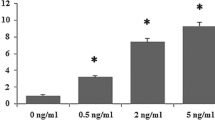
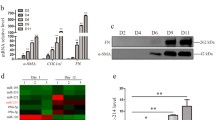
Abstract
In the diseased liver, hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) transdifferentiate into “activated” myofibroblasts that then drive fibrogenesis by promoting the net deposition of extracellular matrix. This regulatory function requires stimulation of the 5-hydroxytryptamine 2B receptor (5-HT2B) on HSCs by serotonin (5-HT), which activates extracellular regulated protein kinases and the transcription factor JunD. However, the regulation mechanisms of 5-HT on microRNAs in the activation of HSCs need a thorough study. In this study, our data show that the expression of miR-221/222 increases with the stimulation of 5-HT and is correlated with the expression levels of alpha 1 type I collagen and α-smooth muscle actin in HSCs. Silencing against 5-HT2B attenuates miR-221/222 expression. Stimulation of stellate cells with 5-HT significantly upregulated miR-221/222 expression, while knockdown of JunD or treatment with the ERK inhibitor PD98059 significantly reduced miR-221/222 expression. miR-221 and miR-222 are potential targets in the quest for a cure for human liver fibrosis.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 5-HT:
-
serotonin
- 5-HT2B:
-
5-hydroxytryptamine 2B receptor
- α-SMA:
-
α-smooth muscle actin
- COL1A1:
-
alpha 1 type I collagen
- DMEM:
-
dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium
- ECM:
-
extracellular matrix
- ERK:
-
extracellular regulated protein kinases
- FBS:
-
fetal bovine serum
- HCC:
-
hepatocellular carcinoma
- HCV:
-
Hepatitis C virus
- HSCs:
-
hepatic stellate cells
- miRNAs:
-
microRNAs
- NASH:
-
non-alcoholic steatohepatitis
- TGF-β:
-
transforming growth factor beta
- UTR:
-
untranslated region
References
Alarcón-Arís D, Recasens A, Galofré M, Carballo-Carbajal I, Zacchi N, Ruiz-Bronchal E, Pavia-Collado R, Chica R, Ferrés-Coy A, Santos M, Revilla R, Montefeltro A, Fariñas I, Artigas F, Vila M, Bortolozzi A (2018) Selective α-Synuclein knockdown in monoamine neurons by intranasal oligonucleotide delivery: potential therapy for Parkinson's disease. Mol Ther 26(2):550–567. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2017.11.015
Barnes E (2018) Unravelling the fate of functional PD1+ T cells in chronic viral hepatitis. J Clin Invest 128:573–576. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI99035
Basak S, Gicheru Y, Kapoor A, Mayer ML, Filizola M, Chakrapani S (2019) Molecular mechanism of setron-mediated inhibition of full-length 5-HT(3A) receptor. Nat Commun 10(1):3225. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-11142-8
Bejjani F, Evanno E, Zibara K, Piechaczyk M, Jariel-Encontre I (2019) The AP-1 transcriptional complex: local switch or remote command? Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer 1872(1):11–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbcan.2019.04.003
Besnier M, Gasparino S, Vono R, Sangalli E, Facoetti A, Bollati V, Cantone L, Zaccagnini G, Maimone B, Fuschi P, Da Silva D, Schiavulli M, Aday S, Caputo M, Madeddu P, Emanueli C, Martelli F, Spinetti G (2018) miR-210 enhances the therapeutic potential of bone-marrow-derived circulating Proangiogenic cells in the setting of limb ischemia. Mol Ther 26(7):1694–1705. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2018.06.003
Buhl CS, Stødkilde-Jørgensen H, Videbech P, Vaag A, Møller N, Lund S, Buhl ES (2018) Escitalopram ameliorates Hypercortisolemia and insulin resistance in low birth weight men with limbic brain alterations. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 103(1):115–124. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2017-01438
Chan JD, Day TA, Marchant JS (2018) Coalescing beneficial host and deleterious antiparasitic actions as an antischistosomal strategy. Elife 7:e35755. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.35755
Chen F, Long Q, Fu D, Zhu D, Ji Y, Han L, Zhang B, Xu Q, Liu B, Li Y, Wu S, Yang C, Qian M, Xu J, Liu S, Cao L, Chin YE, Lam EW, Coppé JP, Sun Y (2018) Targeting SPINK1 in the damaged tumour microenvironment alleviates therapeutic resistance. Nat Commun 9(1):4315. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-06860-4
