Abstract
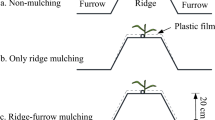
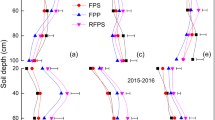
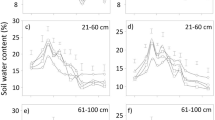
Soil surface mulching and planting density regulation are widely used for effective utilization of limited rainwater resources and improvement of crop productivity in dryland farming. However, the combined effects of mulching type and planting density on maize growth and yield have been seldom studied, especially in different hydrological years. A field experiment was conducted to evaluate the effects of mulching type and planting density on the soil temperature, growth, grain yield (GY), water use efficiency (WUE) and economic benefit of rainfed maize in the drylands of northern China during 2015–2017. Precipitation fluctuated over the three years. There were four mulching types (NM, flat cultivation with non-mulching; SM, flat cultivation with straw mulching; RP, plastic-mulched ridge plus bare furrow; RPFS, plastic-mulched ridge plus straw-mulched furrow) and three planting densities (LD, low planting density, 45.0×103 plants/hm2; MD, medium planting density, 67.5×103 plants/hm2; HD, high planting density, 90.0×103 plants/hm2). Results showed that soil temperature was higher with RP and lower with SM compared with NM, but no significant difference was found between RPFS and NM. More soil water was retained by soil mulching at the early growth stage, but it significantly varied at the middle and late growth stages. Maize growth was significantly improved by soil mulching. With increasing planting density, stem diameter, net photosynthetic rate and chlorophyll content tended to decline, whereas a single-peak trend in biomass yield was observed. Mulching type and planting density did not have significant effect on evapotranspiration (ET), but GY and WUE were significantly affected. There were significant interacting effects of mulching type and planting density on biomass yield, GY, ET and WUE. Compared with NM, RPFS, RP and SM increased GY by 57.5%, 50.8% and 18.9%, and increased WUE by 66.6%, 54.3% and 18.1%, respectively. At MD, GY increased by 41.4% and 25.2%, and WUE increased by 38.6% and 22.4% compared with those of at LD and HD. The highest maize GY (7023.2 kg/hm2) was observed under MD+RPFS, but the value (6699.1 kg/hm2) was insignificant under MD+RP. Similar trends were observed for WUE under MD+RP and MD+RPFS, but no significant difference was observed between these two combinations. In terms of economic benefit, net income under MD+RP was the highest with a 9.8% increase compared with that of under MD+RPFS. Therefore, we concluded that RP cultivation pattern with a suitable planting density (67.5×103 plants/hm2) is promising for rainwater resources utilization and maize production in the drylands of northern China.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abuzar M R, Sadozai G U, Baloch M S, et al. 2011. Effect of plant population densities on yield of maize. Journal of Animal and Plant Science, 21: 692–695.
Allen R G, Pereira L S, Raes D, et al. 1998. Crop evapotranspiration-guidelines for computing crop water requirements. FAO irrigation and drainage paper 56, FAO, Rome.
Berzsenyi Z, Tokatlidis I S. 2012. Density-dependence rather than maturity determines hybrid selection in dryland maize production. Agronomy Journal, 104(2): 331–336.
Blum A. 2009. Effective use of water (EUW) and not water-use efficiency (WUE) is the target of crop yield improvement under drought stress. Field Crops Research, 112(2–3): 119–123.
Borras L, Slafer G A, Otegui M E. 2004. Seed dry weight response to source-sink manipulations in wheat, maize and soybean: a quantitative reappraisal. Field Crops Research, 86(2–3): 131–146.
Campbell G S, Norman J M. 1998. Introduction to Environmental Biophysics. New York: Springer Science+Business Media, 286.
Carpici E B, Celik N, Bayram G. 2010. Yield and quality of forage maize as influenced by plant density and nitrogen rate. Turkish Journal of Food Crop, 15(2): 128–132.
Chen Y, Liu T, Tian X, et al. 2015. Effects of plastic film combined with straw mulch on grain yield and water use efficiency of winter wheat in Loess Plateau. Field Crops Research, 172: 53–58.
Ciampitti I A, Vyn T J. 2012. Physiological perspectives of changes over time in maize yield dependency on nitrogen uptake and associated nitrogen efficiencies: a review. Field Crops Research, 133: 48–67.
Cook H F, Valdes G S B, Lee H C. 2006. Mulch effects on rainfall interception, soil physical characteristics and temperature under Zea mays L. Soil and Tillage Research, 91: 227–235.
Dvorak P, Tomâsek J, Hamouz K, et al. 2015. Reply of mulch systems on weeds and yield components in potatoes. Plant and Soil Environment, 61: 322–327.
Fan J L, Baumgartl T, Scheuermann A, et al. 2015. Modeling effects of canopy and roots on soil moisture and deep drainage. Vadose Zone Journal, 14(2): 1–18.
