Abstract
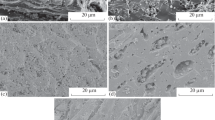
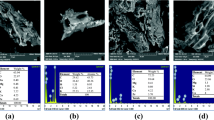
This study investigated the impact of pyrolysis conditions on physical characteristics of date palm fronds biochars and their performances for aqueous uptake of anionic dyes—methyl orange (MO) and Eriochrome Black-T (EBT)—and cationic dyes—methylene blue (MB) and crystal violet (CV). Detailed characterization of the biochars revealed the formation of oxygen functionalities (C=O, C-O-C, and C-O), improved surface characteristics (surface area and pore volume) and high ash content at higher pyrolysis temperature and time. Biochar-derived date palm with a high surface area of 431.82 m2/g and a pore volume of 0.134 cm3/g was obtained at pyrolysis temperature and time 700 °C and 4 h, respectively. For all the four investigated dyes, the adsorption isotherm was mainly described by Redlich–Peterson isotherm model (R2 > 0.95), while the adsorption kinetics well-fitted the pseudo-second order model. The biochar yielded fast dyes adsorption with maximum adsorption capacity for MB, EBT, MO, and CV dye of up to 206.61, 309.59, 163.132, and 934.57 mg/g at 200 mg/L dye concentration, respectively. The adsorption of cationic dyes was pH-independent indicating the involvement of pi–pi and chemical interactions. However, the uptake of the anionic dye was favorable at acidic conditions and was dominated by electrostatic interactions involving ion exchange and chemical reactions. The produced biochars exhibited excellent surface characteristics and enhanced adsorptive performance relative to other similar adsorbents. Thus, the direct pyrolysis of date palm fronds’ waste is a sustainable and economical approach of converting a huge quantity of wastes into excellent adsorbent for effective remediation of dye-contaminated water and wastewater.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adlnasab, L., Ezoddin, M., Karimi, M. A., & Hatamikia, N. (2018). MCM-41@Cu–Fe–LDH magnetic nanoparticles modified with cationic surfactant for removal of alizarin yellow from water samples and its determination with HPLC. Research on Chemical Intermediates, 44, 3249–3265.
Ahmad, M., Ahmad, M., Usman, A. R. A., Al-Faraj, A. S., Abduljabbar, A., Ok, Y. S., & Al-Wabel, M. I. (2019). Date palm waste-derived biochar composites with silica and zeolite: synthesis, characterization and implication for carbon stability and recalcitrant potential. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 41, 1687–1704.
Ahmad, T., Danish, M., Rafatullah, M., Ghazali, A., Sulaiman, O., Hashim, R., & Ibrahim, M. N. M. (2012). The use of date palm as a potential adsorbent for wastewater treatment: a review. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 19, 1464–1484.
Ahmed, M. B., Zhou, J. L., Ngo, H. H., Guo, W., & Chen, M. (2016). Progress in the preparation and application of modified biochar for improved contaminant removal from water and wastewater. Bioresource Technology, 214, 836–851.
Al-Kutti, W., Islam, A. S. & Nasir, M.: (2017) Potential use of date palm ash in cement-based materials, Journal of King Saud University-Engineering Sciences.
Al-Wabel, M. I., Usman, A. R. A., Al-Farraj, A. S., Ok, Y. S., Abduljabbar, A., Al-Faraj, A. I. & Sallam, A. S.: 2017, Date palm waste biochars alter a soil respiration, microbial biomass carbon, and heavy metal mobility in contaminated mined soil, Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 1–18.
Al-Zoubi, H., Zubair, M., Manzar, M. S., Manda, A. A., Blaisi, N. I., Qureshi, A. & Matani, A.: 2020) Comparative adsorption of anionic dyes (Eriochrome Black T and Congo red) onto jojoba residues: isotherm, kinetics and thermodynamic studies, Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering.
Alagha, O., Manzar, M. S., Zubair, M., Anil, I., Mu’azu, N. D., & Qureshi, A. (2020). Comparative adsorptive removal of phosphate and nitrate from wastewater using biochar-MgAl LDH Nanocomposites: coexisting anions effect and mechanistic studies. Nanomaterials, 10, 336.