Chen L, Nan A, Zhang N, Jia Y, Li X, Ling Y, Dai J, Zhang S, Yang Q, Yi Y, Jiang Y (2019) Circular RNA 100146 functions as an oncogene through direct binding to miR-361-3p and miR-615-5p in non-small cell lung cancer. Mol Cancer 18(1):13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-019-0943-0
Cheng Y, Zhu Y, Xu J, Yang M, Chen P, Xu W, Zhao J, Geng L, Gong S (2018) PKN2 in colon cancer cells inhibits M2 phenotype polarization of tumor-associated macrophages via regulating DUSP6-Erk1/2 pathway. Mol Cancer 17(1):13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-017-0747-z
Choi Y, Dienes HP, Krawczynski K (2013) Kinetics of miR-122 expression in the liver during acute HCV infection. PLoS One 8:e76501. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0076501
De Robertis M, Mazza T, Fusilli C, Loiacono L, Poeta ML, Sanchez M, Massi E, Lamorte G, Diodoro MG, Pescarmona E, Signori E, Pesole G, Vescovi AL, Garcia-Foncillas J, Fazio VM (2018) EphB2 stem-related and EphA2 progression-related miRNA-based networks in progressive stages of CRC evolution: clinical significance and potential miRNA drivers. Mol Cancer 17(1):169. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0912-z
Dioufa N, Clark AM, Ma B, Beckwitt CH, Wells A (2017) Bi-directional exosome-driven intercommunication between the hepatic niche and cancer cells. Mol Cancer 16(1):172. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-017-0740-6
Dobnikar L, Taylor AL, Chappell J, Oldach P, Harman JL, Oerton E, Dzierzak E, Bennett MR, Spivakov M, Jørgensen HF (2018) Disease-relevant transcriptional signatures identified in individual smooth muscle cells from healthy mouse vessels. Nat Commun 9:4567. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-06891-x
Dutta RK, Chinnapaiyan S, Rasmussen L, Raju SV, Unwalla HJ (2019) A neutralizing Aptamer to TGFBR2 and miR-145 antagonism rescue cigarette smoke- and TGF-β-mediated CFTR expression. Mol Ther 27(2):442–455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2018.11.017
Ebrahimkhani MR, Oakley F, Murphy LB, Mann J, Moles A, Perugorria MJ, Ellis E, Lakey AF, Burt AD, Douglass A, Wright MC, White SA, Jaffré F, Maroteaux L, Mann DA (2011) Stimulating healthy tissue regeneration by targeting the 5-HT2B receptor in chronic liver disease. Nat Med 17:1668–1673. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.2490
Ehling J, Tacke F (2016) Role of chemokine pathways in hepatobiliary cancer. Cancer Lett 379:173–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2015.06.017
El-Hamouly MS, Azzam AA, Ghanem SE, El-Bassal FI, Shebl N, Shehata AMF (2019) Circulating microRNA-301 as a promising diagnostic biomarker of hepatitis C virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Biol Rep. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-019-05009-w
Elliott B, Millena AC, Matyunina L, Zhang M, Zou J, Wang G, Zhang Q, Bowen N, Eaton V, Webb G, Thompson S, McDonald J, Khan S (2019) Essential role of JunD in cell proliferation is mediated via MYC signaling in prostate cancer cells. Cancer Lett 448:155–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2019.02.005
Fang J, Hong H, Xue X, Zhu X, Jiang L, Qin M, Liang H, Gao L (2019) A novel circular RNA, circFAT1(e2), inhibits gastric cancer progression by targeting miR-548g in the cytoplasm and interacting with YBX1 in the nucleus. Cancer Lett 442:222–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2018.10.040
Fernando O, Tagalakis AD, Awwad S, Brocchini S, Khaw PT, Hart SL, Yu-Wai-Man C (2018) Development of targeted siRNA Nanocomplexes to prevent fibrosis in experimental Glaucoma filtration surgery. Mol Ther 26(12):2812–2822. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2018.09.004
Foster DJ, Brown CR, Shaikh S, Trapp C, Schlegel MK, Qian K, Sehgal A, Rajeev KG, Jadhav V, Manoharan M, Kuchimanchi S, Maier MA, Milstein S (2018) Advanced siRNA designs further improve in vivo performance of GalNAc-siRNA conjugates. Mol Ther 26(3):708–717. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2017.12.021
Fu H, Meadows AS, Ware T, Mohney RP, McCarty DM (2017) Near-complete correction of profound metabolomic impairments corresponding to functional benefit in MPS IIIB mice after IV rAAV9-hNAGLU gene delivery. Mol Ther 25(3):792–802. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2016.12.025
Fu Y, Liu S, Zeng S, Shen H (2018) The critical roles of activated stellate cells-mediated paracrine signaling, metabolism and onco-immunology in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Mol Cancer 17(1):62. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0815-z
