Abstract
Purpose
To examine the rate of occurrence of hearing impairments among the infants who had recovered from viral meningitis under 1 year of age through auditory evoked potential (AEP) test and to investigate the efficacy of the follow-up AEP test in viral meningitis infants.
Methods
Two hundred twenty infants (440 ears) were examined through AEP test once, and 47 (94 ears) of them went back for a second examination and were diagnosed with viral meningitis. The first AEP tests were compared with the second results in 47 infants. I latency, V latency, I–III interpeak latency (IPL), and III–V IPL were checked.
Results
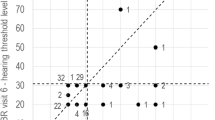
In the first AEP test conducted on 440 ears, the average values of I and V latency and I–III IPL were delayed as compared with normal values. The second AEP results were conducted on 47 infants 92.36 days after the first exam. I latency and V latency of second exam were improved significantly (p < 0.05), but I–III and III–V IPL showed no significant changes. Two hearing impaired patients (4 ears) were confirmed through chart reviews.
Conclusion
The AEP test is a helpful study for early detection of hearing problem. However, in this study, AEP test was too sensitive in acute period, and later, the incidence rate of hearing impairment was relatively low. Therefore, age of onset, severity of neurologic symptom, and clinical examination must be considered before the AEP test.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Logan SA, MacMahon E (2008) Viral meningitis. BMJ 336:36–40. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.39409.673657.AE
Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, Shah SS, Tasker RC, Wilson KM et al (2019) Nelson textbooks of pediatrics 21th ed. Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 7442–7467
Nadol JB Jr (1978) Hearing loss as a sequela of meningitis. Laryngoscope 88:739–755. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.1978.88.5.739
Rosenhall U, Kankkunen A (1981) Hearing alterations following meningitis. 2. Variable hearing. Ear Hear 2:170–176. https://doi.org/10.1097/00003446-198107000-00006
Jiang ZD, Liu XY, Wu YY, Zheng MS, Liu HC (1990) Long-term impairments of brain and auditory functions of children recovered from purulent meningitis. Dev Med Child Neurol 32:473–480. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8749.1990.tb16972.x
Ozdamar O, Kraus N (1983) Auditory brainstem response in infants recovering from bacterial meningitis. Neurologic assessment Arch Neurol 40:499–502. https://doi.org/10.1001/archneur.1983.04210070039011
Guiscafré H, Benitez-Díaz L, Martínez MC, Muñoz O (1984) Reversible hearing loss after meningitis. Prospective assessment using auditory evoked responses. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 93:229–232. https://doi.org/10.1177/000348948409300308
Fortnum HM (1992) Hearing impairment after bacterial meningitis: a review. Arch Dis Child 67:1128–1133. https://doi.org/10.1136/adc.67.9.1128
Lee YB, Kim JM, Koh SE, Chung JS, Chong SY (2001) Determination of follow-up time of abnormal brainstem auditory evoked potential in infancy. J Korean Acad Rehab Med 25:784–790
Park ES, Park CI, Shin JS, Cho BK (1992) Brainstem auditory evoked potentials in infants below 6 months of age. J Korean Acd Rehab Med 16:123–133
Chiappa KH (1997) Evoked potentials in clinical medicine 3rd ed. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, pp 157–278
Galambos R, Hicks G, Wilson MJ (1982) Hearing loss in graduates of a tertiary intensive care nursery. Ear Hear 3:87–90. https://doi.org/10.1097/00003446-198203000-00007
Cohen BA, Schenk VA, Sweeney DB (1988) Meningitis-related hearing loss evaluated with evoked potentials. Pediatr Neurol 4:18–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/0887-8994(88)90019-7
Kotagal S, Rosenberg C, Rudd D, Dunkle LM, Horenstein S (1981) Auditory evoked potentials in bacterial meningitis. Arch Neurol 38:693–695. https://doi.org/10.1001/archneur.1981.00510110053007
Stockard JE, Stockard JJ, Westmoreland BF, Corfits JL (1979) Brainstem auditory-evoked responses. Normal variation as a function of stimulus and subject characteristics. Arch Neurol 36:823–831. https://doi.org/10.1001/archneur.1979.00500490037006
O'Donovan CA, Beagley HA, Shaw M (1980) Latency of brainstem response in children. Br J Audiol 14:23–29. https://doi.org/10.3109/03005368009078896
Bao X, Wong V (1998) Brainstem auditory-evoked potential evaluation in children with meningitis. Pediatr Neurol 19:109–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0887-8994(98)00032-0
Vienny H, Despland PA, Lütschg J, Deonna T, Dutoit-Marco ML, Gander C (1984) Early diagnosis and evolution of deafness in childhood bacterial meningitis: a study using brainstem auditory evoked potentials. Pediatrics 73:579–586
Spanjaard L, Bol P, de Jong MC, Zanen HC (1986) Bacterial meningitis in 366 children in the Netherlands, 1982-1983. Epidemiology and antibiotic therapy. Tijdschr Kindergeneeskd 54:1–8
Duclaux R, Sevin F, Ferber C, Drai MF, Dubreuil C (1993) Brainstem auditory evoked potentials following meningitis in children. Brain Dev 15:340–345. https://doi.org/10.1016/0387-7604(93)90119-s
Acknowledgments
We thank Ji Hwan Cheon, Cheon Rehabilitation Clinic, Gwangju, Republic of Korea, for assisting with the statistical analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, H., Kim, M.W., Nam, D.H. et al. Efficacy of auditory evoked potential follow-up in viral meningitis of infants. Childs Nerv Syst 36, 3077–3083 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-020-04630-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-020-04630-6