Amin, M. T., Alazba, A. A., & Shafiq, M. (2019). Application of biochar derived from date palm biomass for removal of lead and copper ions in a batch reactor: kinetics and isotherm scrutiny. Chemical Physics Letters, 722, 64–73.
Arfi, R. B., Karoui, S., Mougin, K., & Ghorbal, A. (2017). Adsorptive removal of cationic and anionic dyes from aqueous solution by utilizing almond shell as bioadsorbent. Euro-Mediterranean Journal for Environmental Integration, 2, 20.
Biswas, S., Meikap, B. C., & Sen, T. K. (2019). Adsorptive removal of aqueous phase copper (Cu2+) and nickel (Ni2+) metal ions by synthesized biochar–biopolymeric hybrid adsorbents and process optimization by response surface methodology (RSM). Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 230, 197.
Blaisi, N. I., Zubair, M., Ihsanullah, Ali, Kazeem, T. S., Manzar, M. S., Al-Kutti, W. & Al Harthi, M. A.: (2018) Date palm ash-MgAl-layered double hydroxide composite: Sustainable adsorbent for effective removal of methyl orange and Eriochrome Black-T from aqueous phase, Environmental Science and Pollution Research.
Braghiroli, F. L., Bouafif, H., Neculita, C. M., & Koubaa, A. (2018). Activated biochar as an effective sorbent for organic and inorganic contaminants in water. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 229, 230.
Chaukura, N., Murimba, E. C., & Gwenzi, W. (2017). Synthesis, characterisation and methyl orange adsorption capacity of ferric oxide–biochar nano-composites derived from pulp and paper sludge. Applied Water Science, 7, 2175–2186.
Chen, Y.-D., Lin, Y.-C., Ho, S.-H., Zhou, Y., & Ren, N.-Q. (2018). Highly efficient adsorption of dyes by biochar derived from pigments-extracted macroalgae pyrolyzed at different temperature. Bioresource Technology, 259, 104–110.
Cheng, H.-Y., Cheng, B.-H., Shen, X.-C., Li, D.-C., & Jiang, H. (2018). Spectroscopic investigation reveals the interference mechanism of surfactants on the removal of 1-naphthol by activated biochar. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 6, 4196–4205.
Chowdhury, S., Pan, S., Balasubramanian, R. & Das, P.: (2019) Date palm based activated carbon for the efficient removal of organic dyes from aqueous environment, in M. Naushad & E. Lichtfouse (Eds.), Sustainable agriculture reviews 34: date palm for food, medicine and the environment, Cham, Springer International Publishing, pp. 247–263.
Dawood, S., Sen, T. K., & Phan, C. (2017). Synthesis and characterization of slow pyrolysis pine cone bio-char in the removal of organic and inorganic pollutants from aqueous solution by adsorption: Kinetic, equilibrium, mechanism and thermodynamic. Bioresource Technology, 246, 76–81.
Ding, G., Wang, B., Chen, L., & Zhao, S. (2016). Simultaneous adsorption of methyl red and methylene blue onto biochar and an equilibrium modeling at high concentration. Chemosphere, 163, 283–289.
Fan, S., Wang, Y., Wang, Z., Tang, J., Tang, J., & Li, X. (2017). Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution by sewage sludge-derived biochar: adsorption kinetics, equilibrium, thermodynamics and mechanism. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 5, 601–611.
Gokulan, R., Avinash, A., Prabhu, G. G., & Jegan, J. (2019). Remediation of remazol dyes by biochar derived from Caulerpa scalpelliformis—An eco-friendly approach. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 7, 103297.
Ho, Y.-S., & McKay, G. (1999). Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochemistry, 34, 451–465.
Huang, L., Liu, C., Liu, X., & Chen, Z. (2019). Retraction note to: Immobilization of heavy metals in e-waste contaminated soils by combined application of biochar and phosphate fertilizer. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 230, 129.