Gao H, Zhang IY, Zhang L, Song Y, Liu S, Ren H, Liu H, Zhou H, Su Y, Yang Y, Badie B (2018) S100B suppression alters polarization of infiltrating myeloid-derived cells in gliomas and inhibits tumor growth. Cancer Lett 439:91–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2018.07.034
Gautam J, Banskota S, Regmi SC, Ahn S, Jeon YH, Jeong H, Kim SJ, Nam TG, Jeong BS, Kim JA (2016) Tryptophan hydroxylase 1 and 5-HT7 receptor preferentially expressed in triple-negative breast cancer promote cancer progression through autocrine serotonin signaling. Mol Cancer 15(1):75. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-016-0559-6
Gorinski N, Bijata M, Prasad S, Wirth A, Abdel Galil D, Zeug A, Bazovkina D, Kondaurova E, Kulikova E, Ilchibaeva T, Zareba-Koziol M, Papaleo F, Scheggia D, Kochlamazashvili G, Dityatev A, Smyth I, Krzystyniak A, Wlodarczyk J, Richter DW, Strekalova T, Sigrist S, Bang C, Hobuß L, Fiedler J, Thum T, Naumenko VS, Pandey G, Ponimaskin E (2019) Attenuated palmitoylation of serotonin receptor 5-HT1A affects receptor function and contributes to depression-like behaviors. Nat Commun 10(1):3924. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-11876-5
Hall AM, Finck BN (2017) ChREBP refines the hepatic response to fructose to protect the liver from injury. J Clin Invest 127:2533–2535. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI95008
Han J, Wang JZ, Yang X, Yu H, Zhou R, Lu HC, Yuan WB, Lu JC, Zhou ZJ, Lu Q, Wei JF, Yang H (2019) METTL3 promote tumor proliferation of bladder cancer by accelerating pri-miR221/222 maturation in m6A-dependent manner. Mol Cancer 18(1):110. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-019-1036-9
Hassan F, Ni S, Arnett TC, McKell MC, Kennedy MA (2018) Adenovirus-mediated delivery of decoy hyper binding sites targeting oncogenic HMGA1 reduces pancreatic and liver Cancer cell viability. Mol Ther Oncolytics 8:52–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omto.2018.01.002
Hirata M, Tajima H, Miyashita T, Miyata T, Nakanuma S, Makino I, Hayashi H, Oyama K, Takamura H, Ninomiya I, Fushida S, Nakata H, Iseki S, Harada S, Wakayama T, Ohta T (2017) Extravasated platelet aggregation in the livers of rats with drug-induced hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome. Mol Med Rep 15:3147–3152. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2017.6407
Hou LK, Ma YS, Han Y, Lu GX, Luo P, Chang ZY, Xie RT, Yang HQ, Chai L, Cai MX, Wu TM, Yu F, Qin SS, Lv ZW, Wu CY, Fu D (2017) Association of microRNA-33a molecular signature with non-small cell lung Cancer diagnosis and prognosis after chemotherapy. PLoS One 12:e0170431. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0170431
Hu D, Hu Y, Xu W, Yu H, Yang N, Ni S, Fu R (2017) miR-203 inhibits the expression of collagen-related genes and the proliferation of hepatic stellate cells through a SMAD3-dependent mechanism. Mol Med Rep 16(2):1248–1254. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2017.6702
Huang Q, Zhang XW, Ma YS, Lu GX, Xie RT, Yang HQ, Lv ZW, Zhong XM, Liu T, Huang SX, Fu D, Xie C (2017) Up-regulated microRNA-299 corrected with poor prognosis of glioblastoma multiforme patients by targeting ELL2. Jpn J Clin Oncol 47:590–596. https://doi.org/10.1093/jjco/hyw188
Huang Y, Xiang B, Liu Y, Wang Y, Kan H (2018) LncRNA CDKN2B-AS1 promotes tumor growth and metastasis of human hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting let-7c-5p/NAP1L1 axis. Cancer Lett 437:56–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2018.08.024
Jacob J, Favicchio R, Karimian N, Mehrabi M, Harding V, Castellano L, Stebbing J, Giamas G (2016) LMTK3 escapes tumour suppressor miRNAs via sequestration of DDX5. Cancer Lett 372:137–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2015.12.026
Jia Y, Miyamoto S, Soda Y, Takishima Y, Sagara M, Liao J, Hirose L, Hijikata Y, Miura Y, Hara K, Iwanaga A, Ota Y, Tani K (2019) Extremely low organ toxicity and strong antitumor activity of miR-34-regulated oncolytic coxsackievirus B3. Mol Ther Oncolytics 12:246–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omto.2019.01.003
