites. BT phase showed slightly higher phase stability in TCP/BT composites than in HA/BT composites. BT with low concentration behaved as a stabilizer of α-TCP. A reaction between HA and BT occurred at about 900 °C yielding byproducts of CaTiO3 and Ba2TiO4, at the expense of both HA and BT phases. CaTiO3 and Ba2TiO4 phases associated with low BT concentrations were observed in the composites sintered at temperatures between 1100 and 1300 °C. The HA/BT composites having BT concentrations less than 95 wt.% did not show any measurable piezoelectric response. Composites with BT promoted osteoblast adhesion even better than pure HA and TCP.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fukada, E., Yasuda, I.: On the piezoelectric effect of bone. J Phys Soc Jpn. 12, 1158 (1957)
Bassett, C.A., Becker, R.O.: Generation of electric potentials by bone in response to mechanical stress. Science. 137, 1063 (1962)
Fukada, E., Yasuda, I.: Piezoelectric effects in collagen. Jpn J Appl Phys. 3, 117 (1964)
McElhaney, J.H.: The charge distribution on the human femur due to load. J Bone Jt Surg. 49A, 1561 (1967)
Hastings, G.W., Mahmud, F.A.: The electromechanical properties of fluid filled bone: a new dimension. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2, 118 (1991)
Frost, H.M.A.: A 2003 update of bone physiology and Wolff’s Law for clinicians. Angle Orthod. 74, 3 (2004)
Tomofuji, T., Ekuni, D., Azuma, T., Irie, K., Endo, Y., Kasuyama, K., Nagayama, M., Morita, M.: Effects of electrical stimulation on periodontal tissue remodeling in rats. J Periodontal Res. 48, 177 (2013)
Aaron, R.K., Ciombor, D.M.: Therapeutic effects of electromagnetic fields in the stimulation of connective tissue repair. J Cell Biochem. 52, 42 (1993)
Ciombor, D.M., Aaron, R.K.: The role of electrical stimulation in bone repair. Foot Ankle Clin. 10, 579 (2005)
Zhao, M., Penninger, J., Isseroff, R.R.: Electric activation of wound-healing pathways. Adv Skin Wound Care. 1, 567 (2010)
Zhao, Z., Watt, C., Karystinou, A.: Directed migration of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in a physiological direct current electric field. Eur Cell Mater. 22, 344 (2011)
Madou, M.J.: Fundamentals of microfabrication: the science of miniaturization, 2nd edn. CRC Press, Florida (2004)
Feigenbaum, E.: Cochlear implant devices for the profoundly hearing impaired. IEEE Eng Med Bio Mag. 6, 10 (1987)
Rebscher, S.J.: Cochlear implants: design and construction. In: Gray, R.F. (ed.) Cochlear Implants, pp. 74. Croom-Helm, London (1985)
Guo, S., Dong, X., Wang, G., Lu, F., Kang, H., Wang, Y.: Properties evaluation of piezoelectric materials in application of cochlear implant. Ferroelectrics. 413, 272 (2011)
Glattke, T.J.: The inner ear anatomy and physiology. In: Martin, F.N. (eds.) Medical audiology: disorders of hearing, pp. 195. Prentice-Hall, New Jersey (1981)
Park, Y.J., Hwang, K.S., Song, J.E., Ong, J.L., Rawls, H.R.: Growth of calcium phosphate on poling treated ferroelectric BaTiO3 ceramics. Biomaterials. 23, 3859 (2002)
Hwang, K.S., Song, J.E., Jo, J.W., Yang, H.S., Park, Y.J., Ong, J.L., Rawls, H.R.: Effect of poling conditions on growth of calcium phosphate crystal in ferroelectric BaTiO3 ceramics. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 13, 133 (2002)
Park, J.B., Kelly, B.J., Kenner, G.H., Vonrecum, A.F., Grether, M.F., Coffeen, W.W.: Piezoelectric ceramic implants in vivo results. J Biomed Mater Res. 15, 103 (1981)
Kobayashi, T., Nakamura, S., Yamashita, K.: Enhanced osteobonding by negative surface charges of electrically polarized hydroxyapatite. J Biomed Mater Res. 57, 477 (2001)
Ohgaki, M., Kizuki, T., Katsura, M., Yamashita, K.: Manipulation of selective cell adhesion and growth by surface charges of electrically polarized hydroxyapatite. J Biomed Mater Res. 57, 366 (2001)
Nakamura, M., Sekijima, Y., Nakamura, S., Kobayashi, T., Niwa, K., Yamashita, K.: Role of blood coagulation components as intermediators of high osteoconductivity of electrically polarized hydroxyapatite. J Biomed Mater Res. 79A, 627 (2006)
Nakamura, S., Kobayashi, T., Nakamura, M., Itoh, S., Yamashita, K.: Electrostatic surface charge acceleration of bone ingrowth of porous hydroxyapatite/beta tricalcium phosphate ceramics. J Biomed Mater Res. 92A, 267 (2010)
Nakamura, M., Nagai, A., Tanaka, Y., Sekijima, Y., Yamashita, K.: Polarized hydroxyapatite promotes spread and motility of osteoblastic cells. J Biomed Mater Res. 92A, 783 (2010)