Fan J L, Yue W J, Wu L F, et al. 2018. Evaluation of SVM, ELM and four tree-based ensemble models for predicting daily reference evapotranspiration using limited meteorological data in different climates of China. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 263: 225–241.
Gao Z, Feng H Y, Liang X G, et al. 2018. Limits to maize productivity in the North China Plain: A comparison analysis for spring and summer maize. Field Crops Research, 228: 39–47.
Gelmond H. 1978. Problems in crop seed germination. In: Gupta U S. Crop Physiology. New Delhi: Oxford and IBH, 7–15.
Gu X B, Li Y N, Du Y D. 2016. Continuous ridges with film mulching improve soil water content, root growth, seed yield and water use efficiency of winter oilseed rape. Industrial Crops and Products, 85: 139–148.
Han Q F, Li X T, Wang J P, et al. 2004. Simulated study on soil moisture of field under water micro-collecting farming conditions. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 20: 78–82. (in Chinese)
Hu Y J, Ma P H, Zhang B B, et al. 2019. Exploring optimal soil mulching for the wheat-maize cropping system in sub-humid drought-prone regions in China. Agricultural Water Management, 219: 59–71.
Iqbal R, Raza M A S, Saleem M F, et al. 2019. Physiological and biochemical appraisal for mulching and partial rhizosphere drying of cotton. Journal of Arid Land, 11(5): 785–794.
Jia Q M. 2018. Effects of rainwater-harvesting planting with supplemental irrigation and planting densities on the growth and photosynthetic physiology of maize in the semi-arid regions. PhD Dissertation. Yangling: Northwest A&F University. (in Chinese)
Jia Q M, Sun L F, Shahzad A, et al. 2018a. Effect of planting density and pattern on maize yield and rainwater use efficiency in the Loess Plateau in China. Agricultural Water Management, 202: 19–32.
Jia Q M, Sun L F, Mou H Y, et al. 2018b. Effects of planting patterns and sowing densities on grain-filling, radiation use efficiency and yield of maize (Zea mays L.) in semi-arid regions. Agricultural Water Management, 201: 287–298.
Jia Q M, Sun L F, Wang J J, et al. 2018c. Limited irrigation and planting densities for enhanced water productivity and economic returns under the ridge-furrow system in semi-arid regions of China. Field Crops Research, 221: 207–218.
Kuai J, Sun Y Y, Zhou M, et al. 2016. The effect of nitrogen application and planting density on the radiation use efficiency and the stem lignin metabolism in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). Field Crops Research, 199: 89–98.
Li R, Hou X Q, Jia Z K, et al. 2013. Effects on soil temperature, moisture, and maize yield of cultivation with ridge and furrow mulching in the rainfed area of the Loess Plateau, China. Agricultural Water Management, 116: 101–109.
Li Y, Liu C C, Zhang J H., et al. 2018. Variation in leaf chlorophyll concentration from tropical to cold-temperate forests: Association with gross primary productivity. Ecological Indicators, 85: 383–389.
Lin W, Liu W Z, Xue Q W. 2016. Spring maize yield, soil water use and water use efficiency under plastic film and straw mulches in the Loess Plateau. Scientific Report, 6: 1–10.
Liu C A, Jin S L, Zhou L M, et al. 2009. Effects of plastic film mulch and tillage on maize productivity and soil parameters. European Journal of Agronomy, 31(4): 241–249.
Liu J L, Bu L D, Zhu L, et al. 2014. Optimizing plant density and plastic film mulch to increase maize productivity and water use efficiency in semiarid areas. Agronomy Journal, 106(4): 1138–1146.
Liu Q F, Chen Y, Liu Y, et al. 2016. Coupling effects of plastic film mulching and urea types on water use efficiency and grain yield of maize in the Loess Plateau, China. Soil and Tillage Research, 157: 1–10.
Liu T N, Chen J Z, Wang Z Y, et al. 2018. Ridge and furrow planting pattern optimizes canopy structure of summer maize and obtains higher grain yield. Field Crops Research, 219: 242–249.
Mackinnery G. 1941. Absorption of light by chlorophyll solutions. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 140: 315–322.
Maddonni G A, Otegui M E, Cirilo A G. 2001. Plant population density, row spacing and hybrid effects on maize canopy architecture and light attenuation. Field Crops Research, 71(3): 183–193.
Mckee G W. 1964. A coefficient for computing leaf area in hybrid corn. Agronomy Journal, 56: 240–241.
Qiang S C, Zhang F C, Xiang Y Z, et al. 2015. Simulation and validation of critical nitrogen dilution curve for summer maize in Guanzhong Plain during different rainfall years. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 31(17): 168–175. (in Chinese)
Qiang S C, Zhang Y, Fan J L, et al. 2019. Maize yield, rainwater and nitrogen use efficiency as affected by maize genotypes and nitrogen rates on the Loess Plateau of China. Agricultural Water Management, 213: 996–1003.
