Abstract
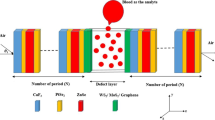
In this paper, a Bloch Surface Waves (BSW) based sensor is proposed to estimate the haemoglobin concentration in human blood. The behaviour of the sensor is analysed using a transfer matrix method. The proposed structure is designed considering one-dimensional photonic crystal, where a defective top layer is deliberately introduced to confine a surface plasmon-like mode called Bloch mode at the top interface. The effective refractive index of top interface changes along with haemoglobin concentration. Thereby, monitoring the angel of incidence to confine BSW mode can helps in determining the haemoglobin concentration. The sensing capability, FWHM and figure-of-merit of the proposed structure are improved by optimizing the defect layer thicknesses, incident angels and wavelengths. Proposed structure shows an average FWHM and average sensitivity of around 0.00508 and 0.0133°/(g/L) respectively.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abd El-Aziz OA, Elsayed HA, Sayed MI (2019) One-dimensional defective photonic crystals for the sensing and detection of protein. Appl Opt 58:8309–8315
Ansarihadipour H, Ziafatikafi H (2012) Structural and spectroscopic changes of human hemoglobin during iron-mediated oxidative stress. J Arak Univ Med Sci 14(6):10–18
Barer R (1952) Interference microscopy and mass determination. Nature 169:366
Barer R (1954) Refractometry of living cells: part I. Basic principles. Quart J Microsc Sci 95:399–423
Barer R (1957) Refractometry and interferometry of living cells. J Opt Soc Am 47(6):545–556
Beutler E, Waalen J (2006) The definition of anemia: what is the lower limit of normal of the blood hemoglobin concentration. Blood 107:1747–1750
Bijalwan A, Rastogi V (2018) Gold–aluminum-based surface plasmon resonance sensor with a high quality factor and figure of merit for the detection of hemoglobin. Appl Opt 57:9230–9237
Bornhop J (1995) Micro volume index of refraction determinations by interferometric backscatter. Appl Opt 34(18):3234–3239
Brahmachari K, Ray M (2016) Modelling and performance analysis of a plasmonic biosensor comprising of silicon and chalcogenide materials for detecting refractive index variations of hemoglobin in near infrared. Optik 127:3517–3522
Chan LL et al (2009) A method for identifying small-molecule aggregators using photonic crystal biosensor microplates. J Assoc Lab Autom 14(6):348–359
Choi CJ et al (2010) Comparison of label-free biosensing in microplate, microfluidic, and spot-based affinity capture assays. Anal Biochem 405(1):1–10
Ciminelli C et al (2013) Label free optical resonant sensors for biochemical applications. Prog Quant Electron 37:51–107
Cunningham B, Li P, Lin B, Pepper J (2002) Colorimetric resonant reflection as a direct biochemical assay technique. Sens Actuator B 81(2):316–328
Dutta HS et al (2017) Analysis of dispersion diagram for high performance refractive index sensor based on photonic crystal waveguides. Photonics Nanostruct Fundam Appl 23:21–27
Frascella F et al (2016) Hydrogel-terminated photonic crystal for label-free detection of angiopoietin-1. J Lightwave Technol 34(15):3641–3645
Friebel M et al (2005) Determination of the complex refractive index of highly concentrated hemoglobin solutions using transmittance and reflectance measurements. J Biomed Opt 10:064019–64025
Friebel M et al (2006) Model function to calculate the refractive index of native hemoglobin in the wavelength range of 250–1100 nm dependent on concentration. Appl Opt 45:2838–2842
Ghosh G (1998) Handbook of thermo-optic coefficients of optical materials with applications. Handbook of optical constants of solids. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Goyal AK, Pal S (2015a) Design and simulation of high sensitive gas sensor using a ring-shaped photonic crystal waveguide. Phys Scr 90:025503
Goyal AK, Pal S (2015b) Design and simulation of high sensitive photonic crystal waveguide sensor. Optik 126(2):240–243
Goyal AK, Dutta HS, Pal S (2016a) Performance optimization of photonic crystal resonator. Opt Quantum Electron 48:431
