Abstract
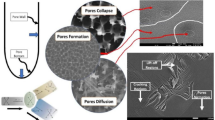
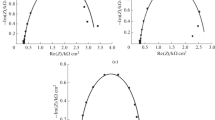
Controlling pore structure, e.g. pore diameter, size and distribution of porous silicon (PS) is highly needed for technological applications such as microfluidic operation and filtration in which the pore size and shape can block the entrance of some species or increase its concentration or purity by separation. In the present study, highly doped p-type silicon is utilized to prepare PS with different pore dimensions by electrochemical etching (anodization) process in HF and C2H5OH mixture. The anodization process was performed under various conditions such as different electrolyte types, temperature, and concentrations, etching potential, current density, and etching duration. This research was to further study the influence of electrochemical etching parameters on pore formation kinetics including pore size, layer thickness and mechanistic aspects of silicon etching. The study offers a fundamental understanding of the fabrication process of porous silicon that may be exploited in nanotechnology applications. The present study confirms that the anodization rate increases with increasing the steady-state current at all the presented conditions. It is demonstrated that adjusting the anodizing potential is very important as it determines whether the anodization will lead to PS formation and/or PS dissolution.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Osaka T, Ogasawara K, Nakahara S (1997) Classification of the pore structure of n-type silicon and its microstructure. J Electrochem Soc 144(9):3226–3237
Föll H, Christophersen M, Carstensen J, Hasse G (2002) Formation and application of porous silicon. Mater Sci Eng R Rep 39(4):93–141
Xu HJ, Li XJ (2008) Silicon nanoporous pillar array: a silicon hierarchical structure with high light absorption and triple-band photoluminescence. Opt Express 16(5):2933–2941
Abd-Elnaiem AM, Moustafa S, Asafa TB (2019) Comparative study of pore characterizations of anodized Al–0.5 wt.% Cu thin films in oxalic and phosphoric acids. Nano 1950140
Abd-Elnaiem AM, Abbady G, Ali D, Asafa TB (2019) Influence of anodizing voltage and electrolyte concentration on Al-1 wt% Si thin films anodized in H2SO4. Mater Res Express 6(8):086468
Lee C-Y, Schmuki P (2015) Engineering of self-organizing electrochemistry: Porous alumina and titania nanotubes. Electrochemical Engineering Across Scales: From Molecules to Processes 15
Martín-Sánchez D, Ponce-Alcántara S, García-Rupérez J (2018) Pore morphology of heavily doped P-Type porous silicon. Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute Proceedings 4(1):14
Li X, Bohn PW (2000) Metal-assisted chemical etching in HF/H 2 O 2 produces porous silicon. Appl Phys Lett 77(16):2572–2574
Dimova-Malinovska D, Sendova-Vassileva M, Tzenov N, Kamenova M (1997) Preparation of thin porous silicon layers by stain etching. Thin Solid Films 297(1):9–12
Vázsonyi É, Szilágyi E, Petrik P, Horváth ZE, Lohner T, Fried M, Jalsovszky G (2001) Porous silicon formation by stain etching. Thin Solid Films 388(1):295–302
Parkhutik V, Matveeva E, Perez R, Alamo J, Beltrán D (2000) Mechanism of large oscillations of anodic potential during anodization of silicon in H 3 PO 4/HF solutions. Mater Sci Eng B 69:553–558
Parkhutika VP, Matveeva E (1999) Observation of new oscillatory phenomena during the electrochemical anodization of silicon. Electrochem Solid-State Lett 2(8):371–374
Harraz FA (2014) Porous silicon chemical sensors and biosensors: a review. Sensors Actuators B Chem 202:897–912
Jung KH, Shih S, Kwong DL (1993) Developments in luminescent porous Si. J Electrochem Soc 140(10):3046
Vasquez RP, Fathauer RW, George T, Ksendzov A, Lin TL (1992) Electronic structure of light-emitting porous Si. Appl Phys Lett 60(8):1004–1006