Ramachandra R A, Chaitanya K V, Vivekanandan M. 2004. Drought-induced responses of photosynthesis and antioxidant metabolism in higher plants. Journal of Plant Physiology, 161(11): 1189–1202.
Ren B Z, Dong S T, Liu P, et al. 2016. Ridge tillage improves plant growth and grain yield of waterlogged summer maize. Agricultural Water Management, 177: 392–399.
Ren X L, Cai T, Chen X L, et al. 2016. Effect of rainfall concentration with different ridge widths on winter wheat production under semiarid climate. European Journal of Agronomy, 77: 20–27.
Rossini M A, Maddonni G A, Otegui M E. 2011. Inter-plant competition for resources in maize crops grown under contrasting nitrogen supply and density: Variability in plant and ear growth. Field Crops Research, 121(3): 373–380.
Sadeghi M. 2013. The determination of plant density on dry matter accumulation, grain yield and yield components of four maize hybrids. International Journal of Agriculture and Crop Sciences, 5: 109.
Sharma P, Abrol V, Sharma R K. 2011. Impact of tillage and mulch management on economics, energy requirement and crop performance in maize-wheat rotation in rainfed subhumid inceptisols, India. European Journal of Agronomy, 34(1): 46–51.
Wang X, Fan J, Xing Y, et al. 2019. The effects of mulch and nitrogen fertilizer on the soil environment of crop plants. Advance in Agronomy, 153: 121–173.
Wang X B, Cai D X, Hoogmoed W B, et al. 2007. Crop residue, manure and fertilizer in dryland maize under reduced tillage in northern China: I grain yields and nutrient use efficiencies. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 79(1): 1–16.
Wang T C, Wei L, Wang H Z, et al. 2011. Responses of rainwater conservation, precipitation-use efficiency and grain yield of summer maize to a furrow-planting and straw-mulching system in northern China. Field Crops Research, 124(2): 223–230.
Wang Y Q, Zhang Y H, Zhou S L, et al. 2018. Meta-analysis of no-tillage effect on wheat and maize water use efficiency in China. Science of the Total Environment, 635: 1372–1382.
Xue J Q, Zhang R H, Li F Y, et al. 2008. Current status, problem and strategy of maize breeding in Shannxi Province. Journal of Maize Science, 16(2): 139–141. (in Chinese)
Yin W, Chen G P, Feng F X, et al. 2017. Straw retention combined with plastic mulching improves compensation of intercropped maize in arid environment. Field Crops Research, 204: 42–51.
Zhang F, Ibrahim M E, Li M, et al. 2019. Integrated model and field experiment to determine the optimum planting density in plastic film mulched rainfed agriculture. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 268: 331–340.
Zhang H J, Dong H Z, Li W J, et al. 2012. Effects of soil salinity and plant density on yield and leaf senescence of field-grown cotton. Journal of Agronomy and Crop Science, 198(1): 27–37.
Zhang S H, Sadras V, Chen X P, et al. 2014. Water use efficiency of dryland maize in the Loess Plateau of China in response to crop management. Field Crops Research, 163: 55–63.
Zhang X D, Zhao J, Yang L C, et al. 2019. Ridge-furrow mulching system regulates diurnal temperature amplitude and wetting-drying alternation behavior in soil to promote maize growth and water use in a semiarid region. Field Crops Research, 233: 121–130.
Zhang Y Q, Wang J D, Gong S H, et al. 2019. Straw mulching enhanced the photosynthetic capacity of field maize by increasing the leaf N use efficiency. Agricultural Water Management, 218: 60–67.
Zheng J, Fan J L, Zhang F C, et al. 2018a. Mulching mode and planting density affect canopy interception loss of rainfall and water use efficiency of dryland maize on the Loess Plateau of China. Journal of Arid Land, 10(5): 794–808.
Zheng J, Fan J L, Zhang F C, et al. 2018b. Rainfall partitioning into throughfall, stemflow and interception loss by maize canopy on the semi-arid Loess Plateau of China. Agricultural Water Management, 195: 25–36.
Zheng J, Fan J L, Zhang F C, et al. 2019. Throughfall and stemflow heterogeneity under the maize canopy and its effect on soil water distribution at the row scale. Science of the Total Environment, 660: 1367–1382.
Zhou L M, Li F M, Jin S L, et al. 2009. How two ridges and the furrow mulched with plastic film affect soil water, soil temperature and yield of maize on the semiarid Loess Plateau of China. Field Crops Research, 113(1): 41–47.
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51879226, 51509208) and the Overseas Expertise Introduction Project for Discipline Innovation (111 Project; B12007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, J., Fan, J., Zou, Y. et al. Ridge-furrow plastic mulching with a suitable planting density enhances rainwater productivity, grain yield and economic benefit of rainfed maize. J. Arid Land 12, 181–198 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40333-020-0001-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40333-020-0001-1