Ji, B., Zhu, L., Song, H., Chen, W., Guo, S., & Chen, F. (2019). Adsorption of methylene blue onto novel biochars prepared from Magnolia grandiflora Linn fallen leaves at three pyrolysis temperatures. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 230, 281.
Kazeem, T. S., Zubair, M., Daud, M., Mu’azu, N. D., & Al-Harthi, M. A. (2019). Graphene/ternary layered double hydroxide composites: efficient removal of anionic dye from aqueous phase. Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering, 36, 1057–1068.
Lee, C.-G., Hong, S.-H., Hong, S.-G., Choi, J.-W., & Park, S.-J. (2019). Production of biochar from food waste and its application for phenol removal from aqueous solution. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 230, 70.
Liu, N., Zhu, M., Wang, H., & Ma, H. (2016). Adsorption characteristics of direct red 23 from aqueous solution by biochar. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 223, 335–342.
Lyu, H., Gao, B., He, F., Zimmerman, A. R., Ding, C., Tang, J., & Crittenden, J. C. (2018). Experimental and modeling investigations of ball-milled biochar for the removal of aqueous methylene blue. Chemical Engineering Journal, 335, 110–119.
Mahdi, Z., El Hanandeh, A., & Yu, Q. (2017). Influence of pyrolysis conditions on surface characteristics and methylene blue adsorption of biochar derived from date seed biomass. Waste and Biomass Valorization, 8, 2061–2073.
Nautiyal, P., Subramanian, K., & Dastidar, M. (2016). Adsorptive removal of dye using biochar derived from residual algae after in-situ transesterification: alternate use of waste of biodiesel industry. Journal of Environmental Management, 182, 187–197.
Oliveira, F. R., Patel, A. K., Jaisi, D. P., Adhikari, S., Lu, H. & Khanal, S. K.: (2017) Environmental application of biochar: current status and perspectives', bioresource technology.
Onorevoli, B., da Silva Maciel, G. P., Machado, M. E., Corbelini, V., Caramão, E. B., & Jacques, R. A. (2018). Characterization of feedstock and biochar from energetic tobacco seed waste pyrolysis and potential application of biochar as an adsorbent. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 6, 1279–1287.
Qiu, Y., Zhang, Q., Li, M., Fan, Z., Sang, W., Xie, C., & Niu, D. (2019). Adsorption of cd(II) from aqueous solutions by modified biochars: comparison of modification methods. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 230, 84.
Qiu, Y., Zheng, Z., Zhou, Z., & Sheng, G. D. (2009). Effectiveness and mechanisms of dye adsorption on a straw-based biochar. Bioresource Technology, 100, 5348–5351.
Sewu, D. D., Boakye, P., Jung, H., & Woo, S. H. (2017a). Synergistic dye adsorption by biochar from co-pyrolysis of spent mushroom substrate and Saccharina japonica. Bioresource Technology, 244, 1142–1149.
Sewu, D. D., Boakye, P., & Woo, S. H. (2017b). Highly efficient adsorption of cationic dye by biochar produced with Korean cabbage waste. Bioresource Technology, 224, 206–213.
Sewu, D. D., Jung, H., Kim, S. S., Lee, D. S., & Woo, S. H. (2019). Decolorization of cationic and anionic dye-laden wastewater by steam-activated biochar produced at an industrial-scale from spent mushroom substrate. Bioresource Technology, 277, 77–86.
Shafiq, M., Alazba, A. A., & Amin, M. T. (2019). Synthesis, characterization, and application of date palm leaf waste-derived biochar to remove cadmium and hazardous cationic dyes from synthetic wastewater. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 12, 63.
Silvestri, S., Gonçalves, M. G., da Silva Veiga, P. A., Matos, T. T. D. S., Peralta-Zamora, P., & Mangrich, A. S. (2019). TiO2 supported on Salvinia molesta biochar for heterogeneous photocatalytic degradation of acid orange 7 dye. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 7, 102879.
Tran, H. N., Lee, C.-K., Vu, M. T., & Chao, H.-P. (2017). Removal of copper, Lead, methylene green 5, and acid red 1 by saccharide-derived spherical biochar prepared at low calcination temperatures: adsorption kinetics, isotherms, and thermodynamics. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 228, 401.