Jiang ZY, Jiang JJ, Ma YS, Li HY, Shi W, Fu PL, Xu CF, Lu JZ, Fu D, Xu JG (2018) Downregulation of miR-223 and miR-19a induces differentiation and promotes recruitment of osteoclast cells in giant-cell tumor of the bone via the Runx2/TWIST-RANK/RANKL pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 505:1003–1009. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.10.025
Kaufmann R (2016) Proteinase-activated receptor 2 (PAR2) in hepatic stellate cells - evidence for a role in hepatocellular carcinoma growth in vivo. Mol Cancer 15:54. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-016-0538-y
Khemlina G, Ikeda S, Kurzrock R (2017) The biology of hepatocellular carcinoma: implications for genomic and immune therapies. Mol Cancer 16:149. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-017-0712-x
Kim J, Jiang J, Badawi M, Schmittgen TD (2017a) miR-221 regulates CD44 in hepatocellular carcinoma through the PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 487:709–715. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.04.121
Kim W, Khan SK, Gvozdenovic-Jeremic J, Kim Y, Dahlman J, Kim H, Park O, Ishitani T, Jho EH, Gao B, Yang Y (2017b) Hippo signaling interactions with Wnt/β-catenin and notch signaling repress liver tumorigenesis. J Clin Invest 127:137–152. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI88486
Koikawa K, Ohuchida K, Ando Y, Kibe S, Nakayama H, Takesue S, Endo S, Abe T, Okumura T, Iwamoto C, Moriyama T, Nakata K, Miyasaka Y, Ohtsuka T, Nagai E, Mizumoto K, Hashizume M, Nakamura M (2018) Basement membrane destruction by pancreatic stellate cells leads to local invasion in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Cancer Lett 425:65–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2018.03.031
Kumar V, Kumar V, Luo J, Mahato RI (2018) Therapeutic potential of OMe-PS-miR-29b1 for treating liver fibrosis. Mol Ther 26(12):2798–2811. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2018.08.022
Lao Y, Li Y, Zhang P, Shao Q, Lin W, Qiu B, Lv Y, Tang L, Su S, Zhang H, Tian C, Sun A, Wei H, Zhang P, Wu Y, Jiang Y, He F (2018) Targeting endothelial Erk1/2-Akt Axis as a regeneration strategy to bypass fibrosis during chronic liver injury in mice. Mol Ther 26(12):2779–2797. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2018.08.016
Lee KS, Iwanir S, Kopito RB, Scholz M, Calarco JA, Biron D, Levine E (2017) Serotonin-dependent kinetics of feeding bursts underlie a graded response to food availability in C. elegans. Nat Commun 8:14221. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms14221
Leichter AL, Sullivan MJ, Eccles MR, Chatterjee A (2017) MicroRNA expression patterns and signalling pathways in the development and progression of childhood solid tumours. Mol Cancer 16:15. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-017-0584-0
Li X, Su Y, Sun B, Ji W, Peng Z, Xu Y, Wu M, Su C (2016) An artificially designed interfering lncRNA expressed by oncolytic adenovirus competitively consumes OncomiRs to exert antitumor efficacy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cancer Ther 15(7):1436–1451. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-16-0096
Li R, Wang Y, Zhang X, Feng M, Ma J, Li J, Yang X, Fang F, Xia Q, Zhang Z, Shang M, Jiang S (2019) Exosome-mediated secretion of LOXL4 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cell invasion and metastasis. Mol Cancer 18(1):18. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-019-0948-8
Liang JQ, Teoh N, Xu L, Pok S, Li X, Chu ESH, Chiu J, Dong L, Arfianti E, Haigh WG, Yeh MM, Ioannou GN, Sung JJY, Farrell G, Yu J (2018) Dietary cholesterol promotes steatohepatitis related hepatocellular carcinoma through dysregulated metabolism and calcium signaling. Nat Commun 9:4490. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-06931-6
Liu T, Wang P, Cong M, Zhang D, Liu L, Li H, Zhai Q, Li Z, Jia J, You H (2016) Matrix metalloproteinase-1 induction by diethyldithiocarbamate is regulated via Akt and ERK/miR222/ETS-1 pathways in hepatic stellate cells. Biosci rep. 2016 36(4). https://doi.org/10.1042/BSR20160111
Liu H, Bi J, Dong W, Yang M, Shi J, Jiang N, Lin T, Huang J (2018) Invasion-related circular RNA circFNDC3B inhibits bladder cancer progression through the miR-1178-3p/G3BP2/SRC/FAK axis. Mol Cancer 17(1):161. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0908-8