Silva, C.C., Thomazini, D., Pinherio, A.G., Aranha, N., Figueiró, S.D., Góes, J.C., Sombra, A.S.B.: Collagen-hydroxyapatite films: piezoelectric properties. Mater Sci Eng B. 86, 210 (2001)
Park, J.B., von Recum, A.F., Kenner, G.H., Kelly, B.J., Coffeen, W.W., Grether, M.F.: Piezoelectric ceramic implants - a feasibility study. J Biomed Mater Res. 14, 269 (1980)
Baxter, F.R., Turner, I.G., Bowen, C.R., Gitting, J.P., Chaudhuri, J.B.: An in vitro study of electrically active hydroxyapatite-barium titanate ceramics using Saos-2 cells. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 20, 1697 (2009)
Jianqing, F., Huipin, Y., Xingdong, Z.: Promotion of osteogenesis by a piezoelectric biological ceramic. Biomaterials. 18, 1531 (1997)
Liu, B., Chen, L., Shao, C., Zhang, F., Zhou, K., Cao, J., Zhang, D.: Improved osteoblasts growth on osteomimetic hydroxyapatite/BaTiO3 composites with aligned lamellar porous structure. Mater Sci Eng C. 61, 8 (2016)
Zhang, Y., Chen, L., Zeng, J., Zhou, K., Zhang, D.: Aligned porous barium titanate/hydroxyapatite composites with high piezoelectric coefficients for bone tissue engineering. Mater Sci Eng C. 39, 143 (2014)
Dubey, A.K., Kakimoto, K.: Impedance spectroscopy and mechanical response of porous nanophase hydroxyapatite–barium titanate composite. Mater Sci Eng C. 63, 211 (2016)
Aba, A., Ergun, C.: Phase stability in hydroxyapatite/barium titanate piezo bioceramics. Defect and Diffusion Forum. 273-276, 1 (2008)
Vouilloz, F.J., Castro, M.S., Vargas, G.E., Gorustovich, A., Fanovich, M.A.: Reactivity of BaTiO3-Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2 phases in composite materials for biomedical applications. Ceram Int. 43, 4212 (2017)
Ergun, C.: Synthesis and characterization of machinable calcium phosphate/lanthanum phosphate composites. J Mater Process Technol. 199, 178 (2008)
Ergun, C.: Novel machinable calcium phosphate/CaTiO3 composites. Ceram Int. 37, 1143 (2011)
Ergun, C., Webster, T.J., Bizios, R., Doremus, R.H.: Hydroxylapatite with substituted Mg, Zn, Cd, and Y: structure and microstructure. J Biomed Mater Res. 59, 305 (2002)
Ergun, C.: Effect of Ti substitution on the structure of hydroxylapatite. J Eur Ceram Soc. 28, 2137 (2008)
Ergun, C.: Enhanced phase stability in hydroxylapatite / zirconia composites with hot isostatic pressing. Ceram Int. 37, 935 (2011)
Zyman, Z., Tkachenko, M.: CO2 gas-activated sintering of carbonated hydroxyapatites. J Eur Ceram Soc. 31, 241 (2011)
Landi, E., Tampieri, A., Celotti, G., Vichi, L., Sandri, M.: Influence of synthesis and sintering parameters on the characteristics of carbonate apatite. Biomaterials. 25, 1763 (2004)
Cotell, C.M., Chrisey, D.B., Grabowski, K.S., Spregue, J.A.: Pulsed laser deposition of hydroxyapatite thin films on Ti-6Al-4V. J Appl Biomater. 3, 87 (1992)
Sardin, G., Varela, M., Morenza, J.L.: Deposition of hydroxyapatite coatings by laser ablation. In: Brown, P.W., Constanz, B. (eds.) Hydroxyapatite and related materials, p. 225. CRC Press, Boca Raton (1994)
Arias, J.L., García-Sanz, F.J., Mayor, M.B., Chiussi, S., Pou, J., León, B., Pérez-Amor, M.: Physicochemical properties of calcium phosphate coatings produced by pulsed laser deposition at different water vapor pressures. Biomaterials. 19, 883 (1998)
Ergun, C., Evis, Z., Webster, T.J., Sahin, F.C.: Synthesis and microstructural characterization of nano-size calcium phosphates with different stoichiometry. Ceram Int. 37, 971 (2011)
Ergun, C., Liu, H., Halloran, J.W., Webster, T.J.: Increased osteoblast adhesion on nanograined hydroxyapatite and tricalcium phosphate containing calcium titanate. J Biomed Mater Res. 80A, 990 (2007)
Sinyaev, V.A., Shustikova, E.S., Levchenko, L.V., Karzhaubaeva, R.A., Tokseitova, G.A.: Amorphous calcium barium monophosphate and its dehydration in air at room temperature. Russian J App Chem. 81, 1899 (2008)
Funding
This project was funded by Istanbul Technical University, Research Project Department, Project #31605 and #31957.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ozcelik, B., Ergun, C. & Liu, H. A study on calcium phosphate/barium titanate composites: phase characterization, piezoelectric property, and cytocompatibility. J Aust Ceram Soc 56, 1197–1216 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41779-020-00468-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41779-020-00468-y