Jabbar AA, Alwan AM, Zayer MQ, Bohan AJ (2020) Efficient single cell monitoring of pathogenic bacteria using bimetallic nanostructures embedded in gradient porous silicon. Mater Chem Phys 241:122359
Zhang XG (2004) Morphology and formation mechanisms of porous silicon. J Electrochem Soc 151(1):C69–C80
Smith RL, Collins SD (1992) Porous silicon formation mechanisms. J Appl Phys 71(8):R1–R22
Propst EK, Kohl PA (1994) The electrochemical oxidation of silicon and formation of porous silicon in acetonitrile. J Electrochem Soc 141(4):1006
Lee CH, Yeh CC, Hsu KYJ (1996) Formation of bottom oxides in porous silicon films by anodic oxidation. Appl Surf Sci 92:621–625
Cantin JL, Schoisswohl M, Grosman A, Lebib S, Ortega C, von Berdeleben HJ, Vazsonyi E, Jalsovszky G, Erostyak J (1996) Anodic oxidation of p-and p+−type porous silicon: surface structural transformations and oxide formation. Thin Solid Films 276(1–2):76–79
Beale MIJ, Chew NG, Uren MJ, Cullis AG, Benjamin JD (1985) Microstructure and formation mechanism of porous silicon. Appl Phys Lett 46(1):86–88
Lévy-Clément C, Lagoubi A, Tomkiewicz M (1994) Morphology of porous n-Type silicon obtained by photoelectrochemical etching: I. Correlations with material and etching parameters. J Electrochem Soc 141(4):958
Gong X, Bustillo J, Blanc L, Gautier G (2020) FEM simulation on elastic parameters of porous silicon with different pore shapes. Int J Solids Struct 190:238–243
Lehmann V, Föll H (1990) Formation mechanism and properties of electrochemically etched trenches in n-type silicon. J Electrochem Soc 137(2):653–659
Hamilton B (1995) Porous silicon. Semicond Sci Technol 10(9):1187–1207
Volovlikova O, Gavrilov S, Lazarenko P (2020) Influence of illumination on porous silicon formed by photo-assisted etching of p-type Si with a different doping level. Micromachines 11(2):199
Albu-Yaron A, Bastide S, Bouchet D, Brun N, Colliex C, Lévy-Clément C (1994) Nanostructural and nanochemical investigation of luminescent photoelectrochemically etched porous n-type silicon. Journal de Physique I 4(8):1181–1197
Ronkel F, Schultze JW (2000) Electrochemical aspects of porous silicon formation. J Porous Mater 7(1–3):11–16
Unagami T (1980) Formation mechanism of porous silicon layer by anodization in HF solution. J Electrochem Soc 127(2):476–483
Solanki CS, Bilyalov RR, Poortmans J, Celis J-P, Nijs J, Mertens R (2004) Self-standing porous silicon films by one-step anodizing. J Electrochem Soc 151(5):C307–C314
Tinsley-Bown AM, Canham LT, Hollings M, Anderson MH, Reeves CL, Cox TI, Nicklin S et al (2000) Tuning the pore size and surface chemistry of porous silicon for immunoassays. Phys Status Solidi A 182(1):547–553
Setzu S, Lérondel G, Romestain R (1998) Temperature effect on the roughness of the formation interface of p-type porous silicon. J Appl Phys 84(6):3129–3133
Ono H, Gomyou H, Morisaki H, Nozaki S, Show Y, Shimasaki M, Iwase M, Izumi T (1993) Effects of anodization temperature on photoluminescence from porous silicon. J Electrochem Soc 140(12):L180–L182
Vico JM, Jansen F, Maex K, Groeseneken G, Vereecken PM (2007) Formation of porous alumina patterns on silicon. ECS Trans 3(21):85–93
Acknowledgements
The present work is financially supported by Jouf University under grant number 111/40; the first and third authors are very grateful.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mebed, A.M., Abd-Elnaiem, A.M. & De Malsche, W. Influence of Anodizing Parameters on the Electrochemical Characteristics and Morphology of Highly Doped P-type Porous Silicon. Silicon 13, 819–829 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-020-00490-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-020-00490-6