Lord CC, Wyler SC, Wan R, Castorena CM, Ahmed N, Mathew D, Lee S, Liu C, Elmquist JK (2017) The atypical antipsychotic olanzapine causes weight gain by targeting serotonin receptor 2C. J Clin Invest 127(9):3402–3406. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI93362
Lu G, Fu D, Jia C, Chai L, Han Y, Liu J, Wu T, Xie R, Chang Z, Yang H, Luo P, Lu G, Ma Y, Jia C, Yang H, Xie R, Luo P, Chai L, Cai H, Cai M, Lv Z, Cong X, Fu D (2017) Reduced miR-125a levels associated with poor survival of patients with hepatocellular cancer. Oncol Lett 14:5952–5958. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2017.6902
Lv Z, Yu F, Zhong X, Ma Y (2017) Reduced miR-105-1 levels are associated with poor survival of patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol Lett 14:7842–7848. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2017.7228
Ma YS, Lv ZW, Yu F, Chang ZY, Cong XL, Zhong XM, Lu GX, Zhu J, Fu D (2018a) MiRNA-302a/d inhibits the self-renewal capability and cell cycle entry of liver cancer stem cells by targeting the E2F7/AKT axis. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 37:252. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-018-0927-8
Ma YS, Wu ZJ, Bai RZ, Dong H, Xie BX, Wu XH, Hang XS, Liu AN, Jiang XH, Wang GR, Jiang JJ, Xu WH, Chen XP, Tan GH, Fu D, Liu JB, Liu Q (2018b) DRR1 promotes glioblastoma cell invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition via regulating AKT activation. Cancer Lett 423:86–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2018.03.015
Ma YS, Yu F, Zhong XM, Lu GX, Cong XL, Xue SB, Xie WT, Hou LK, Pang LJ, Wu W, Zhang W, Cong LL, Liu T, Long HD, Sun R, Sun HY, Lv ZW, Wu CY, Fu D (2018c) miR-30 family reduction maintains self-renewal and promotes tumorigenesis in NSCLC-initiating cells by targeting oncogene TM4SF1. Mol Ther S1525-0016:30447–30447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2018.09.006
Ma YS, Wu ZJ, Zhang HW, Cai B, Huang T, Long HD, Xu H, Zhao YZ, Yin YZ, Xue SB, Li L, Liu CL, Xie RT, Tian LL, Liu JB, Wu XM, Fu D (2019) Dual regulatory mechanisms of expression and mutation involving metabolism-related genes FDFT1 and UQCR5 during CLM. Mol Ther Oncolytics 14:172–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omto.2019.04.008
Machitani M, Sakurai F, Wakabayashi K, Nakatani K, Tachibana M, Kato N, Fujiwara T, Mizuguchi H (2017) Suppression of Oncolytic adenovirus-mediated hepatotoxicity by liver-specific inhibition of NF-κB. Mol Ther Oncolytics 7:76–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omto.2017.10.003
Marquez RT, Bandyopadhyay S, Wendlandt EB, Keck K, Hoffer BA, Icardi MS, Christensen RN, Schmidt WN, McCaffrey AP (2010) Correlation between microRNA expression levels and clinical parameters associated with chronic hepatitis C viral infection in humans. Lab Investig 90(12):1727–1736. https://doi.org/10.1038/labinvest.2010.126
Mauseth B, Camilio KA, Shi J, Hammarström CL, Rekdal Ø, Sveinbjørnsson B, Line PD (2019) The novel Oncolytic compound LTX-401 induces antitumor immune responses in experimental hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Ther Oncolytics 14:139–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omto.2019.05.002
Maziveyi M, Dong S, Baranwal S, Alahari SK (2018) Nischarin regulates focal adhesion and Invadopodia formation in breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer 17(1):21. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0764-6
Mendonsa AM, VanSaun MN, Ustione A, Piston DW, Fingleton BM, Gorden DL (2015) Host and tumor derived MMP13 regulate extravasation and establishment of colorectal metastases in the liver. Mol Cancer 14:49. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-014-0282-0
Migita K, Komori A, Kozuru H, Jiuchi Y, Nakamura M, Yasunami M, Furukawa H, Abiru S, Yamasaki K, Nagaoka S, Hashimoto S, Bekki S, Kamitsukasa H, Nakamura Y, Ohta H, Shimada M, Takahashi H, Mita E, Hijioka T, Yamashita H, Kouno H, Nakamuta M, Ario K, Muro T, Sakai H, Sugi K, Nishimura H, Yoshizawa K, Sato T, Naganuma A, Komatsu T, Oohara Y, Makita F, Tomizawa M, Yatsuhashi H (2015) Circulating microRNA profiles in patients with Type-1 autoimmune hepatitis. PLoS One 10(11):e0136908. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0136908