Ulucan-Altuntas, K. (2019). Removal of humic substances by nano zero-valent iron supported on activated carbon and implementation of response surface methodology. Desalination and Water Treatment, 166, 230–236.
Ulucan-Altuntas, K., & Kuzu, S. L. (2019). Modelling and optimization of dye removal by Fe/Cu bimetallic nanoparticles coated with different cu ratios. Materials Research Express, 6, 1150a1154.
Ulucan-Altuntas, K., Uzun, H. I., Ustundag, C. B., & Debik, E. (2020). Adsorption of copper ion from aqueous solutions by well-crystalized nanosized hydroxyapatite. Materials Research Express, 6, 125545.
Usman, A. R., Abduljabbar, A., Vithanage, M., Ok, Y. S., Ahmad, M., Ahmad, M., Elfaki, J., Abdulazeem, S. S., & Al-Wabel, M. I. (2015). Biochar production from date palm waste: Charring temperature induced changes in composition and surface chemistry. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 115, 392–400.
Vyavahare, G., Jadhav, P., Jadhav, J., Patil, R., Aware, C., Patil, D., Gophane, A., Yang, Y.-H., & Gurav, R. (2019). Strategies for crystal violet dye sorption on biochar derived from mango leaves and evaluation of residual dye toxicity. Journal of Cleaner Production, 207, 296–305.
Wei, S., Zhu, M., Fan, X., Song, J., Peng, P. a., Li, K., Jia, W., & Song, H. (2019). Influence of pyrolysis temperature and feedstock on carbon fractions of biochar produced from pyrolysis of rice straw, pine wood, pig manure and sewage sludge. Chemosphere, 218, 624–631.
Xu, X., Cao, X., Zhao, L., Zhou, H., & Luo, Q. (2014). Interaction of organic and inorganic fractions of biochar with Pb(ii) ion: further elucidation of mechanisms for Pb(ii) removal by biochar. RSC Advances, 4, 44930–44937.
Yang, L., Gao, J., Liu, Y., Zhang, Z., Zou, M., Liao, Q., & Shang, J. (2018). Removal of methyl Orange from water using sulfur-modified nZVI supported on biochar composite. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 229, 355.
Zhao, S.-X., Ta, N., & Wang, X.-D. (2017). Effect of temperature on the structural and physicochemical properties of biochar with apple tree branches as feedstock material. Energies, 10, 1293.
Zhu, X., Liu, Y., Zhou, C., Luo, G., Zhang, S., & Chen, J. (2014). A novel porous carbon derived from hydrothermal carbon for efficient adsorption of tetracycline. Carbon, 77, 627–636.
Zhu, Y., Yi, B., Yuan, Q., Wu, Y., Wang, M., & Yan, S. (2018). Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution by cattle manure-derived low temperature biochar. RSC Advances, 8, 19917–19929.
Zubair, M., Jarrah, N., Khalid, A., Manzar, M. S., Kazeem, T. S., & Al-Harthi, M. A. (2018). Starch-NiFe-layered double hydroxide composites: efficient removal of methyl orange from aqueous phase. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 249, 254–264.
Zubair, M., Jarrah, N., Manzar, M. S., Al-Harthi, M., Daud, M., Mu’azu, N. D., & Haladu, S. A. (2017). Adsorption of eriochrome black T from aqueous phase on MgAl-, CoAl- and NiFe-calcined layered double hydroxides: kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic studies. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 230, 344–352.
Funding
This work is supported by King Abdul-Aziz City for Science and Technology (KACST) at Imam Abdulrahman Bin Faisal University, Saudi Arabia through Project No. 12-Env2229-46 under NSTIP research grants.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 1617 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zubair, M., Mu’azu, N.D., Jarrah, N. et al. Adsorption Behavior and Mechanism of Methylene Blue, Crystal Violet, Eriochrome Black T, and Methyl Orange Dyes onto Biochar-Derived Date Palm Fronds Waste Produced at Different Pyrolysis Conditions. Water Air Soil Pollut 231, 240 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04595-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04595-x