Abstract
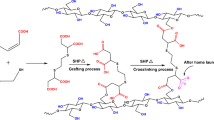
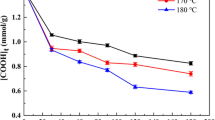
1,2,3,4-Butanetetracarboxylic acid (BTCA) can impart good anti-wrinkle properties to treated cotton fabrics, but it also causes significant strength loss. In this paper, maleic acid (MA) and acrylic acid (AA) were employed to synthesize a low-molecular-weight copolymer (P(MA–AA)) for the anti-wrinkle finishing of cotton fabrics with the hope of reducing strength loss. The best molar ratio of MA:AA and reaction time were 2.5:1 and 5 h, respectively. The molecular weight of P(MA–AA) was determined via mass spectroscopy as 376, and the copolymer consisted of two MA and two AA molecules. The recommended anti-wrinkle finishing conditions were 140 g/L P(MA–AA), finishing bath pH of 1.8, curing temperature of 180 °C and curing time of 2 min. Consequently, the P(MA–AA) showed an outstanding finishing effect on cotton fabrics, compared with BTCA, MA, and citric acid treatments. Additionally, the P(MA–AA)-treated fabrics achieved a wrinkle recovery angle, tearing strength retention, and whiteness index of 255.1° ± 3.50°, 51.2, and 76.20%, respectively. This indicates that P(MA–AA) has a potential for industrial applications.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amornkitbamrung L, Marnul MC, Palani T, Hribernik S, Kovalcik A, Kargl R, Stana-Kleinschek K (2018) Strengthening of paper by treatment with a suspension of alkaline nanoparticles stabilized by trimethylsilyl cellulose. Nano-Struct Nano-Objects 16:363–370
Chen M, Lu B (2001) Synthesis of polymaleic acid crease proofing agent and its application. Text Aux 18:12–14
Chen D, Yang CQ, Qiu X (2005) Aqueous polymerization of maleic acid and cross-linking of cotton cellulose by poly(maleic acid). Ind Eng Chem Res 44:7921–7927
Choi H-M, Welch CM, Morris N (1993) Nonphosphorus catalysts for formaldehyde-free DP finishing of cotton with 1,2,3,4-butanetetracarboxylic acid, part I: Aromatic N-heterocyclic compounds. Text Res J 63:650–657
Choi H-M, Welch CM, Morris N (1994) Nonphosphorus catalysts for formaldehyde-free DP finishing of cotton with 1,2,3,4-butanetetracarboxylic acid part II: sodium salts of fumaric, maleic, and itaconic acids. Text Res J 64:501–507
Hu H, Liu Y, Tu W, Zhang L (2010) Study of particle size change during AA-MA copolymerization in aqueous solution. China Surfactant Deterg Cosmet 40:414–417
Ji B, Tang P, Yan K, Sun G (2015) Catalytic actions of alkaline salts in reactions between 1,2,3,4-butanetetracarboxylic acid and cellulose: II. Esterification. Carbohydr Polym 132:228–236
Ji B, Qi H, Yan K, Sun G (2016a) Catalytic actions of alkaline salts in reactions between 1,2,3,4-butanetetracarboxylic acid and cellulose: I. Anhydride formation. Cellulose 23:259–267
Ji B, Yan K, Sun G (2016b) Investigation on functional properties of 1,2,3,4-butanetetracarboxylic acid cross-linked fabrics impacted by molecular structures and chemical affinity of catalysts. Ind Eng Chem Res 55:5216–5222
Kang H, Liu R, Huang Y (2015) Graft modification of cellulose: methods, properties and applications. Polymer 70:A1–A16
Li M, Xu X (2002) Maleic acid-acrylic copolymer/CA finishing cotton fabric for wrinkle resistance research. J Soochow Univ Eng Sci Ed 22:12–17
Luo M, Li H, Huang C, Zhang H, Xiong L, Chen X, Chen X (2018) Cellulose-based absorbent production from bacterial cellulose and acrylic acid: synthesis and performance. Polymers 10:702–718
Peng H, Yang CQ, Wang X, Wang S (2012) The combination of itaconic acid and sodium hypophosphite as a new cross-linking system for cotton. Ind Eng Chem Res 51:11301–11311
Qi H (2017) Formaldehyde-free anti-wrinkle finishing on cotton fabrics by polycarboxylic acids. Donghua University, Shanghai
Schramm C, Rinderer B, Tessadri R (2014) Non-formaldehyde, crease resistant agent for cotton fabrics based on an organic-inorganic hybrid material. Carbohydr Polym 105:81–89
Udomkichdecha W, Kittinaovarat S, Thanasoonthornroek U, Potiyaraj P, Likitbanakorn P (2003) Acrylic and maleic acids in nonformaldehyde durable press finishing of cotton fabric. Text Res J 73:401–406
Xiao H, Yan K, Ji B (2018) Application of carbohydrate additives in 1,2,3,4-butanetetracarboxylic acid anti-wrinkle finishing of cotton fabrics. J Text Res 39:89–94
Xu W, Wang X (2012) Durable press treatments to improve the durability and wrinkle resistance of cotton and other fabrics. Woodhead Pub Limit 4:70–73
Yang CQ (1991) Characterizing ester crosslinkages in cotton cellulose with FT-IR photoacoustic spectroscopy1. Text Res J 61:298–305
Yang CQ (1993) Infrared-spectroscopy studies of the cyclic anhydrides as the intermediate for the ester cross-linking of cotton cellulose by polycarboxylic acids. I: Identification of the cyclic anhydride intermediate. J Polym Sci, Part A: Polym Chem 31:1187–1193
Yang CQ, Andrews BAK (1991) Infrared spectroscopic studies of the nonformaldehyde durable press finishing of cotton fabrics by use of polycarboxylic acids. J Appl Polym Sci 43:1609–1616
Yang CQ, Bakshi GD (1996) Quantitative analysis of the nonformaldehyde durable press finish on cotton fabric: acid-base titration and infrared spectroscopy. Text Res J 66:377–384
Yang CQ, Wang X (1996) Formation of the cyclic anhydride intermediates and esterification of cotton cellulose by multifunctional carboxylic acids: An infrared spectroscopy study. Text Res J 66:595–603
Yang CQ, Hu C, Lickfield GC (2003) Crosslinking cotton with poly(itaconic acid) and in situ polymerization of itaconic acid: Fabric mechanical strength retention. J Appl Polym Sci 87:2023–2030
Yao W, Wang B, Ye T, Yang Y (2013) Durable press finishing of cotton fabrics with citric acid: enhancement of whiteness and wrinkle recovery by polyol extenders. Ind Eng Chem Res 52:16118–16127
Zhao C, Sun G (2015) Catalytic actions of sodium salts in direct esterification of 3,3′4,4′-benzophenone tetracarboxylic acid with cellulose. Ind Eng Chem Res 54:10553–10559
Zhong Z, Xue W, Li W (2005) Synthesis of MA-IA-AA copolymer and characterization as non-formaldehyde crease-resist finishing agent of cotton fabric. Fine Chem 22:145–148
Acknowledgments
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51803025), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2232020D-21), and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation Project (2018M641893).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liang, T., Yan, K., Zhao, T. et al. Synthesis of a low-molecular-weight copolymer by maleic acid and acrylic acid and its application for the functional modification of cellulose. Cellulose 27, 5665–5675 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03201-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03201-x