Milbreta U, Lin J, Pinese C, Ong W, Chin JS, Shirahama H, Mi R, Williams A, Bechler ME, Wang J, Ffrench-Constant C, Hoke A, Chew SY (2019) Scaffold-mediated sustained, non-viral delivery of miR-219/miR-338 promotes CNS Remyelination. Mol Ther 27(2):411–423. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2018.11.016
Ogawa T, Enomoto M, Fujii H, Sekiya Y, Yoshizato K, Ikeda K, Kawada N (2012) MicroRNA-221/222 upregulation indicates the activation of stellate cells and the progression of liver fibrosis. Gut 61:1600–1609. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2011-300717
Ohtake Y, Sami A, Jiang X, Horiuchi M, Slattery K, Ma L, Smith GM, Selzer ME, Muramatsu SI, Li S (2019) Promoting axon regeneration in adult CNS by targeting liver kinase B. Mol Ther 27(1):102–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2018.10.019
Oura K, Fujita K, Morishita A, Iwama H, Nakahara M, Tadokoro T, Sakamoto T, Nomura T, Yoneyama H, Mimura S, Tani J, Kobara H, Okano K, Suzuki Y, Masaki T (2019) Serum microRNA-125a-5p as a potential biomarker of HCV-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Lett 18(1):882–890. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2019.10385
Pan ZX, Zhang XY, Chen SR, Li CZ (2019) Upregulated exosomal miR-221/222 promotes cervical cancer via repressing methyl-CpG-binding domain protein 2. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 23(9):3645–3653. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201905_17788
Ries AS, Hermanns T, Poeck B, Strauss R (2017) Serotonin modulates a depression-like state in Drosophila responsive to lithium treatment. Nat Commun 8:15738. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms15738
Rose M, Kloten V, Noetzel E, Gola L, Ehling J, Heide T, Meurer SK, Gaiko-Shcherbak A, Sechi AS, Huth S, Weiskirchen R, Klaas O, Antonopoulos W, Lin Q, Wagner W, Veeck J, Gremse F, Steitz J, Knüchel R, Dahl E (2017) ITIH5 mediates epigenetic reprogramming of breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer 16(1):44. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-017-0610-2
Ruddell RG, Oakley F, Hussain Z, Yeung I, Bryan-Lluka LJ, Ramm GA, Mann DA (2006) A role for serotonin (5-HT) in hepatic stellate cell function and liver fibrosis. Am J Pathol 169:861–876. https://doi.org/10.2353/ajpath.2006.050767
Shrivastava S, Petrone J, Steele R, Lauer GM, Di Bisceglie AM, Ray RB (2013) Up-regulation of circulating miR-20a is correlated with hepatitis C virus-mediated liver disease progression. Hepatology 58(3):863–871. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.26296
Singh AK, Zajdel J, Mirrasekhian E, Almoosawi N, Frisch I, Klawonn AM, Jaarola M, Fritz M, Engblom D (2017) Prostaglandin-mediated inhibition of serotonin signaling controls the affective component of inflammatory pain. J Clin Invest 127(4):1370–1374. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI90678
Singhal A, Agrawal A, Ling J (2018) Regulation of insulin resistance and type II diabetes by hepatitis C virus infection: a driver function of circulating miRNAs. J Cell Mol Med 22(4):2071–2085. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.13553
Song H, Zhang L, Luo Y, Zhang S, Li B (2018) Effects of collagen peptides intake on skin ageing and platelet release in chronologically aged mice revealed by cytokine array analysis. J Cell Mol Med 22(1):277–288. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.13317
Valdmanis PN, Kim HK, Chu K, Zhang F, Xu J, Munding EM, Shen J, Kay MA (2018) miR-122 removal in the liver activates imprinted microRNAs and enables more effective microRNA-mediated gene repression. Nat Commun 9(1):5321. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-07786-7
Wang H, Chen W, Jin M, Hou L, Chen X, Zhang R, Zhang J, Zhu J (2018a) CircSLC3A2 functions as an oncogenic factor in hepatocellular carcinoma by sponging miR-490-3p and regulating PPM1F expression. Mol Cancer 17(1):165. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0909-7
Wang L, Tong X, Zhou Z, Wang S, Lei Z, Zhang T, Liu Z, Zeng Y, Li C, Zhao J, Su Z, Zhang C, Liu X, Xu G, Zhang HT (2018b) Circular RNA hsa_circ_0008305 (circPTK2) inhibits TGF-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis by controlling TIF1γ in non-small cell lung cancer. Mol Cancer 17(1):140. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0889-7