Goyal AK, Dutta HS, Pal S (2016b) Design and analysis of photonic crystal micro-cavity based optical sensor platform. AIP Conf Proc 1724:020005
Goyal AK, Dutta HS, Pal S (2018) Porous photonic crystal structure for sensing applications. J Nanophoton 12(4):040501
Heeres JT et al (2009) Identifying modulators of protein-protein interactions using photonic crystal biosensors. J Am Chem Soc 131(51):18202
Heidarzadeh H (2019) Analysis and simulation of a plasmonic biosensor for haemoglobin concentration detection using noble metal nano-particles resonances. Commun Opt. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optcom.2019.124940
Homola J et al (1999) Surface plasmon resonance sensors: review. Sens Actuators B 54:3–15
Joannopoulos JD, Johnson SG, Winn JN, Meade RD (2008) Photonic crystals: molding the flow of light. Princeton University Press, New Jersey
Karlsson R, Stahleberg R (1995) Surface plasmon resonance detection and multispot sensing for direct monitoring of interactions involving low-molecular-weight analytes and for determination of low affinities. Anal Biochem 228(2):274–280
Keshavarz A, Zangenehzadeh S, Hatef A (2020) Optimization of surface plasmon resonance-based biosensors for monitoring hemoglobin levels in human blood. Nanosci Appl. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-020-01252-x
Konopsky VN et al (2013) Photonic crystal biosensor based on optical surface waves. Sensors 13(3):2566–2578
Lidiya AE et al (2019) Detecting hemoglobin content blood glucose using surface plasmon resonance in D-shaped photonic crystal fiber. Opt Fiber Technol 50:132–138
Liscidini M, Sipe JE (2009) Analysis of Bloch-surface-wave assisted diffraction-based biosensors. J Opt Soc Am B 26(2):279–289
Maeno K et al (2016) Polymer-based photonic crystal cavity sensor for optical detection in the visible wavelength region. Anal Sci 32:117–120
Paeder V et al (2011) Detection of protein aggregation with a Bloch surface wave based sensor. Sens Actuators B Chem 157(1):260–264
Pochi Y (1977) Electromagnetic propagation in periodic stratified media I. General theory. J Opt Soc Am 67(4):423–438
Quyang Q et al (2016) Sensitivity enhancement of transition metal dichalcogenides/silicon nanostructure-based surface plasmon resonance biosensor. Sci Rep 6:28190
Rivolo P et al (2012) Real time secondary antibody detection by means of silicon-based multilayers sustaining Bloch surface waves. Sens Actuators B Chem 161(1):1046–1052
Saleh EA, Teich MC (2007) Fundamentals of photonics. Wiley-Interscience, Hoboken
Seitz WR (1984) Chemical sensors based on fiber optics. Anal Chem 56:16A
Sharma AK (2013) Plasmonic biosensor for detection of hemoglobin concentra-tion in human blood: design considerations. J Appl Phys 114:044701
Shinn M, Robertson WM (2005) Surface plasmon-like sensor based on surface electromagnetic waves in a photonic band-gap material. Sens Actuators B Chem 105(2):360–364
Sinibaldi A et al (2013) A full ellipsometric approach to optical sensing with Bloch surface waves on photonic crystals. Opt Express 21(20):23331–23344
Swain KP, Palai G (2016) Estimation of human-hemoglobin using honeycomb structure: an application of photonic crystal. Optik 127:3333–3336
Tavousi A, Rakhshani MR, Birjandi MA (2018) High sensitivity label-free refractometer based biosensor applicable to glycated hemoglobin detection in human blood using all-circular photonic crystal ring resonators. Opt Commun 429:166–174
White IM et al (2008) On the performance quantification of resonant refractive index sensors. Opt Express 16:1020–1028
Yablonovitch E (1987) Inhibited spontaneous emission in solid-state physics and electronics. Phys Rev Lett 58(20):2059–2062
Zhao Y, Zhao X, Gu Z (2010) Photonic crystals in bioassays. Adv Funct Mater 20(18):2970–2988
Acknowledgement
Authors are thankful to all members of ECE department for their help and cooperation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goyal, A.K., Pal, S. Design analysis of Bloch surface wave based sensor for haemoglobin concentration measurement. Appl Nanosci 10, 3639–3647 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-020-01437-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-020-01437-4