Wang Y, Liang H, Jin F, Yan X, Xu G, Hu H, Liang G, Zhan S, Hu X, Zhao Q, Liu Y, Jiang ZY, Zhang CY, Chen X, Zen K (2019) Injured liver-released miRNA-122 elicits acute pulmonary inflammation via activating alveolar macrophage TLR7 signaling pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 116(13):6162–6171. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1814139116
Wei T, Chen W, Wen L, Zhang J, Zhang Q, Yang J, Liu H, Chen BW, Zhou Y, Feng X, Yang Q, Bai X, Liang T (2016) G protein-coupled estrogen receptor deficiency accelerates liver tumorigenesis by enhancing inflammation and fibrosis. Cancer Lett 382:195–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2016.08.012
Weiskirchen S, Tag CG, Sauer-Lehnen S, Tacke F, Weiskirchen R (2017) Isolation and culture of primary murine hepatic stellate cells. Methods Mol Biol 1627:165–191. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-7113-8_11
Wu CY, Ma Sun K, Xu L, Jing Y, Han Z, Chen X, Cai C, Zhao P, Zhao X, Yang L, Wei L (2017) Autophagy-deficient Kupffer cells promote tumorigenesis by enhancing mtROS-NF-κB-IL1α/β-dependent inflammation and fibrosis during the preneoplastic stage of hepatocarcinogenesis. Cancer Lett 388:198–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2016.12.004
Xie S, Yu X, Li Y, Ma H, Fan S, Chen W, Pan G, Wang W, Zhang H, Li J, Lin Z (2018) Upregulation of lncRNA ADAMTS9-AS2 promotes salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma metastasis via PI3K/Akt and MEK/Erk signaling. Mol Ther 26(12):2766–2778. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2018.08.018
Xu MY, Chen R, Yu JX, Liu T, Qu Y, Lu LG (2016) AZGP1 suppresses epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and hepatic carcinogenesis by blocking TGFβ1-ERK2 pathways. Cancer Lett 374:241–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2016.02.025
Xu W, Qian J, Zeng F, Li S, Guo W, Chen L, Li G, Zhang Z, Wang QJ, Deng F (2019a) Protein kinase ds promote tumor angiogenesis through mast cell recruitment and expression of angiogenic factors in prostate cancer microenvironment. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 38(1):114. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-019-1118-y
Xu J, Su Y, Xu A, Fan F, Mu S, Chen L, Chu Z, Zhang B, Huang H, Zhang J, Deng J, Ai L, Sun C, Hu Y (2019b) miR-221/222-mediated inhibition of autophagy promotes dexamethasone resistance in multiple myeloma. Mol Ther 27(3):559–570. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2019.01.012
Xu Q, Long Q, Zhu D, Fu D, Zhang B, Han L, Qian M, Guo J, Xu J, Cao L, Chin YE, Coppé JP, Lam EW, Campisi J, Sun Y (2019c) Targeting amphiregulin (AREG) derived from senescent stromal cells diminishes cancer resistance and averts programmed cell death 1 ligand (PD-L1)-mediated immunosuppression. Aging Cell:e13027. https://doi.org/10.1111/acel.13027
Xue S, Yin J, Shao J, Yu Y, Yang L, Wang Y, Xie M, Fussenegger M, Ye H (2017) A synthetic-biology-inspired therapeutic strategy for targeting and treating Hepatogenous diabetes. Mol Ther 25(2):443–455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2016.11.008
Yan Y, Jiang W, Tan Y, Zou S, Zhang H, Mao F, Gong A, Qian H, Xu W (2017) hucMSC exosome-derived GPX1 is required for the recovery of hepatic oxidant injury. Mol Ther 25(2):465–479. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2016.11.019
Yin Z, Jiang K, Li R, Dong C, Wang L (2018) Multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells play critical roles in hepatocellular carcinoma initiation, progression and therapy. Mol Cancer 17(1):178. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0926-6
Yu F, Chen B, Dong P, Zheng J (2017) HOTAIR epigenetically modulates PTEN expression via MicroRNA-29b: a novel mechanism in regulation of liver fibrosis. Mol Ther 25(1):205–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2016.10.015
Yu F, Liu JB, Wu ZJ, Xie WT, Zhong XJ, Hou LK, Wu W, Lu HM, Jiang XH, Jiang JJ, Cao ZY, Cong GJ, Shi MX, Jia CY, Lu GX, Song YC, Chai L, Lv ZW, Ma YS, Huang T, Zhong XM, Zhang HW, Cong XL, Xu H, Lu GX, Yu F, Xue SB, Lv ZW, Fu D (2018a) Proteogenomic characterization and comprehensive integrative genomic analysis of human colorectal cancer liver metastasis. Mol Cancer 17:139. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0890-1
Yu F, Liu JB, Wu ZJ, Xie WT, Zhong XJ, Hou LK, Wu W, Lu HM, Jiang XH, Jiang JJ, Cao ZY, Cong GJ, Shi MX, Jia CY, Lu GX, Song YC, Chai L, Lv ZW, Wu CY, Ma YS, Fu D (2018b) Tumor suppressive microRNA-124a inhibits stemness and enhances gefitinib sensitivity of non-small cell lung cancer cells by targeting ubiquitin-specific protease 14. Cancer Lett 427:74–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2018.04.022
Yu Y, Luo W, Yang ZJ, Chi JR, Li YR, Ding Y, Ge J, Wang X, Cao XC (2018c) miR-190 suppresses breast cancer metastasis by regulation of TGF-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Mol Cancer 17(1):70. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0818-9
Yu M, Luo H, Fan M, Wu X, Shi B, Di S, Liu Y, Pan Z, Jiang H, Li Z (2018d) Development of GPC3-specific chimeric antigen receptor-engineered natural killer cells for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Ther 26(2):366–378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2017.12.012
Yu Y, Yin W, Yu ZH, Zhou YJ, Chi JR, Ge J, Cao XC (2019) miR-190 enhances endocrine therapy sensitivity by regulating SOX9 expression in breast cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 38(1):22. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-019-1039-9
Yuzhalin AE, Lim SY, Kutikhin AG, Gordon-Weeks AN (2018) Dynamic matrisome: ECM remodeling factors licensing cancer progression and metastasis. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer 1870(2):207–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbcan.2018.09.002
Zeybel M, Luli S, Sabater L, Hardy T, Oakley F, Leslie J, Page A, Moran Salvador E, Sharkey V, Tsukamoto H, Chu DCK, Singh US, Ponzoni M, Perri P, DiPaolo D, Mendivil EJ, Mann J, Mann DA (2017) A proof-of-concept for epigenetic therapy of tissue fibrosis: inhibition of liver fibrosis progression by 3-Deazaneplanocin a. Mol Ther 25(1):218–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2016.10.004
Zhai W, Li S, Zhang J, Chen Y, Ma J, Kong W, Gong D, Zheng J, Xue W, Xu Y (2018) Sunitinib-suppressed miR-452-5p facilitates renal cancer cell invasion and metastasis through modulating SMAD4/SMAD7 signals. Mol Cancer 17(1):157. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0906-x
Zhang B, Fu D, Xu Q, Cong X, Wu C, Zhong X, Ma Y, Lv Z, Chen F, Han L, Mubbach F, Ungefroren H, Günther B, Katenkamp K, Henklein P, Westermann M, Settmacher U, Lenk L, Sebens S, Müller JP, Böhmer FD, Qian M, Chin YE, Lam EW, Chiao P, Sun Y (2018) The senescence-associated secretory phenotype is potentiated by feedforward regulatory mechanisms involving Zscan4 and TAK1. Nat Commun 9:1723. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-04010-4
Zhao Y, Ge CC, Wang J, Wu XX, Li XM, Li W, Wang SS, Liu T, Hou JZ, Sun H, Fang D, Xie SQ (2017) MEK inhibitor, PD98059, promotes breast cancer cell migration by inducing β-catenin nuclear accumulation. Oncol Rep 38(5):3055–3063. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2017.5955
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Dr. Hongwei Zhang for data analysis and critical discussion of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported partly by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81,972,214, 81,772,932, 81,472,202, 81,201,535, 81,302,065, 81,671,716, 81,301,993, 81,372,175 and 81,472,209), The Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (22,120,170,212 and 22,120,170,117), Shanghai Natural Science Foundation (12ZR1436000), Shanghai Municipal Commission of Health and Family Planning (201540228), Wu Jieping Medical Foundation (320.6750.14326), Construction of Clinical Medical Center for tumor biological samples in Nantong (HS2016004) and Jiangsu 333 Program (BRA2017205).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YX, YSM, WS and DF designed the study. YX, YSM, JBL, ZJW, XPW and DF performed the cytological experiments. YSM, XPW, LPL, GRW, WS and DF performed the statistical analyses and interpreted the data. YX, JBL, ZJW, GRW and DF contributed to study materials and consumables. YX, ZJW and DF wrote the manuscript. YX, YSM, JBL and ZJW contributed equally to this work. All authors agreed with the results and conclusions.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiang, Y., Ma, YS., Liu, JB. et al. Serotonin-induced miR-221/222 contribute to the activation of hepatic stellate cells. Biologia 75, 997–1007 (2020). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-019-00376-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-019-00376-y